What are macromolecules? Cells are built primarily from the largest
... You should learn this list so well that you don't even hesitate to say what the four types of organic macromolecules are. This list is really important to understanding cells, so really memorize it well. It will pop up again and again throughout the semester. Carbohydrates are the "sugars." Both the ...
... You should learn this list so well that you don't even hesitate to say what the four types of organic macromolecules are. This list is really important to understanding cells, so really memorize it well. It will pop up again and again throughout the semester. Carbohydrates are the "sugars." Both the ...
Chapter 8
... involve the use of techniques including applied mathematics, informatics, statistics, computer science, artificial intelligence, chemistry, and ...
... involve the use of techniques including applied mathematics, informatics, statistics, computer science, artificial intelligence, chemistry, and ...
1 Lecture 6: Protein Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Structure +
... A few additional divisions in the above are also useful. For example, frequently found 2° structure patterns are termed “super secondary structures”; some proteins fold into one or more independent 3° structure “domains”; and the 4° structural association can occur between identical or dissimilar su ...
... A few additional divisions in the above are also useful. For example, frequently found 2° structure patterns are termed “super secondary structures”; some proteins fold into one or more independent 3° structure “domains”; and the 4° structural association can occur between identical or dissimilar su ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... remains dissolved, it can often renature when the chemical and physical aspects of its environment are restored to normal. ...
... remains dissolved, it can often renature when the chemical and physical aspects of its environment are restored to normal. ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... remains dissolved, it can often renature when the chemical and physical aspects of its environment are restored to normal. ...
... remains dissolved, it can often renature when the chemical and physical aspects of its environment are restored to normal. ...
ppt - Avraham Samson`s Lab
... number of degrees of freedom in a polypeptide chain, the molecule has an astronomical number of possible conformations. For example, a polypeptide of 100 residues will have 99 peptide bonds, and therefore 198 different phi and psi bond angles. If each of these bond angles can be in one of three stab ...
... number of degrees of freedom in a polypeptide chain, the molecule has an astronomical number of possible conformations. For example, a polypeptide of 100 residues will have 99 peptide bonds, and therefore 198 different phi and psi bond angles. If each of these bond angles can be in one of three stab ...
Protein Concentration Determination In nearly any biochemistry
... will generally fall between 4.0 and 15; however, examples of proteins at either extremes have been observed, eg. parvalbumin (0.0), serum albumin (5.8), trypsin (14.3) and lysozyme (26.5). Thus, the absorbance at 280 nm will only give an estimation of the protein concentration unless the extinction ...
... will generally fall between 4.0 and 15; however, examples of proteins at either extremes have been observed, eg. parvalbumin (0.0), serum albumin (5.8), trypsin (14.3) and lysozyme (26.5). Thus, the absorbance at 280 nm will only give an estimation of the protein concentration unless the extinction ...
sg 10
... After irradiation with X-rays, Neurospora spores were allowed to on various minimal media plates supplemented with one the metabolites in the pathway above. While the spores were able to grow on minimal media supplemented with metabolite D, but not on plates supplemented with either A, B, or C. Whic ...
... After irradiation with X-rays, Neurospora spores were allowed to on various minimal media plates supplemented with one the metabolites in the pathway above. While the spores were able to grow on minimal media supplemented with metabolite D, but not on plates supplemented with either A, B, or C. Whic ...
AP Biology
... After irradiation with X-rays, Neurospora spores were allowed to on various minimal media plates supplemented with one the metabolites in the pathway above. While the spores were able to grow on minimal media supplemented with metabolite D, but not on plates supplemented with either A, B, or C. Whic ...
... After irradiation with X-rays, Neurospora spores were allowed to on various minimal media plates supplemented with one the metabolites in the pathway above. While the spores were able to grow on minimal media supplemented with metabolite D, but not on plates supplemented with either A, B, or C. Whic ...
Renaturation of telomere-binding proteins after the fractionation by
... if large number of gel slices have to be handled. However, there is a simpler method, described by Ossipow et al. (1993), which is based on the observation that mild non-ionic detergents, such as Triton X-100, remove SDS from protein-SDS complexes and sequester it into micelles that do not interfere ...
... if large number of gel slices have to be handled. However, there is a simpler method, described by Ossipow et al. (1993), which is based on the observation that mild non-ionic detergents, such as Triton X-100, remove SDS from protein-SDS complexes and sequester it into micelles that do not interfere ...
Bio 210 Cell Chemistry Lecture 5 “Proteins and Nucleic Acids”
... acetyl choline receptor: nerve cell ...
... acetyl choline receptor: nerve cell ...
Ming Li Talk about Bioinformatics - the David R. Cheriton School of
... energy by forming the internal hydrophobic bonds for alpha and beta structures since the in unfolded state, equally stable hydrogen bonds can also be formed to water molecules!! Thus secondary structure formation cannot be thermodynamic driving force of protein folding. On the other hand, there is ...
... energy by forming the internal hydrophobic bonds for alpha and beta structures since the in unfolded state, equally stable hydrogen bonds can also be formed to water molecules!! Thus secondary structure formation cannot be thermodynamic driving force of protein folding. On the other hand, there is ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... 7. The protein ______ participates in oxygen dispersal in muscle. 8. A polypeptide can fold into an individual unit of structure called a ______________. 9. A protein that contains more than one subunit is called ______. 10. A secondary structure which forms a coiled shape with a specific repeating ...
... 7. The protein ______ participates in oxygen dispersal in muscle. 8. A polypeptide can fold into an individual unit of structure called a ______________. 9. A protein that contains more than one subunit is called ______. 10. A secondary structure which forms a coiled shape with a specific repeating ...
protein - Portal UniMAP
... compact and water-soluble In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the pro ...
... compact and water-soluble In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the pro ...
week 10_protein
... compact and water-soluble In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the pro ...
... compact and water-soluble In their function, usually require them to bind precisely to other molecules Each protein has a unique and complex surface that contains cavities and clefts whose structure is complementary to specific ligands. After ligand binding, a conformational change occurs in the pro ...
PE 690 weight training PPt
... • Body either excrete it, turn it to fat, or use it for energy. • Types of protein (whey, casein, soy, rice) • The major proteins in milk are casein and whey. These two milk proteins are both excellent sources, but they differ in one important aspect—whey is a fast-digesting protein and casein is a ...
... • Body either excrete it, turn it to fat, or use it for energy. • Types of protein (whey, casein, soy, rice) • The major proteins in milk are casein and whey. These two milk proteins are both excellent sources, but they differ in one important aspect—whey is a fast-digesting protein and casein is a ...
Protein regulation: The statistical theory of
... regulation is called allosteric1–4. Advances in understanding allosteric mechanisms can be made through the use of NMR spectroscopy, which provides a variety of tools for characterizing the structure and dynamics of proteins3–6. Particularly attractive in this context is the use of chemical shifts, ...
... regulation is called allosteric1–4. Advances in understanding allosteric mechanisms can be made through the use of NMR spectroscopy, which provides a variety of tools for characterizing the structure and dynamics of proteins3–6. Particularly attractive in this context is the use of chemical shifts, ...
Basic Biochemistry - Personal Webspace for QMUL
... ____ by applying an electric charge through a polymer gel A polyacrylamide gel is almost always used The technique is known as: Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis ==> PAGE Polyacrylamide is chemically inert Figure 3-7b, page 71 (3-7b, page 74) The gel forms as ‘SPAGHETTI-LIKE’ STRANDS The ...
... ____ by applying an electric charge through a polymer gel A polyacrylamide gel is almost always used The technique is known as: Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis ==> PAGE Polyacrylamide is chemically inert Figure 3-7b, page 71 (3-7b, page 74) The gel forms as ‘SPAGHETTI-LIKE’ STRANDS The ...
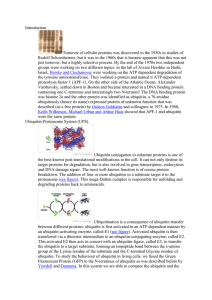
Introduction
... Turnover of cellular proteins was discovered in the 1930s in studies of Rudolf Schoenheimer, but it was in the 1960s that is became apparent that this was not just turnover, but a highly selective process. By the end of the 1970s two independent groups were working on two different topics: in the la ...
... Turnover of cellular proteins was discovered in the 1930s in studies of Rudolf Schoenheimer, but it was in the 1960s that is became apparent that this was not just turnover, but a highly selective process. By the end of the 1970s two independent groups were working on two different topics: in the la ...
Document
... the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting data to find out if humans' pattern-recognition and puzzle-solving abilities make them more efficient than existing computer programs at pattern-folding tasks. If this turns out to be true, we can the ...
... the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting data to find out if humans' pattern-recognition and puzzle-solving abilities make them more efficient than existing computer programs at pattern-folding tasks. If this turns out to be true, we can the ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.