a secondary-side phase-shift-controlled llc resonant converter with
... A novel secondary-side phase-shift-controlled (SS-PSC) LLC resonant converter is proposed for applications requiring hold-up time operation, such as distributed power systems and server power supplies. High efficiency at the normal input voltage is achieved because the proposed SSPSC LLC converter a ...
... A novel secondary-side phase-shift-controlled (SS-PSC) LLC resonant converter is proposed for applications requiring hold-up time operation, such as distributed power systems and server power supplies. High efficiency at the normal input voltage is achieved because the proposed SSPSC LLC converter a ...
Frequency response of feedback amplifiers
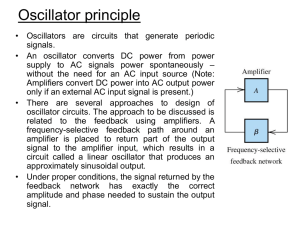
... amplitude with time, eventually, the amplitude is clipped by the amplifier so that a constant-amplitude oscillation results. • On the other hand, if exact unity loop gain magnitude is designed, a slight reduction in gain would result in oscillations that decays to zero. • One important thing to note ...
... amplitude with time, eventually, the amplitude is clipped by the amplifier so that a constant-amplitude oscillation results. • On the other hand, if exact unity loop gain magnitude is designed, a slight reduction in gain would result in oscillations that decays to zero. • One important thing to note ...
27th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing
... Fig. 1. Circuit diagram of a voltage converter based on AOZ 1284 As could be recognized from provided schematic, the switching transistor is integrated on the chip. The circuit operation is based on Continuous-Conduction Mode (CCM) in fixed frequency. The inbuilt transistor is N-MOSFET switch. The i ...
... Fig. 1. Circuit diagram of a voltage converter based on AOZ 1284 As could be recognized from provided schematic, the switching transistor is integrated on the chip. The circuit operation is based on Continuous-Conduction Mode (CCM) in fixed frequency. The inbuilt transistor is N-MOSFET switch. The i ...
AD534 数据手册DataSheet 下载1
... bias currents, noise and drift can be achieved by decreasing SF. This has the overall effect of increasing signal gain without the customary increase in noise. Note that the peak input signal is always limited to 1.25 SF (i.e., ± 5 V for SF = 4 V) so the overall transfer function will show a maximum ...
... bias currents, noise and drift can be achieved by decreasing SF. This has the overall effect of increasing signal gain without the customary increase in noise. Note that the peak input signal is always limited to 1.25 SF (i.e., ± 5 V for SF = 4 V) so the overall transfer function will show a maximum ...
Digital Insulation Resistance Testers
... testing insulation in power system wiring and motor winding. It also measures voltage and checks continuity and ground connections with its Lo-Ohms function. Easy to use with a simple user interface, the 1520 provides insulation resistance testing up to to 4000 MΩ, with three output voltages: 250 V, ...
... testing insulation in power system wiring and motor winding. It also measures voltage and checks continuity and ground connections with its Lo-Ohms function. Easy to use with a simple user interface, the 1520 provides insulation resistance testing up to to 4000 MΩ, with three output voltages: 250 V, ...
The DatasheetArchive - Datasheet Search Engine
... bandwidth of 4 MHz. The JFET input stage of the OP282/OP482 ensures bias current is typically a few picoamps and below 500 pA over the full temperature range. Offset voltage is under 3 mV for the dual and under 4 mV for the quad. ...
... bandwidth of 4 MHz. The JFET input stage of the OP282/OP482 ensures bias current is typically a few picoamps and below 500 pA over the full temperature range. Offset voltage is under 3 mV for the dual and under 4 mV for the quad. ...
TS4100,01,02 EVB User Guide
... UG177: TS4100-01-02 EVB User's Guide The TS410x series of multiplexers offer no compromise performance for the best signal integrity, simple design, and low power operation as they can operate at a supply voltage as low as 0.8 V while accepting an input signal swing above the supply voltage up to 5. ...
... UG177: TS4100-01-02 EVB User's Guide The TS410x series of multiplexers offer no compromise performance for the best signal integrity, simple design, and low power operation as they can operate at a supply voltage as low as 0.8 V while accepting an input signal swing above the supply voltage up to 5. ...
Dual 1 MSPS, 12-Bit, 2-Channel SAR ADC with Serial Interface AD7866
... The AD7866 is a dual 12-bit high speed, low power, successive approximation ADC. The part operates from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and features throughput rates up to 1 MSPS. The device contains two ADCs, each preceded by a low noise, wide bandwidth track-and-hold amplifier that can handl ...
... The AD7866 is a dual 12-bit high speed, low power, successive approximation ADC. The part operates from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and features throughput rates up to 1 MSPS. The device contains two ADCs, each preceded by a low noise, wide bandwidth track-and-hold amplifier that can handl ...
Design and Simulation of High Speed Low Power CMOS
... performance limiting blocks in such ADCs are typically inter-stage gain amplifiers and comparators. The accuracy of such comparators, which is defined by its offset, along with power consumption, speed is of keen interest in achieving overall higher performance of ADCs. In the past, pre-amplifier ba ...
... performance limiting blocks in such ADCs are typically inter-stage gain amplifiers and comparators. The accuracy of such comparators, which is defined by its offset, along with power consumption, speed is of keen interest in achieving overall higher performance of ADCs. In the past, pre-amplifier ba ...
Modulation
... Modulation is a technique used for encoding information into a RF channel. Typically the process of modulation combines an information signal with a carrier signal to create a new composite signal that can be transmitted over a wireless link. In theory a message signal can be directly sent into spac ...
... Modulation is a technique used for encoding information into a RF channel. Typically the process of modulation combines an information signal with a carrier signal to create a new composite signal that can be transmitted over a wireless link. In theory a message signal can be directly sent into spac ...
MTC-1X - maselec
... The IMAGE circuit consists of two functions. Both are controlled with rotary switches. 3.3.1 Elliptical Filter This FILTER cuts signals that are out of phase and converts non-correlated signal components to mono below the frequency that the control is set to. For example: If a signal below the set f ...
... The IMAGE circuit consists of two functions. Both are controlled with rotary switches. 3.3.1 Elliptical Filter This FILTER cuts signals that are out of phase and converts non-correlated signal components to mono below the frequency that the control is set to. For example: If a signal below the set f ...
Data and Signal
... Depending on some type of typical signal formats or modulation schemes, a few terminologies evolved to classify different types of signals. So, we can have either a base band or broadband signalling. Base-band is defined as one that uses digital signalling, which is inserted in the transmission chan ...
... Depending on some type of typical signal formats or modulation schemes, a few terminologies evolved to classify different types of signals. So, we can have either a base band or broadband signalling. Base-band is defined as one that uses digital signalling, which is inserted in the transmission chan ...
SWITCHED CAPACITOR CIRCUITS
... In the precision Gain-2 circuit, C1 = C2, while the basic amplifier has C1 = 2C2, resulting in a smaller feedback factor and a slower circuit The gain error is inversely proportional to the feedback factor, so the precision circuit is more accurate for a given amplifier gain A C2 + C1 + Cp ⎞ ...
... In the precision Gain-2 circuit, C1 = C2, while the basic amplifier has C1 = 2C2, resulting in a smaller feedback factor and a slower circuit The gain error is inversely proportional to the feedback factor, so the precision circuit is more accurate for a given amplifier gain A C2 + C1 + Cp ⎞ ...
AD8519 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... condition occurs, the U1 stage is taken out of the VOUT equation and VOUT is equal to VIN × R5 × (R4 || R1 + R2 + R3). Note that Node A should be VIN inverted or virtual ground, but in this condition, Node A is simply tracking VIN. Given a sine wave input centered around virtual ground, glitches are ...
... condition occurs, the U1 stage is taken out of the VOUT equation and VOUT is equal to VIN × R5 × (R4 || R1 + R2 + R3). Note that Node A should be VIN inverted or virtual ground, but in this condition, Node A is simply tracking VIN. Given a sine wave input centered around virtual ground, glitches are ...
MT-055 TUTORIAL Chopper Stabilized (Auto-Zero) Precision Op Amps
... In this circuit, A1 is the main amplifier, and A2 is the nulling amplifier. In the sample mode (switches in "S" position), the nulling amplifier, A2, monitors the input offset voltage of A1 and drives its output to zero by applying a suitable correcting voltage at A1's null pin. Note, however, that ...
... In this circuit, A1 is the main amplifier, and A2 is the nulling amplifier. In the sample mode (switches in "S" position), the nulling amplifier, A2, monitors the input offset voltage of A1 and drives its output to zero by applying a suitable correcting voltage at A1's null pin. Note, however, that ...
8 MHz Rail-to-Rail Operational Amplifiers AD8519/AD8529
... The operation of the basic circuit (shown in Figure 23) should be examined before considering the slew rate further. U1 is set up to have two states of operation. D1 and D2 diodes switch the output between the two states. State one is an inverter with a gain of +1, and state two is a simple unity ga ...
... The operation of the basic circuit (shown in Figure 23) should be examined before considering the slew rate further. U1 is set up to have two states of operation. D1 and D2 diodes switch the output between the two states. State one is an inverter with a gain of +1, and state two is a simple unity ga ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).