Igneous Rocks and Their Origin
... • Lab expmts require high P & T to form large grains • Outcrops: See intrusions into country rock -Contact/chill zones, baked and metamorphosed • Xenoliths of country rock found in igneous intrusions ...
... • Lab expmts require high P & T to form large grains • Outcrops: See intrusions into country rock -Contact/chill zones, baked and metamorphosed • Xenoliths of country rock found in igneous intrusions ...
Igneous Rocks
... intrusive igneous rocks. These rocks are usually coarsegrained. Members of this family typically contain quartz, feldspar (orthoclase, plagioclase, or both), mica, and hornblende. Granite, for which this family is named, is one of the coarsest-grained rocks in the family. Granite usually ranges from ...
... intrusive igneous rocks. These rocks are usually coarsegrained. Members of this family typically contain quartz, feldspar (orthoclase, plagioclase, or both), mica, and hornblende. Granite, for which this family is named, is one of the coarsest-grained rocks in the family. Granite usually ranges from ...
WEEK 10: IGNEOUS ROCKS
... Igneous Rocks can be broken up into two main categories a. INTRUSIVE & EXTRUSIVE INTRUSIVE igneous rocks: a. Cool slowly underground over 100’s of years PLUTONIC b. Because they cool slowly these rocks are large crystals. Their grain size will be larger than 1mm. They will have a coarse or very co ...
... Igneous Rocks can be broken up into two main categories a. INTRUSIVE & EXTRUSIVE INTRUSIVE igneous rocks: a. Cool slowly underground over 100’s of years PLUTONIC b. Because they cool slowly these rocks are large crystals. Their grain size will be larger than 1mm. They will have a coarse or very co ...
Rocks from Lava
... before large crystals have time to form. That’s why extrusive igneous rocks usually have a smooth, sometimes glassy appearance. Extrusive igneous rocks can form in two ways. In one way, volcanoes erupt and shoot out lava and ash. Also, large cracks in Earth’s crust, called fissures, can open up. Whe ...
... before large crystals have time to form. That’s why extrusive igneous rocks usually have a smooth, sometimes glassy appearance. Extrusive igneous rocks can form in two ways. In one way, volcanoes erupt and shoot out lava and ash. Also, large cracks in Earth’s crust, called fissures, can open up. Whe ...
No Slide Title
... IGNEOUS PROCESSES AND IGNEOUS ROCKS IGNEOUS ROCKS AND PLATE TECTONICS Most igneous rocks are associated with plate boundaries. Gabbros and basalts at: Mid-oceanic ridges Intraplate hot spots or mantle plumes Rifting continents Andesites and Diorites found at subduction zones. Particularly ocean-con ...
... IGNEOUS PROCESSES AND IGNEOUS ROCKS IGNEOUS ROCKS AND PLATE TECTONICS Most igneous rocks are associated with plate boundaries. Gabbros and basalts at: Mid-oceanic ridges Intraplate hot spots or mantle plumes Rifting continents Andesites and Diorites found at subduction zones. Particularly ocean-con ...
Classifying Igneous Rock
... Explain your answer. 2. Do all extrusive igneous rocks contain crystals? Explain your answer. 3. Why do some igneous rocks have bubble holes? 4. List two extrusive rocks that contain crystals. 5. Granite and obsidian are similar chemically. How are they different? ...
... Explain your answer. 2. Do all extrusive igneous rocks contain crystals? Explain your answer. 3. Why do some igneous rocks have bubble holes? 4. List two extrusive rocks that contain crystals. 5. Granite and obsidian are similar chemically. How are they different? ...
Geology - Nayland College
... 2)Relating to or involving volcanic processes: "igneous activity". • Igneous … think ignite … think fire … think lava or magna ...
... 2)Relating to or involving volcanic processes: "igneous activity". • Igneous … think ignite … think fire … think lava or magna ...
earth sciences 3313a igneous petrology
... Volcanoes are one of the main natural hazards to mankind. It is therefore important to understand the mechanisms and processes controlling volcanic eruptions. It is also clear that the materials which constitute the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and crust ultimately originated from the Earth’s interio ...
... Volcanoes are one of the main natural hazards to mankind. It is therefore important to understand the mechanisms and processes controlling volcanic eruptions. It is also clear that the materials which constitute the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and crust ultimately originated from the Earth’s interio ...
Be a Rock Hound
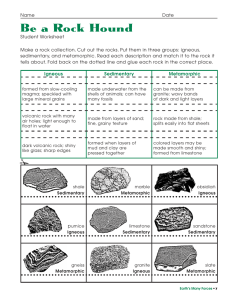
... Be a Rock Hound Student Worksheet Make a rock collection. Cut out the rocks. Put them in three groups: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Read each description and match it to the rock it tells about. Fold back on the dotted line and glue each rock in the correct place. Igneous ...
... Be a Rock Hound Student Worksheet Make a rock collection. Cut out the rocks. Put them in three groups: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Read each description and match it to the rock it tells about. Fold back on the dotted line and glue each rock in the correct place. Igneous ...
Igneous Rocks Power Point
... Greenstone is a weakly metamorphosed (altered) basalt that is, as its name suggests, greenish to gray. ...
... Greenstone is a weakly metamorphosed (altered) basalt that is, as its name suggests, greenish to gray. ...
Chapter 4 Exercises 1. Observations and experiments show that rate
... 7. Plutons are more likely than dikes to show the effects of fractional crystallization because they contain a larger volume of melted material and have less surface area for their size and thus are likely to cool more slowing than dikes. 8. The origin of a rock composed almost entirely of olivine w ...
... 7. Plutons are more likely than dikes to show the effects of fractional crystallization because they contain a larger volume of melted material and have less surface area for their size and thus are likely to cool more slowing than dikes. 8. The origin of a rock composed almost entirely of olivine w ...
Lecture 4
... Texture: Texture is size, shape and arrangement of mineral grains in a rock. Texture of rock can either of coarse-crystalline or it can be glassy or amorphous. The texture of the rock is governed by the cooling time of the magma. Crystallization is governed by slow cooling, however, glassy texture o ...
... Texture: Texture is size, shape and arrangement of mineral grains in a rock. Texture of rock can either of coarse-crystalline or it can be glassy or amorphous. The texture of the rock is governed by the cooling time of the magma. Crystallization is governed by slow cooling, however, glassy texture o ...
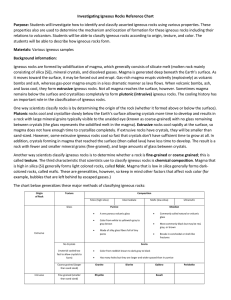
Investigating Igneous Rocks Reference Chart Purpose: Students will
... Purpose: Students will investigate how to identify and classify assorted igneous rocks using various properties. These properties also are used to determine the mechanism and location of formation for these igneous rocks including their relations to volcanism. Students will be able to classify igneo ...
... Purpose: Students will investigate how to identify and classify assorted igneous rocks using various properties. These properties also are used to determine the mechanism and location of formation for these igneous rocks including their relations to volcanism. Students will be able to classify igneo ...
Rock posters - igneous PDF - EAL Nexus
... Source | This resource was originally developed from a resource on TES by j33ffa , Charlotte Hurley and Alison Fisher and has been adapted by EAL Nexus. ...
... Source | This resource was originally developed from a resource on TES by j33ffa , Charlotte Hurley and Alison Fisher and has been adapted by EAL Nexus. ...
Jenkins_GSAtalk_v17may16
... Conclusions • Relict igneous texture to mylonitic fabrics. • REE abundances similar to Proterozoic and Archean dikes. – Not floor rocks. – Not Stillwater cumulates. – No known roof rocks have been identified. ...
... Conclusions • Relict igneous texture to mylonitic fabrics. • REE abundances similar to Proterozoic and Archean dikes. – Not floor rocks. – Not Stillwater cumulates. – No known roof rocks have been identified. ...
The Rock Cycle
... underground chamber, cools very slowly, and forms rocks full of large crystals. Extrusive Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks that form above the Earth’s surface. These rocks, also called volcanic rocks, form when lava cools quickly at or above the Earth’s surface. ...
... underground chamber, cools very slowly, and forms rocks full of large crystals. Extrusive Igneous Rocks: Igneous rocks that form above the Earth’s surface. These rocks, also called volcanic rocks, form when lava cools quickly at or above the Earth’s surface. ...
Minerals - WordPress.com
... 4. What type of mineral are most igneous rocks made of? (1 pt) a. Carbonate b. Oxide c. Native element ...
... 4. What type of mineral are most igneous rocks made of? (1 pt) a. Carbonate b. Oxide c. Native element ...
Igneous Rock Identification - ppt as pdf
... Plutonic rocks (gabbro-diorite-granite) are coarse-grained and cooled slowly at depth Volcanic rocks (basalt-andesite-rhyolite) are typically fine-grained and cooled rapidly at the Earth’s surface ...
... Plutonic rocks (gabbro-diorite-granite) are coarse-grained and cooled slowly at depth Volcanic rocks (basalt-andesite-rhyolite) are typically fine-grained and cooled rapidly at the Earth’s surface ...
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province

The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province (MLIP) is a major Mesoproterozoic large igneous province of the southwestern, western and northwestern Canadian Shield in Canada. It consists of a group of related igneous rocks that were formed during a massive igneous event starting about 1,270 million years ago. The large igneous province extends from the Arctic in Nunavut to near the Great Lakes in Northwestern Ontario where it meets with the smaller Matachewan dike swarm. Included in the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are the large Muskox layered intrusion, the Coppermine River flood basalt sequence and the massive northwesterly trending Mackenzie dike swarm.As a large igneous province, it is an extremely large area of related igneous rocks that were emplaced over an extremely short geological time span. The igneous rocks comprising the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province originated from processes not associated with normal plate tectonics and seafloor spreading. It is one of the several large igneous provinces scattered throughout the Canadian landscape, which can be thousands of kilometres in volume and area. The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province is also one of the largest Proterozoic magmatic provinces on Earth, as well as the world's largest and best-preserved continental flood basalt terrain. Igneous rocks of the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are generally mafic in composition, including basalt and gabbro.Even though the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province is classified as a large igneous province like other extremely large accumulations of igneous rocks on Earth, it is much larger than large igneous province standards. The standard size classification for large igneous provinces is a minimum areal extent of 100,000 km2 (39,000 sq mi). However, the Mackenzie dike swarm itself occupies an area of at least 2,700,000 km2 (1,000,000 sq mi), making the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province larger than the Ontong Java Plateau in the southwestern Pacific Ocean and the U.S. state of Alaska.