INTRODUCTION TO OHM`S LAW
... changing. From zero, current and voltage builds up and reach its max peak in the positive value at 90 degrees and then back to zero and again to the negative peak value. In this regard, Its only possible to calculate instantaneous values of voltage and current throughout its cycle. For AC Ohms law c ...
... changing. From zero, current and voltage builds up and reach its max peak in the positive value at 90 degrees and then back to zero and again to the negative peak value. In this regard, Its only possible to calculate instantaneous values of voltage and current throughout its cycle. For AC Ohms law c ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
BJT-definitions and models
... 1 – The collector must be positive than the emitter. 2 – The base-emitter and base-collector circuits behave like diodes. Normally the baseemitter diode is conducting and the base-collector diode is reverse-biased 3 – When 1 and 2 are obeyed Ic is proportional to Ib (Ic = beta . Ib) Both Ib and Ic f ...
... 1 – The collector must be positive than the emitter. 2 – The base-emitter and base-collector circuits behave like diodes. Normally the baseemitter diode is conducting and the base-collector diode is reverse-biased 3 – When 1 and 2 are obeyed Ic is proportional to Ib (Ic = beta . Ib) Both Ib and Ic f ...
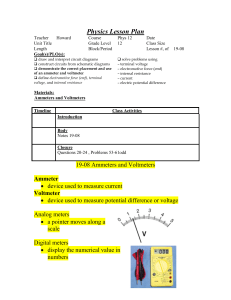
Science Lesson Plan
... The ammeter must be connected in series to function. An analogue voltmeter is also a galvanometer and a resistor but they are connected in series and the resistance is very large so that very little current passes through the voltmeter. ...
... The ammeter must be connected in series to function. An analogue voltmeter is also a galvanometer and a resistor but they are connected in series and the resistance is very large so that very little current passes through the voltmeter. ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is between 3 an ...
... Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is between 3 an ...
0 - 30 v Adjustable voltage, current stabilized voltage supply
... (inverse Clockwise rotation To the minimum).Adjust the RV1 to make output voltage as 0V(may appear negative voltage and the value is very small,please use Digital multimeter do this).The maximum output voltage no need to adjust,it is about 33V when the input voltage is AC 24V. 2.Current Calibration ...
... (inverse Clockwise rotation To the minimum).Adjust the RV1 to make output voltage as 0V(may appear negative voltage and the value is very small,please use Digital multimeter do this).The maximum output voltage no need to adjust,it is about 33V when the input voltage is AC 24V. 2.Current Calibration ...
Project Report for RELAY DRIVER
... The ULN2001A, ULN2002A, ULN2003 and ULN2004A are high voltage, high current darlington arrays each containing seven open collector darlington pairs with common emitters. Each channel rated at 500mA and can withstand peak currents of 600mA. Suppression diodes are included for inductive load driving a ...
... The ULN2001A, ULN2002A, ULN2003 and ULN2004A are high voltage, high current darlington arrays each containing seven open collector darlington pairs with common emitters. Each channel rated at 500mA and can withstand peak currents of 600mA. Suppression diodes are included for inductive load driving a ...
1. dia - Shrek
... samples. Calibration procedures are usually described in the equipment manuals. The input resistance (or “impedance”) of the voltmeter should be at least 10 0000 higher than the resistance of the sample bar. The input impedance is usually listed in the equipment specifications. Note that some voltme ...
... samples. Calibration procedures are usually described in the equipment manuals. The input resistance (or “impedance”) of the voltmeter should be at least 10 0000 higher than the resistance of the sample bar. The input impedance is usually listed in the equipment specifications. Note that some voltme ...
EX: a) Find a symbolic expression for v3 in the circuit below using
... KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special configurations, which are lacking in this circuit. Although is and R2 are a Norton form, converting to a Thevenin form would cause ix to disappear, making t ...
... KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special configurations, which are lacking in this circuit. Although is and R2 are a Norton form, converting to a Thevenin form would cause ix to disappear, making t ...
Section C The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) (Chapter 4 of your text)
... Section C The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) (Chapter 4 of your text) Section C1: Introduction & Goals The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is the first three-terminal active device that we’re going to discuss. In this section, we’re going to discover the basic principles of transistor operation ...
... Section C The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) (Chapter 4 of your text) Section C1: Introduction & Goals The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is the first three-terminal active device that we’re going to discuss. In this section, we’re going to discover the basic principles of transistor operation ...
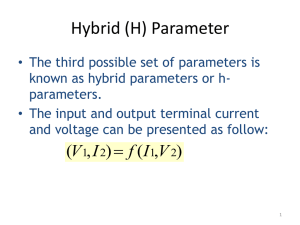
Inverse Transmission Parameter
... Hybrid (H) Parameter • The third possible set of parameters is known as hybrid parameters or hparameters. • The input and output terminal current and voltage can be presented as follow: ...
... Hybrid (H) Parameter • The third possible set of parameters is known as hybrid parameters or hparameters. • The input and output terminal current and voltage can be presented as follow: ...
Series & Parallel Circuits
... • Remember that charge cannot be created or destroyed and current is amount charge moving per second • The potential difference is shared by each device in the circuit. • Also call voltage drop because as the current passes through each device uses some of the total voltage until it is all used up ...
... • Remember that charge cannot be created or destroyed and current is amount charge moving per second • The potential difference is shared by each device in the circuit. • Also call voltage drop because as the current passes through each device uses some of the total voltage until it is all used up ...
Ohm`s Law
... relates voltage, current, and resistance. Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854) studied the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance and formulated the equation that bears his name. ...
... relates voltage, current, and resistance. Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854) studied the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance and formulated the equation that bears his name. ...
DTB143TK
... Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants contained herein are shown as examples of standard use and operation. Please pay careful attention to the peripheral conditions when designing circuits and deciding upon circuit constants in the set. Any data, including, but not limited to applicati ...
... Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants contained herein are shown as examples of standard use and operation. Please pay careful attention to the peripheral conditions when designing circuits and deciding upon circuit constants in the set. Any data, including, but not limited to applicati ...
Cellular Neuroscience (207) Ian Parker
... 1. The area of the plates is increased 2. The separation between the plates is decreased 3. The dielectric constant of the insulator is increased Capacitors store electricity, but cannot pass a steady current ...
... 1. The area of the plates is increased 2. The separation between the plates is decreased 3. The dielectric constant of the insulator is increased Capacitors store electricity, but cannot pass a steady current ...
Basic Electricity Study Guide
... Voltage is the force, push or pressure which makes the electrons move. 3. How did we define current in terms of electron movement? Current is the actual number or amount of electrons that are moving at any given time. 4. How did we define resistance in terms of electron movement? Resistance is the s ...
... Voltage is the force, push or pressure which makes the electrons move. 3. How did we define current in terms of electron movement? Current is the actual number or amount of electrons that are moving at any given time. 4. How did we define resistance in terms of electron movement? Resistance is the s ...