Protein thermodynamics: Are native proteins
... demonstrated by showing that both the aldehyde and alcohol components could be readily exchanged. Mechanistic and mass spectrometric studies suggested that the iminium ion framed in Fig. 1b acts as the key intermediate in both aldehyde and alcohol scrambling, and found no evidence of the alternative ...
... demonstrated by showing that both the aldehyde and alcohol components could be readily exchanged. Mechanistic and mass spectrometric studies suggested that the iminium ion framed in Fig. 1b acts as the key intermediate in both aldehyde and alcohol scrambling, and found no evidence of the alternative ...
Gene Section TGFBI (transforming growth factor, beta-induced, 68kDa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... cell-matrix interactions, cell adhesion, migration and differentiation. The protein may be involved in endochondrial bone formation in cartilage. The roles of TGFBI in malignant progression are controversial. Some studies suggested that TGFBI suppresses the progression of ovarian, lung cancer and ne ...
... cell-matrix interactions, cell adhesion, migration and differentiation. The protein may be involved in endochondrial bone formation in cartilage. The roles of TGFBI in malignant progression are controversial. Some studies suggested that TGFBI suppresses the progression of ovarian, lung cancer and ne ...
BI ACE_02 .
... When the amino acids have been built up into proteins, the buffering capacity is retained. This is due to the presence of additional amino and carboxyl groups of the basic and acid residues of the protein. Hence, proteins play and important part as the buffer for cells and organisms. For instance, t ...
... When the amino acids have been built up into proteins, the buffering capacity is retained. This is due to the presence of additional amino and carboxyl groups of the basic and acid residues of the protein. Hence, proteins play and important part as the buffer for cells and organisms. For instance, t ...
1. The formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids is an
... 27. An allosteric interaction between a ligand and a protein is one in which: A) binding of a molecule to a binding site affects binding of additional molecules to the same site. B) binding of a molecule to a binding site affects binding properties of another site on the protein. C) binding of the l ...
... 27. An allosteric interaction between a ligand and a protein is one in which: A) binding of a molecule to a binding site affects binding of additional molecules to the same site. B) binding of a molecule to a binding site affects binding properties of another site on the protein. C) binding of the l ...
Bio slides on cells - proteinsynthesis1unity
... nucleus is moved systemically along the ribosome where transfer RNA adds individual amino acid molecules to the lengthening protein chain ...
... nucleus is moved systemically along the ribosome where transfer RNA adds individual amino acid molecules to the lengthening protein chain ...
Protein-surface interactions: insights from atomistic - Cnr-Nano
... Understanding and controlling the interaction of proteins with inorganic surfaces and nanoparticles is a key task in nanobiotechnology. On the one hand, inorganic components within a biological system (e.g., nanoparticles for drug delivery, for diagnostic or accidentally uptaken [1]; surgical implan ...
... Understanding and controlling the interaction of proteins with inorganic surfaces and nanoparticles is a key task in nanobiotechnology. On the one hand, inorganic components within a biological system (e.g., nanoparticles for drug delivery, for diagnostic or accidentally uptaken [1]; surgical implan ...
Document
... • Proteins with common sequence features have similar biological function, • This allow for the characterization of newly discovered proteins. Example - protein kinases Enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of amino acid residues. All known protein kinases have the same common sequence region (d ...
... • Proteins with common sequence features have similar biological function, • This allow for the characterization of newly discovered proteins. Example - protein kinases Enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of amino acid residues. All known protein kinases have the same common sequence region (d ...
F-11 INVESTIGATOR Name Henry F. Epstein Address
... Liu, F., Thatcher, J.D., Barral, J.M. and Epstein, H.F. (1995). Bifunctional glyoxylate cycle protein of Caenorhabditis elegans: A developmentally regulated protein of intestine and muscle. Dev. Biol. 169, 399-414. Liu, F., Thatcher, J.D., and Epstein, H.F. (1997). Induction of glyosylate cycle expr ...
... Liu, F., Thatcher, J.D., Barral, J.M. and Epstein, H.F. (1995). Bifunctional glyoxylate cycle protein of Caenorhabditis elegans: A developmentally regulated protein of intestine and muscle. Dev. Biol. 169, 399-414. Liu, F., Thatcher, J.D., and Epstein, H.F. (1997). Induction of glyosylate cycle expr ...
Slide 1
... It dramatically reduces the time, labor and cost for producing proteins with specific properties. The system can be used to create effective vaccines, more sensitive and specific diagnostics, and virtually any therapeutic where antibodies ...
... It dramatically reduces the time, labor and cost for producing proteins with specific properties. The system can be used to create effective vaccines, more sensitive and specific diagnostics, and virtually any therapeutic where antibodies ...
D - Protein Information Resource
... was developed based on literature data sets about five types of protein post-translational modifications, glycosylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation and hydroxylation, provided in iProLINK. The algorithm showed that Naive Bayes and Support Vector Machine classifiers perform consistentl ...
... was developed based on literature data sets about five types of protein post-translational modifications, glycosylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation and hydroxylation, provided in iProLINK. The algorithm showed that Naive Bayes and Support Vector Machine classifiers perform consistentl ...
Proteins perform most functions in the cell [1].
... Get in the habit of writing legibly, neatly, and in a NORMAL, MEDIUM-SIZED FONT. Please SCAN documents properly and upload them to Archie. Avoid taking photographs of or uploading dark, washed out, side ways, or upside down homework. Please use the scanner in the school’s media lab if one is not at ...
... Get in the habit of writing legibly, neatly, and in a NORMAL, MEDIUM-SIZED FONT. Please SCAN documents properly and upload them to Archie. Avoid taking photographs of or uploading dark, washed out, side ways, or upside down homework. Please use the scanner in the school’s media lab if one is not at ...
1 Protein Secretion: Targeting to the ER I. Introduction nucleus ER
... little bit bigger (and ran higher on an SDS-PAGE gel) than the protein isolated from the secreted immunoglobulin. He figured the in vitro synthesized protein must have an extra set of amino acids at either the N- or the C-terminus, and protein sequencing revealed that it was at the N-terminus. This ...
... little bit bigger (and ran higher on an SDS-PAGE gel) than the protein isolated from the secreted immunoglobulin. He figured the in vitro synthesized protein must have an extra set of amino acids at either the N- or the C-terminus, and protein sequencing revealed that it was at the N-terminus. This ...
Macromolecules WebQuest
... A fat is a lipid that contains _________ glycerol linked to _________ fatty acids by Fats are often called _________ because of their structure Fats are lipids that are mostly _________ molecules Draw a fat and label the parts Some fatty acids contain _________bonds This causes _________in ...
... A fat is a lipid that contains _________ glycerol linked to _________ fatty acids by Fats are often called _________ because of their structure Fats are lipids that are mostly _________ molecules Draw a fat and label the parts Some fatty acids contain _________bonds This causes _________in ...
Macromolecules Quiz
... Matching--Select the macromolecule that best matches the statement. Letters may be used once, more than once or not at all. a. Proteins b. Carbohydrates c. Lipids d. Nucleic Acids 1. These macromolecules possess large nonpolar regions making them insoluble in water. 2. This macromolecule is compose ...
... Matching--Select the macromolecule that best matches the statement. Letters may be used once, more than once or not at all. a. Proteins b. Carbohydrates c. Lipids d. Nucleic Acids 1. These macromolecules possess large nonpolar regions making them insoluble in water. 2. This macromolecule is compose ...
GRAMD2 antibody - middle region (ARP44634_P050)
... This is a rabbit polyclonal antibody against GRAMD2. It was validated on Western Blot using a cell lysate as a positive control. Aviva Systems Biology strives to provide antibodies covering each member of a whole protein family of your interest. We also use our best efforts to provide you antibodies ...
... This is a rabbit polyclonal antibody against GRAMD2. It was validated on Western Blot using a cell lysate as a positive control. Aviva Systems Biology strives to provide antibodies covering each member of a whole protein family of your interest. We also use our best efforts to provide you antibodies ...
Unidirectional tandem gene arrays
... become limited for large recombinant DNA molecules. Golden Gate Shuffling is a protocol to assemble separate DNA fragments together into an acceptor vector in one step and one tube. The principle of the cloning strategy is based on the ability of type IIs restriction enzymes to cut outside of thei ...
... become limited for large recombinant DNA molecules. Golden Gate Shuffling is a protocol to assemble separate DNA fragments together into an acceptor vector in one step and one tube. The principle of the cloning strategy is based on the ability of type IIs restriction enzymes to cut outside of thei ...
Practice Exam II
... a). The difference in Gibbs free energy between the reactant and product before catalysis. b). The difference in Gibbs free energy between the reactant and product after catalysis. c). The difference in Gibbs free energy between an enzyme in the active (R-state) and inactive (T-state) ...
... a). The difference in Gibbs free energy between the reactant and product before catalysis. b). The difference in Gibbs free energy between the reactant and product after catalysis. c). The difference in Gibbs free energy between an enzyme in the active (R-state) and inactive (T-state) ...
Protein Surgery Increases Protein Demands in the Body Getting
... A healthy person should consume .08 gram protein/ kg of body weight. A quick equation to remember is 1 gram protein/ 3 pounds of body weight. 40 grams for a 120 pound person 50 grams for a 150 pounds 60 grams for 180 pounds Protein Needs after Surgery The highest protein demand for healing purposes ...
... A healthy person should consume .08 gram protein/ kg of body weight. A quick equation to remember is 1 gram protein/ 3 pounds of body weight. 40 grams for a 120 pound person 50 grams for a 150 pounds 60 grams for 180 pounds Protein Needs after Surgery The highest protein demand for healing purposes ...
6.3 Reading guide macromolecule
... Draw the number of bars needed to show a double bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a single bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a triple bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C What thre ...
... Draw the number of bars needed to show a double bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a single bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C Draw the number of bars needed to show a triple bond between the following two carbon atoms. C C What thre ...
Amino Acid Instruction Sheet
... Atom (/ˈatəm/): the basic unit of matter, sometimes described as building blocks. Amino Acid (əˈmēnō/ /ˈasid/): building blocks of larger molecules called proteins. The amino acids are arranged like beads on a string. There are 21 common amino acids in proteins. Building Block (): a basic element or ...
... Atom (/ˈatəm/): the basic unit of matter, sometimes described as building blocks. Amino Acid (əˈmēnō/ /ˈasid/): building blocks of larger molecules called proteins. The amino acids are arranged like beads on a string. There are 21 common amino acids in proteins. Building Block (): a basic element or ...
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
... • The coat of proteins, around the RNA strand, protect it from any enzymes trying to kill it. • But, in order for TMV to spread it has to release it’s coat of proteins for the RNA to enter a cell • The proteins, situated outside the cell, repel against each other. This allows the cell to release RNA ...
... • The coat of proteins, around the RNA strand, protect it from any enzymes trying to kill it. • But, in order for TMV to spread it has to release it’s coat of proteins for the RNA to enter a cell • The proteins, situated outside the cell, repel against each other. This allows the cell to release RNA ...
VIII. PROTEINS, continued
... amino acids. Helps to give each protein its unique shape. __________________ interactions – amino acids with non-polar R groups cluster together at core of protein. _________________ bridges – important in reinforcing shape of protein; covalent bonds that form between sulfhydryl R groups of amin ...
... amino acids. Helps to give each protein its unique shape. __________________ interactions – amino acids with non-polar R groups cluster together at core of protein. _________________ bridges – important in reinforcing shape of protein; covalent bonds that form between sulfhydryl R groups of amin ...
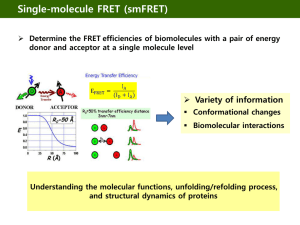
Single molecule analysis - Biomolecular Engineering Laboratory
... Single molecule-based technologies enabling us to manipulate and probe individual molecules Answer many of fundamental biological questions : - Protein functions : Dynamics and recognition - Biomolecular interactions - Biological phenomenon ...
... Single molecule-based technologies enabling us to manipulate and probe individual molecules Answer many of fundamental biological questions : - Protein functions : Dynamics and recognition - Biomolecular interactions - Biological phenomenon ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.










![Proteins perform most functions in the cell [1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014430699_1-2242d98249553cc613e120034bd15855-300x300.png)