protein targeting
... A cytosolic ribnucleoprotein particle that transiently binds to both the ER signal sequence and large ribosomal subunit ...
... A cytosolic ribnucleoprotein particle that transiently binds to both the ER signal sequence and large ribosomal subunit ...
BIOMOLECULES UNIT 3 Chemistry Review: Atoms
... cumulatively are strong, (Gecko feet), but not as strong as the other types. Hydrogen bonds- attraction between water molecules, and other molecules Elements- pure substances that cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means. Compounds- pure substances formed from 2 or more elements in a part ...
... cumulatively are strong, (Gecko feet), but not as strong as the other types. Hydrogen bonds- attraction between water molecules, and other molecules Elements- pure substances that cannot be broken down by physical or chemical means. Compounds- pure substances formed from 2 or more elements in a part ...
NMR - University of Puget Sound
... Protein interiors compact (more efficient packing than organic molecule crystals!) ...
... Protein interiors compact (more efficient packing than organic molecule crystals!) ...
2013 version with answers.
... sometimes find a Ser or Asp or so in a helix, but hardly ever will you find them conserved in the whole family, unless they have a functional role. 11) Why does a salt bridge care (much) less about the inter-atomic distance than a Van der Waals interaction? Use formulas to illustrate your answer. Va ...
... sometimes find a Ser or Asp or so in a helix, but hardly ever will you find them conserved in the whole family, unless they have a functional role. 11) Why does a salt bridge care (much) less about the inter-atomic distance than a Van der Waals interaction? Use formulas to illustrate your answer. Va ...
407_lecture_9
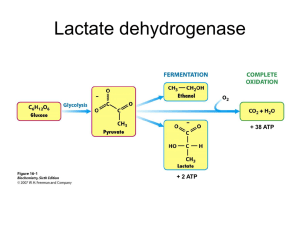
... • Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in virtually every biochemical reaction) • Structural components of cells (both inside and outside of cells in tissues) • Regulatory functions (if/when a cell divides, which genes are expressed, etc.) • Carrier and transport functions (ions, small ...
... • Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in virtually every biochemical reaction) • Structural components of cells (both inside and outside of cells in tissues) • Regulatory functions (if/when a cell divides, which genes are expressed, etc.) • Carrier and transport functions (ions, small ...
De niet-covalente interacties
... • Association of apolar groups/molecules in water results in the release of water molecules that surround the apolar surface in a stiff, ice-like structure. • The released water molecules have more possibilities to interact with other water molecules in solution. • This results in an increase of the ...
... • Association of apolar groups/molecules in water results in the release of water molecules that surround the apolar surface in a stiff, ice-like structure. • The released water molecules have more possibilities to interact with other water molecules in solution. • This results in an increase of the ...
UNIT 2: BIOCHEMISTRY/ENZYMES
... • 1. a picture of a food that contains each type of molecule (you may not be able to find one for nucleic acids, which is fine). • 2. For each molecule, include a description, as well as a drawing of what the actual carbon molecule looks like. • 3. Your placemats will be laminated and ready for you ...
... • 1. a picture of a food that contains each type of molecule (you may not be able to find one for nucleic acids, which is fine). • 2. For each molecule, include a description, as well as a drawing of what the actual carbon molecule looks like. • 3. Your placemats will be laminated and ready for you ...
Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein ab114419 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Additional notes ...
... Additional notes ...
Abstracts - Weizmann Institute of Science
... A single yeast cell is a few microns in diameter and yet contains about a hundred million proteins. Interactions between these proteins are crucial for most cellular functions, which has fuelled efforts to characterize how proteins assemble into functional complexes. Considerable information thus ex ...
... A single yeast cell is a few microns in diameter and yet contains about a hundred million proteins. Interactions between these proteins are crucial for most cellular functions, which has fuelled efforts to characterize how proteins assemble into functional complexes. Considerable information thus ex ...
What is PCM Synergy? PCM synergy is a quality blend is a multi
... PCM synergy is a quality blend is a multi-functional protein supplement that guarantees a good supply of protein building blocks for the individual. Furthermore, PCM synergy contains a high level of BCAAs (branch chain amino acids) which are vital in the manufacture, maintenance and repair of muscle ...
... PCM synergy is a quality blend is a multi-functional protein supplement that guarantees a good supply of protein building blocks for the individual. Furthermore, PCM synergy contains a high level of BCAAs (branch chain amino acids) which are vital in the manufacture, maintenance and repair of muscle ...
Characterisation of glycogenic and ketogenic metabolic pathways
... Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing research [8]. Whey is an abundant source of branched-chain amino acids that stimulates protein synthesis. In particular ...
... Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing research [8]. Whey is an abundant source of branched-chain amino acids that stimulates protein synthesis. In particular ...
Summer 2011 Proposal for UNCA Undergraduate Research
... binding and SRF activation to determine the precise structural features that conferred upon G12 the ability to stimulate this cellular growth pathway. In addition, I will examine variation in HSP90 across a variety of taxa to identify residues for mutation; these studies should facilitate mapping o ...
... binding and SRF activation to determine the precise structural features that conferred upon G12 the ability to stimulate this cellular growth pathway. In addition, I will examine variation in HSP90 across a variety of taxa to identify residues for mutation; these studies should facilitate mapping o ...
Protein Degradation As discussed in last the last lecture, newly
... not able to fold, and how these errant proteins are delivered to the translocation machinery to be exported back to the cytoplasm is not known. IV. The Unfolded Protein Response What we do know is an interesting phenomenon known as the unfolded protein response (UPR). When a lot of “junk” proteins a ...
... not able to fold, and how these errant proteins are delivered to the translocation machinery to be exported back to the cytoplasm is not known. IV. The Unfolded Protein Response What we do know is an interesting phenomenon known as the unfolded protein response (UPR). When a lot of “junk” proteins a ...
Chapter 5: PROTEINS
... ● amino acids differ from each other at their “side” or “R” chains ● because they are so different, and can be put together in almost infinite combinations, proteins are among ...
... ● amino acids differ from each other at their “side” or “R” chains ● because they are so different, and can be put together in almost infinite combinations, proteins are among ...
An insight into the (un)stable protein formulation
... an answer. Classical protein-biochemical methods use, for example, analytical size-exclusion chromatography to detect multimeric aggregates in the presence of intact monomers. In most cases, however, the denaturation observed in this way begins mechanistically already at an earlier point of time. Of ...
... an answer. Classical protein-biochemical methods use, for example, analytical size-exclusion chromatography to detect multimeric aggregates in the presence of intact monomers. In most cases, however, the denaturation observed in this way begins mechanistically already at an earlier point of time. Of ...
Exam 1
... 27. The technique called the Edman Degradation can be used to sequence polypeptides by identifying the amino acid at the _______________________ end of the peptide. 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate bindi ...
... 27. The technique called the Edman Degradation can be used to sequence polypeptides by identifying the amino acid at the _______________________ end of the peptide. 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate bindi ...
the ubiquitin system and a putative stimulatory role
... Among eukaryotes, ubiquitin is highly conserved, meaning that the amino acid sequence does not differ much when very different organisms are compared. Ub is a heat-stable protein that folds up into a compact globular structure. It is found throughout the cell and can exist either in free form or as ...
... Among eukaryotes, ubiquitin is highly conserved, meaning that the amino acid sequence does not differ much when very different organisms are compared. Ub is a heat-stable protein that folds up into a compact globular structure. It is found throughout the cell and can exist either in free form or as ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Identified first in bacterial genetic screens ...
... Identified first in bacterial genetic screens ...
Gene Section S100B (S100 calcium binding protein B) in Oncology and Haematology
... effect seems to be dependent on the concentration of S100B and occurs at nanomolar concentrations. But micromolar levels of extracellular S100B stimulate apoptosis in vitro. Calcium binding induces a conformational change in S100B that allows the interaction with a variety of target proteins. These ...
... effect seems to be dependent on the concentration of S100B and occurs at nanomolar concentrations. But micromolar levels of extracellular S100B stimulate apoptosis in vitro. Calcium binding induces a conformational change in S100B that allows the interaction with a variety of target proteins. These ...
Test Your Knowledge – Chapter 3 Name
... e. DNA and RNA. c. fatty acids. 13. Citric acid makes lemons taste sour. Which of the following is a functional group that would cause a molecule such as citric acid to be acidic? a. hydroxyl b. hydrocarbon c. amino d. carbonyl e. carboxyl 14. Which of the following ranks the molecules in the correc ...
... e. DNA and RNA. c. fatty acids. 13. Citric acid makes lemons taste sour. Which of the following is a functional group that would cause a molecule such as citric acid to be acidic? a. hydroxyl b. hydrocarbon c. amino d. carbonyl e. carboxyl 14. Which of the following ranks the molecules in the correc ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.