Ultramafic Rocks
... • Their lavas comprise 70% of the earth’s surface • Sea floor spreading is the mechanism of their origin ...
... • Their lavas comprise 70% of the earth’s surface • Sea floor spreading is the mechanism of their origin ...
igneous rocks
... If an igneous rock is extrusive (volcanic) that means it formed on or close to the Earth’s surface where temperatures are cooler than deep within the earth. This would give the igneous rock samples small or possibly no crystal structure at all. ...
... If an igneous rock is extrusive (volcanic) that means it formed on or close to the Earth’s surface where temperatures are cooler than deep within the earth. This would give the igneous rock samples small or possibly no crystal structure at all. ...
5. North Atlantic Tertiary Igneous Province (NATP)
... 2. 63 mya uplift & updoming of continental crust raises Britain high above sea-level & actively eroded 3. 60 mya eruption from fissures onto continental crust of extensive sheets of basaltic lava (flood basalts) 4. 58 mya large volcanoes erupted more lavas onto the land. The roots of these volcanoes ...
... 2. 63 mya uplift & updoming of continental crust raises Britain high above sea-level & actively eroded 3. 60 mya eruption from fissures onto continental crust of extensive sheets of basaltic lava (flood basalts) 4. 58 mya large volcanoes erupted more lavas onto the land. The roots of these volcanoes ...
Igneous Rock PPT notes
... rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. ...
... rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. ...
12.15-Rock-Cycle
... - Wind, water and/or ice transport these particles to floodplains and the sea by erosion. - The pressure of many layers changes the bottom layers into sediments. ...
... - Wind, water and/or ice transport these particles to floodplains and the sea by erosion. - The pressure of many layers changes the bottom layers into sediments. ...
BOOK REVIEWS 179 background information on the Data
... Jersey, U.S.A. (Prentice Hall, Inc.), 1983. xii+ 417 pp. 228 figs. Price s This book has much to commend it, and some failings. It presumes an elementary knowledge of igneous petrology for its readers, and seeks to enhance their knowledge to a relatively advanced level. As such it occupies the overc ...
... Jersey, U.S.A. (Prentice Hall, Inc.), 1983. xii+ 417 pp. 228 figs. Price s This book has much to commend it, and some failings. It presumes an elementary knowledge of igneous petrology for its readers, and seeks to enhance their knowledge to a relatively advanced level. As such it occupies the overc ...
Igneous Rocks
... GEOLOGISTS RECOGNIZE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS 1) Igneous – rocks that cool from a molten state. 2) Sedimentary – rocks that form from the eroded and weathered particles of pre-existing rocks, a “re-cycled rock”. 3) Metamorphic – rocks that form by the alteration of pre-existing rocks through heat and pr ...
... GEOLOGISTS RECOGNIZE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS 1) Igneous – rocks that cool from a molten state. 2) Sedimentary – rocks that form from the eroded and weathered particles of pre-existing rocks, a “re-cycled rock”. 3) Metamorphic – rocks that form by the alteration of pre-existing rocks through heat and pr ...
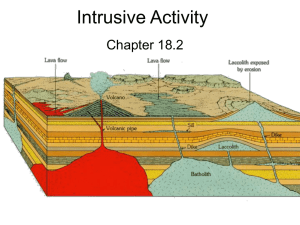
Intrusive Activity
... A. Magma can force the overlying rock apart and enter the newly formed fissures. B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may ...
... A. Magma can force the overlying rock apart and enter the newly formed fissures. B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may ...
Igneous Rocks - Skyline R2 School
... Igneous rocks Rock formed when hard liquid rock cools and hardens ...
... Igneous rocks Rock formed when hard liquid rock cools and hardens ...
Igneous Rock
... lava to __________, the more time mineral crystals have to grow and the ________________ the texture of the resulting igneous rock. Intrusive igneous rock (Plutonic) – The type of igneous rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies _________ the Earth’s surface. - Usually has a _________________ ...
... lava to __________, the more time mineral crystals have to grow and the ________________ the texture of the resulting igneous rock. Intrusive igneous rock (Plutonic) – The type of igneous rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies _________ the Earth’s surface. - Usually has a _________________ ...
Document
... When large quantities of magma pour on to the surface through fault lines, the lava flows that result can spread over huge areas and over time this may be repeated to give a great thickness of igneous rock. Examples can be found in Northern Ireland and in the Deccan Plateau of India. There are thous ...
... When large quantities of magma pour on to the surface through fault lines, the lava flows that result can spread over huge areas and over time this may be repeated to give a great thickness of igneous rock. Examples can be found in Northern Ireland and in the Deccan Plateau of India. There are thous ...
Science Practice set 4
... 1. Rocks are classified into the three major groups (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) by A. their color B. their size C. their formation d. the types of minerals in them 2. Igneous rocks are formed when ___________ cools. A. magma B. sediment C. water D. stone 3. How do sedimentary rocks form? ...
... 1. Rocks are classified into the three major groups (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) by A. their color B. their size C. their formation d. the types of minerals in them 2. Igneous rocks are formed when ___________ cools. A. magma B. sediment C. water D. stone 3. How do sedimentary rocks form? ...
Igneous Rocks Notes
... WHAT IS AN IGNEOUS ROCK? A rock formed as the result of _______________________________________. ________________- molten rock beneath the earth’s surface ________________- molten rock above the earth’s surface Most are ____________________, composed of more than one mineral IDENTIFICATION Based on ...
... WHAT IS AN IGNEOUS ROCK? A rock formed as the result of _______________________________________. ________________- molten rock beneath the earth’s surface ________________- molten rock above the earth’s surface Most are ____________________, composed of more than one mineral IDENTIFICATION Based on ...
Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
... GEOL 2312 IGNEOUS AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY Lecture 1 Introduction to Igneous Petrology and Earth’s Physical and Chemical Structure ...
... GEOL 2312 IGNEOUS AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY Lecture 1 Introduction to Igneous Petrology and Earth’s Physical and Chemical Structure ...
Basalts and Ultramafic Volcanic Rocks
... Global distribution of flood basalt provinces. There are no "volcanoes" as such found in these provinces !! ...
... Global distribution of flood basalt provinces. There are no "volcanoes" as such found in these provinces !! ...
Name: : Earth Science Mr. Herman Exeter SHS Chapter 10.3
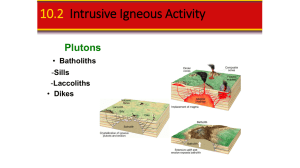
... Sills and Laccoliths are plutons that form when magma is intruded close to the surface. Sills resemble buried lava flows and may exhibit columnar joints. Laccoliths are lens-shaped masses that arch overlying strata upward. ...
... Sills and Laccoliths are plutons that form when magma is intruded close to the surface. Sills resemble buried lava flows and may exhibit columnar joints. Laccoliths are lens-shaped masses that arch overlying strata upward. ...
GUIDED NOTES – IGNEOUS ROCKS Name Date
... – The Vietnam memorial is made of black granite ( an igneous rock). ...
... – The Vietnam memorial is made of black granite ( an igneous rock). ...
Igneous Intrusions
... cools inside Earth’s interior—may be called a pluton. Dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks are sometimes called plutons. However, some scientists identify only the largest, thickest intrusions as plutons. A pluton reaches Earth’s surface only after uplift, weathering, or both take place. As ...
... cools inside Earth’s interior—may be called a pluton. Dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks are sometimes called plutons. However, some scientists identify only the largest, thickest intrusions as plutons. A pluton reaches Earth’s surface only after uplift, weathering, or both take place. As ...
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province

The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province (MLIP) is a major Mesoproterozoic large igneous province of the southwestern, western and northwestern Canadian Shield in Canada. It consists of a group of related igneous rocks that were formed during a massive igneous event starting about 1,270 million years ago. The large igneous province extends from the Arctic in Nunavut to near the Great Lakes in Northwestern Ontario where it meets with the smaller Matachewan dike swarm. Included in the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are the large Muskox layered intrusion, the Coppermine River flood basalt sequence and the massive northwesterly trending Mackenzie dike swarm.As a large igneous province, it is an extremely large area of related igneous rocks that were emplaced over an extremely short geological time span. The igneous rocks comprising the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province originated from processes not associated with normal plate tectonics and seafloor spreading. It is one of the several large igneous provinces scattered throughout the Canadian landscape, which can be thousands of kilometres in volume and area. The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province is also one of the largest Proterozoic magmatic provinces on Earth, as well as the world's largest and best-preserved continental flood basalt terrain. Igneous rocks of the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are generally mafic in composition, including basalt and gabbro.Even though the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province is classified as a large igneous province like other extremely large accumulations of igneous rocks on Earth, it is much larger than large igneous province standards. The standard size classification for large igneous provinces is a minimum areal extent of 100,000 km2 (39,000 sq mi). However, the Mackenzie dike swarm itself occupies an area of at least 2,700,000 km2 (1,000,000 sq mi), making the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province larger than the Ontong Java Plateau in the southwestern Pacific Ocean and the U.S. state of Alaska.