DELCON Presentation - Weidmuller B2B Portal
... Pulse Transformer Solid state relays based on own development since end of 70´s Own development and assembly in Nummela, near Helsinki Effective use of local sub-suppliers ...
... Pulse Transformer Solid state relays based on own development since end of 70´s Own development and assembly in Nummela, near Helsinki Effective use of local sub-suppliers ...
AC to DC converter with zener diode regulation
... passes low-frequency signals and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency.If we can reduce the value of ripple voltage we will get smooth waveshape.The most common meaning of ripple in electrical science is the small unwanted residual periodic variation of the direct curr ...
... passes low-frequency signals and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency.If we can reduce the value of ripple voltage we will get smooth waveshape.The most common meaning of ripple in electrical science is the small unwanted residual periodic variation of the direct curr ...
national semiconductor (lmv722m) ultra low noise dual op amp
... The LMV721 (Single) and LMV722 (Dual) are low noise, low voltage, and low power op amps, that can be designed into a wide range of applications. The LMV721/LMV722 has a unity gain bandwidth of 10MHz, a slew rate of 5V/us, and a quiescent current of 930uA/amplifier at 2.2V. The LMV721/722 are designe ...
... The LMV721 (Single) and LMV722 (Dual) are low noise, low voltage, and low power op amps, that can be designed into a wide range of applications. The LMV721/LMV722 has a unity gain bandwidth of 10MHz, a slew rate of 5V/us, and a quiescent current of 930uA/amplifier at 2.2V. The LMV721/722 are designe ...
BPR-23-D - アイステーシス
... 23 GHz Balanced PhotoReceiver, Differential Output The Optilab BPR-23-D series is a balanced 23 GHz linear photoreceiver with a differential output. It features differential gain of up to 5000 Ω and has a high Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR). The BPR-23-D is ideal for digital system operating up ...
... 23 GHz Balanced PhotoReceiver, Differential Output The Optilab BPR-23-D series is a balanced 23 GHz linear photoreceiver with a differential output. It features differential gain of up to 5000 Ω and has a high Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR). The BPR-23-D is ideal for digital system operating up ...
SSM2143 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... two parts together, measured on an Audio Precision at the SSM2143’s output. This configuration was tested with 500 feet ...
... two parts together, measured on an Audio Precision at the SSM2143’s output. This configuration was tested with 500 feet ...
B Analog Signal Input
... where m is the gain and b is the zero crossing point or Input (ma -> offset. The gain may be calculated from: m=(y2-y1)/x2-x1) where x1, y1 is one coordinate pair on the graph and x2, y2 is the other. Therefore, when you have chosen to enter non-default coordinates you are in fact setting the gain f ...
... where m is the gain and b is the zero crossing point or Input (ma -> offset. The gain may be calculated from: m=(y2-y1)/x2-x1) where x1, y1 is one coordinate pair on the graph and x2, y2 is the other. Therefore, when you have chosen to enter non-default coordinates you are in fact setting the gain f ...
Sensor Signal Conditioning for Biomedical Instrumentation
... 27.3.3 The Instrumentation Amplifier............................................................................ 585 27.4 The Analog-to-Digital Conversion Process..................................................................... 589 27.4.1 The Sampling Process.................................. ...
... 27.3.3 The Instrumentation Amplifier............................................................................ 585 27.4 The Analog-to-Digital Conversion Process..................................................................... 589 27.4.1 The Sampling Process.................................. ...
TD351
... The TD351 input is compatible with optocouplers or pulse transformers. The input is triggered by the signal edge and allows the use of low-sized, low-cost pulse transformers. Input is active low and output is driven high when input is driven low. The IN input is internally clamped at about 5 V to 7 ...
... The TD351 input is compatible with optocouplers or pulse transformers. The input is triggered by the signal edge and allows the use of low-sized, low-cost pulse transformers. Input is active low and output is driven high when input is driven low. The IN input is internally clamped at about 5 V to 7 ...
Document
... Transconductance is the ratio of output current, to input voltage. Transimpedance is the ratio of output voltage, to input current. ...
... Transconductance is the ratio of output current, to input voltage. Transimpedance is the ratio of output voltage, to input current. ...
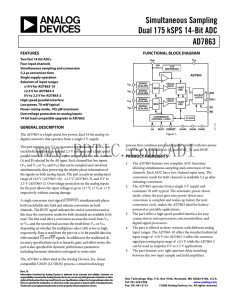
AD7863 数据手册DataSheet下载
... Digital Ground. Ground reference for digital circuitry. Convert Start Input. Logic input. A high-to-low transition on this input puts both track/holds into their hold mode and starts conversion on both channels. Data Bit 6 to Data Bit 0. Three-state TTL outputs. Analog Ground. Ground reference for m ...
... Digital Ground. Ground reference for digital circuitry. Convert Start Input. Logic input. A high-to-low transition on this input puts both track/holds into their hold mode and starts conversion on both channels. Data Bit 6 to Data Bit 0. Three-state TTL outputs. Analog Ground. Ground reference for m ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).