Relationship between Hot Spot Residues and Ligand Binding Hot
... structures of a target protein in aqueous solutions containing high concentrations of organic cosolvents and then superimposing the structures to find consensus binding sites that accommodate a number of the organic probes binding in welldefined orientations.12,13 The MSCS method has been used by seve ...
... structures of a target protein in aqueous solutions containing high concentrations of organic cosolvents and then superimposing the structures to find consensus binding sites that accommodate a number of the organic probes binding in welldefined orientations.12,13 The MSCS method has been used by seve ...
Can correct protein models be identified?
... first generation of decoys was generated by putting the sequence from a particular protein onto the backbone of another protein. Novotny studied different parameters distinguishing between models built on the native and an incorrect backbone (Novotny et al. 1988). Later, Sippl developed knowledge-ba ...
... first generation of decoys was generated by putting the sequence from a particular protein onto the backbone of another protein. Novotny studied different parameters distinguishing between models built on the native and an incorrect backbone (Novotny et al. 1988). Later, Sippl developed knowledge-ba ...
Chapter 4.32
... traverses the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi compartments. In N-glycosylation, a preformed oligosaccharide moiety is transferred en bloc from a long-chain isoprenoid lipid (dolichol) onto the specific N-glycosylation site via an N-glycosidic linkage to the asparagine (Asn) residue of a nascent ...
... traverses the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi compartments. In N-glycosylation, a preformed oligosaccharide moiety is transferred en bloc from a long-chain isoprenoid lipid (dolichol) onto the specific N-glycosylation site via an N-glycosidic linkage to the asparagine (Asn) residue of a nascent ...
Nucleosomes released from oviduct nuclei during brief micrococcal
... 5 ml fractions were collected. The monomer nucleosome peak, eluting between fractions 40 and 60, was collected, concentrated, and separated by electrophoresis on a 3 mm thick polyacrylamide 'DNP' slab gel [13] containing 40 mM NaCl. At the end of the electrophoresis a vertical gel s t r i p was cut ...
... 5 ml fractions were collected. The monomer nucleosome peak, eluting between fractions 40 and 60, was collected, concentrated, and separated by electrophoresis on a 3 mm thick polyacrylamide 'DNP' slab gel [13] containing 40 mM NaCl. At the end of the electrophoresis a vertical gel s t r i p was cut ...
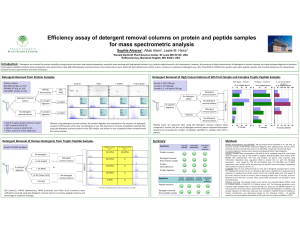
Efficiency assay of detergent removal columns on - G
... and suppress peptide ionization when analyzed by mass spectrometry. New (GB‐S10) detergent removal columns from G‐Biosciences were tested for their efficiency to remove anionic, nonionic or zwitterionic detergents (e.g. SDS, TritonX100 or CHAPS) from protein and tryptic peptide samples with minimal ...
... and suppress peptide ionization when analyzed by mass spectrometry. New (GB‐S10) detergent removal columns from G‐Biosciences were tested for their efficiency to remove anionic, nonionic or zwitterionic detergents (e.g. SDS, TritonX100 or CHAPS) from protein and tryptic peptide samples with minimal ...
J Molecular Biology 307:939-949, 2001
... Multiple alignment-to-sequence searches can identify genuine relations that are not found by sequence-to-sequence searches.1 ± 6 This is the result of identifying what residues are preferred in the conserved sequence regions of the family members and of not using sequence regions that are not conser ...
... Multiple alignment-to-sequence searches can identify genuine relations that are not found by sequence-to-sequence searches.1 ± 6 This is the result of identifying what residues are preferred in the conserved sequence regions of the family members and of not using sequence regions that are not conser ...
Protein Targeting to the Nuclear Pore. What Can
... Harley M.S. Smith and Natasha V. Raikhel* Department of Energy Plant Research Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan 48824–1312 Characteristic of eukaryotic cells are the numerous types of membrane-bound organelles or compartments found in the cytoplasm, with each type carryin ...
... Harley M.S. Smith and Natasha V. Raikhel* Department of Energy Plant Research Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan 48824–1312 Characteristic of eukaryotic cells are the numerous types of membrane-bound organelles or compartments found in the cytoplasm, with each type carryin ...
Function and biotechnology of extremophilic enzymes in low water
... activity in extreme conditions is their effects on water structure and dynamics. When water activity is perturbed by extreme temperatures, high salinity, or other extreme conditions, normally structured liquid water may become limiting to enzymes, with deleterious consequences to enzyme structure an ...
... activity in extreme conditions is their effects on water structure and dynamics. When water activity is perturbed by extreme temperatures, high salinity, or other extreme conditions, normally structured liquid water may become limiting to enzymes, with deleterious consequences to enzyme structure an ...
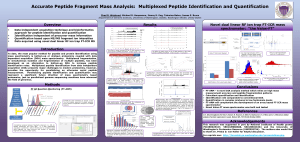
Accurate Peptide Fragment Mass Analysis: Multiplexed
... mass spectrometry is bottom-up or shotgun proteomics coupled with data dependent acquisition (DDA) mass spectrometry. Multiplexed fragmentation, or simultaneous isolation and fragmentation of multiple peptides, has been developed as an alternative to bottom-up DDA to increase peptide identification ...
... mass spectrometry is bottom-up or shotgun proteomics coupled with data dependent acquisition (DDA) mass spectrometry. Multiplexed fragmentation, or simultaneous isolation and fragmentation of multiple peptides, has been developed as an alternative to bottom-up DDA to increase peptide identification ...
Cystic Fibrosis and CFTR Gene - Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... VI-3.1. Class 1: mutations altering the production of the protein. These mutations result in the total or partial absence of the protein. This class includes the nonsense mutations and those that produce a premature stop codon (anomalies of splicing and frameshift mutations). In certain cases the m ...
... VI-3.1. Class 1: mutations altering the production of the protein. These mutations result in the total or partial absence of the protein. This class includes the nonsense mutations and those that produce a premature stop codon (anomalies of splicing and frameshift mutations). In certain cases the m ...
AMIN domains have a predicted role in localization of diverse
... relating to murein hydrolysis suggests that it participates in cell-wall remodeling. Strikingly, the other set of architectures combine the AMIN domain with domains that form unrelated, but functionally comparable, transport structures across the Gram-negative outer membranes. These include the secr ...
... relating to murein hydrolysis suggests that it participates in cell-wall remodeling. Strikingly, the other set of architectures combine the AMIN domain with domains that form unrelated, but functionally comparable, transport structures across the Gram-negative outer membranes. These include the secr ...
I. CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE, cont
... that are formed from interactions between 2 or more polypeptide chains folded together. Examples include hemoglobin, collagen, chlorophyll ...
... that are formed from interactions between 2 or more polypeptide chains folded together. Examples include hemoglobin, collagen, chlorophyll ...
Continued..
... which is found in a widely varying family of DNA-binding proteins. The conserved cysteine and histidine residues in this sequence motif form ligands to a zinc ion, which is essential to stabilize the tertiary structure. Conservation is sometimes of a class of residues rather than a specific resi ...
... which is found in a widely varying family of DNA-binding proteins. The conserved cysteine and histidine residues in this sequence motif form ligands to a zinc ion, which is essential to stabilize the tertiary structure. Conservation is sometimes of a class of residues rather than a specific resi ...
3.1 Life`s molecular diversity is based on the
... 3.3 Cells make a huge number of large molecules from a small set of small molecules Monomers are linked together to form polymers through dehydration reactions, which remove water Polymers are broken apart by hydrolysis, the addition of water All biological reactions of this sort are mediated ...
... 3.3 Cells make a huge number of large molecules from a small set of small molecules Monomers are linked together to form polymers through dehydration reactions, which remove water Polymers are broken apart by hydrolysis, the addition of water All biological reactions of this sort are mediated ...
chapter 11
... • A protein may have from about 50 to many thousands of amino acids, joined linearly by way of peptide bonds. • The information for determining the sequence of amino acids resides in the DNA of most cells. • A gene is the region of DNA responsible for the coding of a protein. • There are thousands o ...
... • A protein may have from about 50 to many thousands of amino acids, joined linearly by way of peptide bonds. • The information for determining the sequence of amino acids resides in the DNA of most cells. • A gene is the region of DNA responsible for the coding of a protein. • There are thousands o ...
Protein-RNA interactions: Structural analysis and functional classes
... structures have been solved. However, the publication of the structure of the 50S and 30S ribosome subunits in 2000,1,2 and the advent of the structural genomics projects means that structural information for more than 350 protein–RNA complexes is currently available. This increased volume of data m ...
... structures have been solved. However, the publication of the structure of the 50S and 30S ribosome subunits in 2000,1,2 and the advent of the structural genomics projects means that structural information for more than 350 protein–RNA complexes is currently available. This increased volume of data m ...
Evaluation of the Progress of Protein Hydrolysis
... the functional, organoleptic, and nutritional value of a foodstuff. Advances in the technology of protein hydrolysate production has allowed the use of unconventional protein sources for animal and human food. The following test parameters must be defined for the production of a protein hydrolysate: ...
... the functional, organoleptic, and nutritional value of a foodstuff. Advances in the technology of protein hydrolysate production has allowed the use of unconventional protein sources for animal and human food. The following test parameters must be defined for the production of a protein hydrolysate: ...
Microsoft Word
... -Casein is easily degradable protein due to its random coil structure. -Casein are grouped under intrinsically unstructured proteins. The aperoidicity of the protein is due to the presence of 8.5% proline residues uniformly distributed in the polypeptide chain. The flexibility and randomness in th ...
... -Casein is easily degradable protein due to its random coil structure. -Casein are grouped under intrinsically unstructured proteins. The aperoidicity of the protein is due to the presence of 8.5% proline residues uniformly distributed in the polypeptide chain. The flexibility and randomness in th ...
Genetic Research Produces a More Nutritious
... hanced levels of protein and essential amino acids. therefore is a good source of energy. Also, the leaves Egnin’s team achieved this higher protein level by are edible, producing more food products and less incorporating a synthetic storage protein gene into the waste. Onboard the spacecraft there ...
... hanced levels of protein and essential amino acids. therefore is a good source of energy. Also, the leaves Egnin’s team achieved this higher protein level by are edible, producing more food products and less incorporating a synthetic storage protein gene into the waste. Onboard the spacecraft there ...
Protein kinases - Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal
... How many phosphorylation sites are there? If there are ~10,000 proteins per cell with an average length of 400 aa (~ 17% of which are Ser, Thr or Tyr), then there are ~700,000 potential phosphorylation sites for any given kinase (including hidden residues). Although protein kinases have relatively ...
... How many phosphorylation sites are there? If there are ~10,000 proteins per cell with an average length of 400 aa (~ 17% of which are Ser, Thr or Tyr), then there are ~700,000 potential phosphorylation sites for any given kinase (including hidden residues). Although protein kinases have relatively ...
Nutrient Metabolism
... phases (Table 2). Horses were interval trained twice a week and were walked at 1.5 m/s for 30 min on a mechanical walker on rest days. Standard exercise test (SET). Before conditioning, but after the dietary accommodation period, all horses performed a standard exercise test (SET-U). The SET consist ...
... phases (Table 2). Horses were interval trained twice a week and were walked at 1.5 m/s for 30 min on a mechanical walker on rest days. Standard exercise test (SET). Before conditioning, but after the dietary accommodation period, all horses performed a standard exercise test (SET-U). The SET consist ...
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA FOR DUPLICATED SACCHAROMYCES
... A weak nuclear localization signal was detected for UGP1 by Yeast Protein Localization Server. Nuclear localization prediction was stronger for YHL012W. Huh et al. report cytoplasmic location for UGP1, but no location for YHL012W [6]. S2.3. Comments on UGP1 and YHL012W The identity between UGP1 and ...
... A weak nuclear localization signal was detected for UGP1 by Yeast Protein Localization Server. Nuclear localization prediction was stronger for YHL012W. Huh et al. report cytoplasmic location for UGP1, but no location for YHL012W [6]. S2.3. Comments on UGP1 and YHL012W The identity between UGP1 and ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.