IGNEOUS ROCK - CoconinoHighSchool
... (<20 m wide) shallow intrusions that show a discordant relationship to the rocks in which they intrude. ...
... (<20 m wide) shallow intrusions that show a discordant relationship to the rocks in which they intrude. ...
Rock Cycle & Igneous Rocks
... Also formed when volcanoes erupt, causing the magma to rise above the earth's surface. When magma appears above the earth, it is called lava. Igneous rocks are formed as the lava cools ...
... Also formed when volcanoes erupt, causing the magma to rise above the earth's surface. When magma appears above the earth, it is called lava. Igneous rocks are formed as the lava cools ...
Proterozoic Rocks
... Adirondack Terrane • Mylonite zone at NW contact with Frontenac Terrane • Large anorthosite-gabbro-charnockite complexes • Siliciclastic, carbonate, and evaporite metasediments • Felsic metavolcanics • 1.3 – 1.1 Ga intrusions ...
... Adirondack Terrane • Mylonite zone at NW contact with Frontenac Terrane • Large anorthosite-gabbro-charnockite complexes • Siliciclastic, carbonate, and evaporite metasediments • Felsic metavolcanics • 1.3 – 1.1 Ga intrusions ...
Igneous Processes Page 1 of 2 Intrusive igneous activity I. Plutons
... c. Laccolith—bulged body parallel to sedimentary beds d. Batholith—large intrusive body perhaps hundreds of km wide B. May take millions of years to cool II. Origin of magma—formed by melting solid rock ...
... c. Laccolith—bulged body parallel to sedimentary beds d. Batholith—large intrusive body perhaps hundreds of km wide B. May take millions of years to cool II. Origin of magma—formed by melting solid rock ...
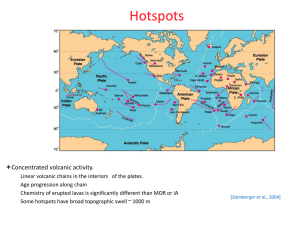
Do deep mantle plumes explain the Mesozoic igneous features of
... volcanism that appear to be unrelated to plate boundary processes (Tuzo Wilson, 1963). So the term “hotspot” was originally defined purely as a surface feature with an unknown cause of volcanism. Jason Morgan (1971) and others proposed that hotspots and linear chains of intraplate volcanoes are made ...
... volcanism that appear to be unrelated to plate boundary processes (Tuzo Wilson, 1963). So the term “hotspot” was originally defined purely as a surface feature with an unknown cause of volcanism. Jason Morgan (1971) and others proposed that hotspots and linear chains of intraplate volcanoes are made ...
Afar - Do plumes exist?
... 30-15Ma stage one of rifting between Arabia and Africa creating the Red Sea. 10km rifting 20Ma Main period of extension. ...
... 30-15Ma stage one of rifting between Arabia and Africa creating the Red Sea. 10km rifting 20Ma Main period of extension. ...
Lesson: Rock Cycle-Focus on Igneous Rocks
... in the mantle and crust. Pose the question: “Why do magma’s show a limited range of compositions?” This requires prior knowledge of the structure of the Earth lessons. The Earth is layered, based on physical properties such as density. Since partial melting only occurs in a small portion of the Eart ...
... in the mantle and crust. Pose the question: “Why do magma’s show a limited range of compositions?” This requires prior knowledge of the structure of the Earth lessons. The Earth is layered, based on physical properties such as density. Since partial melting only occurs in a small portion of the Eart ...
doc
... in the mantle and crust. Pose the question: “Why do magma’s show a limited range of compositions?” This requires prior knowledge of the structure of the Earth lessons. The Earth is layered, based on physical properties such as density. Since partial melting only occurs in a small portion of the Eart ...
... in the mantle and crust. Pose the question: “Why do magma’s show a limited range of compositions?” This requires prior knowledge of the structure of the Earth lessons. The Earth is layered, based on physical properties such as density. Since partial melting only occurs in a small portion of the Eart ...
Igneous Rock - East Hanover Township School District
... A) Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to Earth's surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above the surface as lava, and then cools forming rock. B) Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. ...
... A) Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to Earth's surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above the surface as lava, and then cools forming rock. B) Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. ...
GLOSSARY MINERAL – a naturally occurring inorganic element or
... Batholith – a large pluton that has more than 100km2 of exposed surface and no known floor. Caldera – a large, basin-shaped depression formed by the inward collapse of a volcano after an eruption. Country Rock – pre-existing rocks into which plutonic rocks intrude. Desert Varnish – a thin, shiny blu ...
... Batholith – a large pluton that has more than 100km2 of exposed surface and no known floor. Caldera – a large, basin-shaped depression formed by the inward collapse of a volcano after an eruption. Country Rock – pre-existing rocks into which plutonic rocks intrude. Desert Varnish – a thin, shiny blu ...
EGU2009-944-2
... period during Early Triassic to Early Jurassic. This cooling event coincides temporally with the process of rifting that caused Pangaea continental break-up and the opening of the North Atlantic. Other authors report similar cooling histories from Early Triassic to Middle Jurassic from other parts o ...
... period during Early Triassic to Early Jurassic. This cooling event coincides temporally with the process of rifting that caused Pangaea continental break-up and the opening of the North Atlantic. Other authors report similar cooling histories from Early Triassic to Middle Jurassic from other parts o ...
Chapter 3 - Igneous Rocks
... Silica rich (felsic) magma/lavas are thick, viscous and resist flow Silica poor (mafic) magma/lavas are thinner, have a lower viscosity and don’t ...
... Silica rich (felsic) magma/lavas are thick, viscous and resist flow Silica poor (mafic) magma/lavas are thinner, have a lower viscosity and don’t ...
18.3 – Intrusive Activity
... • Intrusive igneous rock body, including batholiths, stocks,sills & dikes • Formed through mountain-building processes and oceanic-oceanic collisions • Can be exposed at Earth’s surface to uplift and erosion ...
... • Intrusive igneous rock body, including batholiths, stocks,sills & dikes • Formed through mountain-building processes and oceanic-oceanic collisions • Can be exposed at Earth’s surface to uplift and erosion ...
18.3 power point - Trimble County Schools
... • Intrusive igneous rock body, including batholiths, stocks,sills & dikes • Formed through mountain-building processes and oceanic-oceanic collisions • Can be exposed at Earth’s surface to uplift and erosion ...
... • Intrusive igneous rock body, including batholiths, stocks,sills & dikes • Formed through mountain-building processes and oceanic-oceanic collisions • Can be exposed at Earth’s surface to uplift and erosion ...
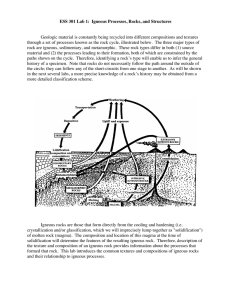
ESS 301 Lab 1: Igneous Processes, Rocks, and Structures Geologic
... material at areas such as mid-ocean ridges, and result in burial of material at subduction zones to depths where it undergoes partial melting. Specific tectonic processes are confined to certain portions of the convection cycle, so the characteristic igneous rocks associated with each process are ty ...
... material at areas such as mid-ocean ridges, and result in burial of material at subduction zones to depths where it undergoes partial melting. Specific tectonic processes are confined to certain portions of the convection cycle, so the characteristic igneous rocks associated with each process are ty ...
Introducing Igneous Rocks
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the water ...
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the water ...
rocks-sec 2 igneous
... Some heat was left over from when Earth was formed, which originally was molten ...
... Some heat was left over from when Earth was formed, which originally was molten ...
Igneous Processes
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the wate ...
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the wate ...
Igneous Rock - East Hanover Township School District
... A) Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to Earth's surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above the surface as lava, and then cools forming rock. B) Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. ...
... A) Extrusive igneous rocks, or volcanics, form when magma makes its way to Earth's surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above the surface as lava, and then cools forming rock. B) Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks have small crystals. Examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. ...
Igneous Rocks
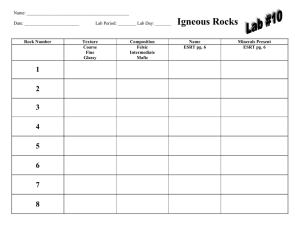
... INTRODUCTION: Please read this as it contains information that will help you complete this lab successfully. Igneous rocks are rocks that form from the cooling of molten magma (under ground) or lava (above ground). The word igneous means "fireformed." Cooling can be immediate or over long periods of ...
... INTRODUCTION: Please read this as it contains information that will help you complete this lab successfully. Igneous rocks are rocks that form from the cooling of molten magma (under ground) or lava (above ground). The word igneous means "fireformed." Cooling can be immediate or over long periods of ...
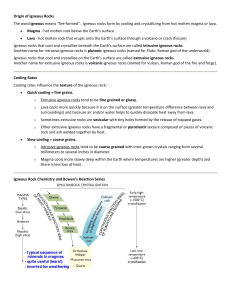
Origin of Igneous Rocks The word igneous means "fire
... Classification of rocks is always based on objective, observable, measurable data (such as grain size and the percentages of various minerals), and not on interpretations. The igneous rocks classification diagram below shows varying percentages of minerals in each of the four major categories of ig ...
... Classification of rocks is always based on objective, observable, measurable data (such as grain size and the percentages of various minerals), and not on interpretations. The igneous rocks classification diagram below shows varying percentages of minerals in each of the four major categories of ig ...
Flood13
... erupted lava. The majority of well-dated flood basalt provinces have main stage durations on the order of only 1 - 4 ma. The better the dating, the shorter the time interval. These short eruption durations, combined with the large volumes, correspond to eruption rates that are 10 - 100 times those s ...
... erupted lava. The majority of well-dated flood basalt provinces have main stage durations on the order of only 1 - 4 ma. The better the dating, the shorter the time interval. These short eruption durations, combined with the large volumes, correspond to eruption rates that are 10 - 100 times those s ...
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province

The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province (MLIP) is a major Mesoproterozoic large igneous province of the southwestern, western and northwestern Canadian Shield in Canada. It consists of a group of related igneous rocks that were formed during a massive igneous event starting about 1,270 million years ago. The large igneous province extends from the Arctic in Nunavut to near the Great Lakes in Northwestern Ontario where it meets with the smaller Matachewan dike swarm. Included in the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are the large Muskox layered intrusion, the Coppermine River flood basalt sequence and the massive northwesterly trending Mackenzie dike swarm.As a large igneous province, it is an extremely large area of related igneous rocks that were emplaced over an extremely short geological time span. The igneous rocks comprising the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province originated from processes not associated with normal plate tectonics and seafloor spreading. It is one of the several large igneous provinces scattered throughout the Canadian landscape, which can be thousands of kilometres in volume and area. The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province is also one of the largest Proterozoic magmatic provinces on Earth, as well as the world's largest and best-preserved continental flood basalt terrain. Igneous rocks of the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are generally mafic in composition, including basalt and gabbro.Even though the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province is classified as a large igneous province like other extremely large accumulations of igneous rocks on Earth, it is much larger than large igneous province standards. The standard size classification for large igneous provinces is a minimum areal extent of 100,000 km2 (39,000 sq mi). However, the Mackenzie dike swarm itself occupies an area of at least 2,700,000 km2 (1,000,000 sq mi), making the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province larger than the Ontong Java Plateau in the southwestern Pacific Ocean and the U.S. state of Alaska.