DC1279 - LT3517EUF Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide
... protection, shutdown control pin, analog LED current dimming control, and externally programmable switching frequency (with sync) make the LT3517 an extremely versatile and powerful LED driving IC. The LT3517 has a 45V switch with 1.5A peak switch current limit rating. DC1279 has overvoltage protect ...
... protection, shutdown control pin, analog LED current dimming control, and externally programmable switching frequency (with sync) make the LT3517 an extremely versatile and powerful LED driving IC. The LT3517 has a 45V switch with 1.5A peak switch current limit rating. DC1279 has overvoltage protect ...
SGM9121 8MHz 5th Order Video Driver with 6dB Gain
... low-frequency compensation for the high pass filter formed by the 150Ω load and the output capacitor. In video applications, the cutoff frequency must be low enough to pass the vertical sync interval to avoid field tilt. This cutoff frequency should be less than 5Hz, and the coupling capacitor must ...
... low-frequency compensation for the high pass filter formed by the 150Ω load and the output capacitor. In video applications, the cutoff frequency must be low enough to pass the vertical sync interval to avoid field tilt. This cutoff frequency should be less than 5Hz, and the coupling capacitor must ...
May 2000 New Rail-to-Rail Output Op Amps Bring Precision Performance to Low Voltage Systems
... trade slightly higher input bias currents of 500pA for three times higher speed. This series of amplifiers brings the performance of the LT1112 to low voltage applications that need the wide rail-to-rail output dynamic range. The graph of Figure 2 shows the input bias currents of the LT1884 over the ...
... trade slightly higher input bias currents of 500pA for three times higher speed. This series of amplifiers brings the performance of the LT1112 to low voltage applications that need the wide rail-to-rail output dynamic range. The graph of Figure 2 shows the input bias currents of the LT1884 over the ...
Chapter # 3 Data and Signals
... A nonperiodic composite signal has a bandwidth of 200 kHz, with a middle frequency of 140 kHz and peak amplitude of 20 V. The two extreme frequencies have an amplitude of 0. Draw the frequency domain of the signal. ...
... A nonperiodic composite signal has a bandwidth of 200 kHz, with a middle frequency of 140 kHz and peak amplitude of 20 V. The two extreme frequencies have an amplitude of 0. Draw the frequency domain of the signal. ...
mae511
... The input bits of the counter are all set to low and the outputs are used to create the desired control signals. We denote the output bits of the counter, from least significant to most significant, QA, QB , QC , and QD. Sending the signal QA · QC to the LOAD input causes the counter to reset to all ...
... The input bits of the counter are all set to low and the outputs are used to create the desired control signals. We denote the output bits of the counter, from least significant to most significant, QA, QB , QC , and QD. Sending the signal QA · QC to the LOAD input causes the counter to reset to all ...
TLC1550 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect. NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in ...
... LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect. NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in ...
LR9641 DESCRIPTION FEATURES
... protects the IC itself and its downstream system against input voltage surges. With this OVP function, the IC can stand off input voltage as high as 42V, making it an ideal solution for industrial applications such as smart meters as well as automotive applications. In automotive systems, power come ...
... protects the IC itself and its downstream system against input voltage surges. With this OVP function, the IC can stand off input voltage as high as 42V, making it an ideal solution for industrial applications such as smart meters as well as automotive applications. In automotive systems, power come ...
Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDT Construction The
... Null Position – This is also called the central position as the soft iron core will remain in the exact center of the former. Thus the linking magnetic flux produced in the two secondary windings will be equal. The voltage induced because of them will also be equal. Thus the resulting voltage VS1-VS ...
... Null Position – This is also called the central position as the soft iron core will remain in the exact center of the former. Thus the linking magnetic flux produced in the two secondary windings will be equal. The voltage induced because of them will also be equal. Thus the resulting voltage VS1-VS ...
Maxim max912
... Note 1: Input Offset Voltage (VOS) is defined as the average of the two input offset voltages, measured by forcing first one output, then the other to 1.4V. Input Offset Current (IOS) is defined the same way. Note 2: Propagation Delay (tPD) and Differential Propagation Delay (∆tPD) cannot be measure ...
... Note 1: Input Offset Voltage (VOS) is defined as the average of the two input offset voltages, measured by forcing first one output, then the other to 1.4V. Input Offset Current (IOS) is defined the same way. Note 2: Propagation Delay (tPD) and Differential Propagation Delay (∆tPD) cannot be measure ...
ADA4665-2 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... operation with ISY of 500 μA typically and 900 μΑ over the extended industrial temperature. These devices offer 3MHz unity gain bandwidth. They also feature low input bias currents of 1pA and 10 mA output drive. The combination of low supply currents, low offsets, very low input bias currents, and w ...
... operation with ISY of 500 μA typically and 900 μΑ over the extended industrial temperature. These devices offer 3MHz unity gain bandwidth. They also feature low input bias currents of 1pA and 10 mA output drive. The combination of low supply currents, low offsets, very low input bias currents, and w ...
Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission
... • Noise limits data rate that can be achieved • For digital data, to what extent do these impairments limit data rate? • Channel Capacity: The maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a given communication path, or channel, under given conditions ...
... • Noise limits data rate that can be achieved • For digital data, to what extent do these impairments limit data rate? • Channel Capacity: The maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a given communication path, or channel, under given conditions ...
Signal Resistance of the Current Mirror
... .. so the current in R is equal to the voltage at X divided by R and it will flow upwards if the voltage at X is positive. The bottom of both hie, and hoe for Transistor 1, is also at 0 V, so the current in all of those resistances will flow downwards if the voltage at X is positive; the same will ...
... .. so the current in R is equal to the voltage at X divided by R and it will flow upwards if the voltage at X is positive. The bottom of both hie, and hoe for Transistor 1, is also at 0 V, so the current in all of those resistances will flow downwards if the voltage at X is positive; the same will ...
OPA365 - Texas Instruments
... output to swing from 0V to a positive full-scale voltage and have high accuracy. An example is an op amp employed to drive a single-supply ADC having an input range from 0V to +5V. Rail-to-rail output amplifiers with very light output loading may achieve an output level within millivolts of 0V (or + ...
... output to swing from 0V to a positive full-scale voltage and have high accuracy. An example is an op amp employed to drive a single-supply ADC having an input range from 0V to +5V. Rail-to-rail output amplifiers with very light output loading may achieve an output level within millivolts of 0V (or + ...
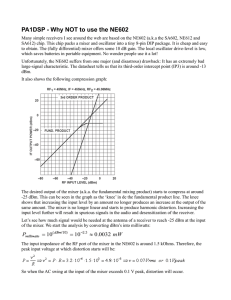
PA1DSP - Why NOT to use the NE602
... shows that increasing the input level by an amount no longer produces an increase at the output of the same amount. The mixer is no longer linear and starts to produce harmonic distortion. Increasing the input level further will result in spurious signals in the audio and desensitization of the rece ...
... shows that increasing the input level by an amount no longer produces an increase at the output of the same amount. The mixer is no longer linear and starts to produce harmonic distortion. Increasing the input level further will result in spurious signals in the audio and desensitization of the rece ...
Question Bank
... D) none 7. An OP-AMP is used as a zero crossing detector. If the maximum output available from the OPAMP is ±12 volts peak to peak, and the slew rate of the OP-AMP is 12 V/µsec, then the maximum frequency of the input signal that can be applied without causing a reduction in the peak to peak output ...
... D) none 7. An OP-AMP is used as a zero crossing detector. If the maximum output available from the OPAMP is ±12 volts peak to peak, and the slew rate of the OP-AMP is 12 V/µsec, then the maximum frequency of the input signal that can be applied without causing a reduction in the peak to peak output ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).