Video Transcript - Rose
... find Rt. We don’t have any independent sources, so Vt is zero. The circuit is purely resistive. At terminals S, T, we have purely a Thévenin resistance. This means that we need to apply a source to the Thévenin circuit. We’ll choose a 1 A current source. That causes a voltage across Rt. In our case, ...
... find Rt. We don’t have any independent sources, so Vt is zero. The circuit is purely resistive. At terminals S, T, we have purely a Thévenin resistance. This means that we need to apply a source to the Thévenin circuit. We’ll choose a 1 A current source. That causes a voltage across Rt. In our case, ...
Voltage Transducer LV 100/SP47 I = 10 mA V = 100..2500 V
... Primary resistor R 1 : the transducer’s optimum accuracy is obtained at the nominal primary current. As far as possible, R 1 should be calculated so that the nominal voltage to be measured corresponds to a primary current of 10 mA. Example: Voltage to be measured VPN = 1000 V ...
... Primary resistor R 1 : the transducer’s optimum accuracy is obtained at the nominal primary current. As far as possible, R 1 should be calculated so that the nominal voltage to be measured corresponds to a primary current of 10 mA. Example: Voltage to be measured VPN = 1000 V ...
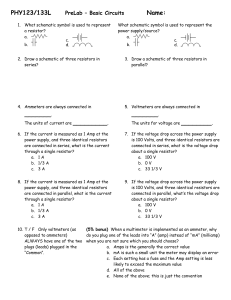
Basic Ciruits
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
PWM voltage regulator
... Many microcontrollers feature a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) output that can be low-pass filtered to produce a variable dc voltage. Without additional circuitry, however, this technique is limited to controlling very low-power loads. The circuit here illustrates a scheme that lets this dc voltage con ...
... Many microcontrollers feature a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) output that can be low-pass filtered to produce a variable dc voltage. Without additional circuitry, however, this technique is limited to controlling very low-power loads. The circuit here illustrates a scheme that lets this dc voltage con ...
LA5744TP - ON Semiconductor
... This IC prevents the current from increasing when the outputs are shorted by setting the switching frequency to 30kHz if the VOS pin voltage falls below 0.8V. Note 3 : If the soft start function is not used, the IC will start up with the overcurrent protection function operating. At this time, the s ...
... This IC prevents the current from increasing when the outputs are shorted by setting the switching frequency to 30kHz if the VOS pin voltage falls below 0.8V. Note 3 : If the soft start function is not used, the IC will start up with the overcurrent protection function operating. At this time, the s ...
RPI-352
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
PROBLEM SET Current, Voltage, and Resistance
... a. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 1 second? b. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 5 seconds? 2. (I) If electric current flows in only one direction it is called _____ current. Current that changes direction is called _____ current. 3. (I)In the United States alternati ...
... a. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 1 second? b. How many coulombs of charge flow by the point in 5 seconds? 2. (I) If electric current flows in only one direction it is called _____ current. Current that changes direction is called _____ current. 3. (I)In the United States alternati ...
In regard to charges, when is there a repulsive force between two
... What is the potential difference across a resistor that dissipates 5.00 W of power and has a current of 5.0 A? What is the potential difference across a resistor that dissipates 25.00 W of power and has a current of 7.0 A? What is the potential difference across a resistor that dissipates 15.00 W of ...
... What is the potential difference across a resistor that dissipates 5.00 W of power and has a current of 5.0 A? What is the potential difference across a resistor that dissipates 25.00 W of power and has a current of 7.0 A? What is the potential difference across a resistor that dissipates 15.00 W of ...
BCR401R
... The BCR401R is a cost efficient LED driver to drive low power LED’s. The advantages towards resistor biasing are: • homogenous light output despite varying forward voltages in different LED strings • homogenous light output of LED’s despite voltage drop across long supply lines • homogenous light ou ...
... The BCR401R is a cost efficient LED driver to drive low power LED’s. The advantages towards resistor biasing are: • homogenous light output despite varying forward voltages in different LED strings • homogenous light output of LED’s despite voltage drop across long supply lines • homogenous light ou ...
The ABC`s of electric energy and power
... A blue wire that provides a return path for a.c. but carries no voltage. ...
... A blue wire that provides a return path for a.c. but carries no voltage. ...
Transient Response
... function of time. When done, Simulation complete should appear in the lower left . A plot will be generated where the number of curves will be equal the number of voltage and current markers on the schematic. Note that the curve displayed in this example is not quite sinusoidal. ...
... function of time. When done, Simulation complete should appear in the lower left . A plot will be generated where the number of curves will be equal the number of voltage and current markers on the schematic. Note that the curve displayed in this example is not quite sinusoidal. ...
HANDOUK SG RELAY Features Input: DC control Double SCR AC
... 240VAC, 380VAC, 480VAC versions. Input Voltage specifications have 3 to 15VDC, 15 to 32VDC and 3 to 32VDC. ...
... 240VAC, 380VAC, 480VAC versions. Input Voltage specifications have 3 to 15VDC, 15 to 32VDC and 3 to 32VDC. ...
Lab #1: Ohm`s Law (and not Ohm`s Law)
... • Remember why circuits containing them can have currents that change with time ...
... • Remember why circuits containing them can have currents that change with time ...
SG RELAY Features Input: DC control Double SCR AC output or
... 240VAC, 380VAC, 480VAC versions. Input Voltage specifications have 3 to 15VDC, 15 to 32VDC and 3 to 32VDC. ...
... 240VAC, 380VAC, 480VAC versions. Input Voltage specifications have 3 to 15VDC, 15 to 32VDC and 3 to 32VDC. ...
13.3 Section Review and Problems File
... 8. A digital camera uses one 6 V battery. The circuit that runs the flash and takes the pictures has a resistance of 3 ohms. What is the current in the circuit? Looking for: Solution: Given: Equation: 9. The motor in a toy car has a resistance of 3 ohms and needs 1.5 amperes of current to run proper ...
... 8. A digital camera uses one 6 V battery. The circuit that runs the flash and takes the pictures has a resistance of 3 ohms. What is the current in the circuit? Looking for: Solution: Given: Equation: 9. The motor in a toy car has a resistance of 3 ohms and needs 1.5 amperes of current to run proper ...
The Criterion for the Tangential Sensitivity Measurement Application
... The often asked question concerning whether 8 dB refers to voltage or power is not a valid one. The number of decibels is defined as 10 log10 (P1 ÷ P2) where P1 and P2 are power levels to be compared. If output voltages are to be compared, the ratio (V1 ÷ V2)2 may be substituted for (P1 ÷ P2). In th ...
... The often asked question concerning whether 8 dB refers to voltage or power is not a valid one. The number of decibels is defined as 10 log10 (P1 ÷ P2) where P1 and P2 are power levels to be compared. If output voltages are to be compared, the ratio (V1 ÷ V2)2 may be substituted for (P1 ÷ P2). In th ...
Input offset voltage
... input transistors. Since the input transistors cannot be made identical, there exists a difference in bias currents ...
... input transistors. Since the input transistors cannot be made identical, there exists a difference in bias currents ...
SNC1P0 Ohm`s Law Practice
... A German scientist named Georg Simon Ohm was able to relate electrical current, voltage and resistance mathematically with an equation called Ohm's Law. Ohm's law : ...
... A German scientist named Georg Simon Ohm was able to relate electrical current, voltage and resistance mathematically with an equation called Ohm's Law. Ohm's law : ...