unit 6 - writing and balancing chemical equations
... 14. acetic acid neutralizes a solution of strontium hydroxide 15. bubbles of hydrogen gas and a solution of strontium chloride are produced when metallic strontium is dropped into hydrochloric acid 16. a sample of mercury (I) oxide (solid) is heated until it decomposes 17. solid tetraphosphorus deco ...
... 14. acetic acid neutralizes a solution of strontium hydroxide 15. bubbles of hydrogen gas and a solution of strontium chloride are produced when metallic strontium is dropped into hydrochloric acid 16. a sample of mercury (I) oxide (solid) is heated until it decomposes 17. solid tetraphosphorus deco ...
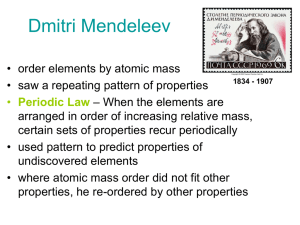
Dmitri Mendeleev
... • reactive, but less than corresponding alkali metal • form stable, insoluble oxides from which they are normally extracted • oxides are basic = alkaline earth • reactivity with water to form H2, ...
... • reactive, but less than corresponding alkali metal • form stable, insoluble oxides from which they are normally extracted • oxides are basic = alkaline earth • reactivity with water to form H2, ...
ELEMENTS
... Melting and Freezing Melting point - the temperature at which the solids melts to form a liquid. Substances with high (low) melting points have strong (weak) attractive forces between the particles. ...
... Melting and Freezing Melting point - the temperature at which the solids melts to form a liquid. Substances with high (low) melting points have strong (weak) attractive forces between the particles. ...
Single Replacement Reactions
... chemically combined in a compound. The tendency of a particular element to combine with other substances is a measure of the activity of the element. The more active an element is, the more likely it is to combine. In a single replacement reaction, an uncombined element replaces a less active elemen ...
... chemically combined in a compound. The tendency of a particular element to combine with other substances is a measure of the activity of the element. The more active an element is, the more likely it is to combine. In a single replacement reaction, an uncombined element replaces a less active elemen ...
The Atom and how it is organized - Cashmere
... The atoms of all elements are made up of a central nucleus with orbiting electrons. ◦ A nucleus is made up of positively charged PROTONS and neutral NEUTRONS. ◦ ELECTRONS are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. ...
... The atoms of all elements are made up of a central nucleus with orbiting electrons. ◦ A nucleus is made up of positively charged PROTONS and neutral NEUTRONS. ◦ ELECTRONS are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. ...
1 Packet #3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions How is
... Unfortunately, Carbon does not exist solely as Carbon-12. Carbon-13 also exists. ...
... Unfortunately, Carbon does not exist solely as Carbon-12. Carbon-13 also exists. ...
Notes 2 Balancing
... • Products and reactants of a reaction are made up of the same number and types of atoms. • The molecules may change but the atoms within them do not. • If you have H, O, and C are the reactant side of a reaction, you must have ___ , ___ , and ____ on the product side. • The ONLY thing we can change ...
... • Products and reactants of a reaction are made up of the same number and types of atoms. • The molecules may change but the atoms within them do not. • If you have H, O, and C are the reactant side of a reaction, you must have ___ , ___ , and ____ on the product side. • The ONLY thing we can change ...
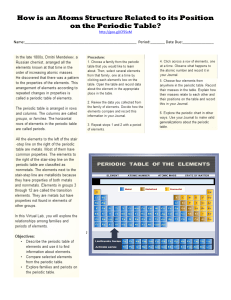
How is an Atoms Structure Related to its Position on the Periodic
... Journal – The Periodic Table How is an Atom’s Structure Related to its Position on the Periodic Table? ...
... Journal – The Periodic Table How is an Atom’s Structure Related to its Position on the Periodic Table? ...
Periodic_table_questions
... (ii) The electron arrangement of chlorine is 2.8.7. How many electron shells does it have? ...
... (ii) The electron arrangement of chlorine is 2.8.7. How many electron shells does it have? ...
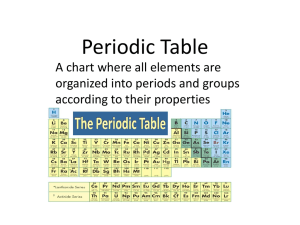
Periodic Table
... • All atoms what to have a balanced charge but they also want to have a full valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the ...
... • All atoms what to have a balanced charge but they also want to have a full valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the ...
Week 9 (wk9) - Riverside Local Schools
... elements in the periodic table were arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge, or the number of… 2. The PERIODIC LAW states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their… 3. When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, el ...
... elements in the periodic table were arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge, or the number of… 2. The PERIODIC LAW states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their… 3. When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, el ...
ATOMIC THEORY OF MATTER
... which involve electron interactions. The electrons act as the “glue” between atoms. – If electrons are shared between two atoms, the bond is a covalent bond. I.e., the bond between two non-metal atoms. – If electrons are transferred to produce ions, the bond is ionic. • Ions are charged particles wh ...
... which involve electron interactions. The electrons act as the “glue” between atoms. – If electrons are shared between two atoms, the bond is a covalent bond. I.e., the bond between two non-metal atoms. – If electrons are transferred to produce ions, the bond is ionic. • Ions are charged particles wh ...
Alexandre-Emile Béguyer de Chancourtois
... discovered helium as a decay product of uranium and matched it to the emission spectrum of an unknown element in the sun that was discovered in 1868. He went on to discover neon, krypton and xenon, and realised these represented a new group in the Periodic Table.” 2 ...
... discovered helium as a decay product of uranium and matched it to the emission spectrum of an unknown element in the sun that was discovered in 1868. He went on to discover neon, krypton and xenon, and realised these represented a new group in the Periodic Table.” 2 ...
2202 Chapter 1 - Eric G. Lambert School
... -Hydroxide OH-Carbonate CO32-Nitrate NO3-Sulfate SO42-Hydrogen Carbonate HCO3-Hydrogen Sulfate HSO4-Phosphate PO438:12 PM ...
... -Hydroxide OH-Carbonate CO32-Nitrate NO3-Sulfate SO42-Hydrogen Carbonate HCO3-Hydrogen Sulfate HSO4-Phosphate PO438:12 PM ...
YEAR 9 REVISION LIST November Exam 2013
... For example, there are two isotopes of chlorine: one isotope has 18 neutrons, so when added to the 17 protons gives it a relative atomic mass of 35. This isotope is known as chlorine-35 (35Cl) the other isotope has 20 neutrons, so when added to the 17 protons has a relative atomic mass of 37. Th ...
... For example, there are two isotopes of chlorine: one isotope has 18 neutrons, so when added to the 17 protons gives it a relative atomic mass of 35. This isotope is known as chlorine-35 (35Cl) the other isotope has 20 neutrons, so when added to the 17 protons has a relative atomic mass of 37. Th ...
ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... organize reactants and products Be sure to include symbols showing states of each reactant and product Be sure to write the correct formula ...
... organize reactants and products Be sure to include symbols showing states of each reactant and product Be sure to write the correct formula ...
Elements and the Periodic Table Section One
... Malleable: a term used to describe material that can be hammered or rolled into shape (pg. ...
... Malleable: a term used to describe material that can be hammered or rolled into shape (pg. ...
Worksheet 3 - contentextra
... Complex ion A chemical species typically consisting of a central ion, usually a transition metal ion, surrounded by a fixed number of ligands which form dative covalent (coordinate) bonds with the central metal ion. Coordination number The number of ligands surrounding a central metal ion, or the n ...
... Complex ion A chemical species typically consisting of a central ion, usually a transition metal ion, surrounded by a fixed number of ligands which form dative covalent (coordinate) bonds with the central metal ion. Coordination number The number of ligands surrounding a central metal ion, or the n ...
UNIT 3 –TEST REVIEW 1 Atoms of which of the
... Which of these groups (columns) in the Periodic Table is made up PRIMARILY of elements that are gases at room temperature? A Group 1 B Group 2 C Group 12 D Group 18 ...
... Which of these groups (columns) in the Periodic Table is made up PRIMARILY of elements that are gases at room temperature? A Group 1 B Group 2 C Group 12 D Group 18 ...
Chemistry Textbook Notes
... Water is a raw material, a necessity for all living things, a solvent, a transport medium and a thermal regulator. Surface tension is the resistance of a liquid to increase its surface area. Higher surface tension means it beads in a spherical drop rather than spread out. Viscosity is the resistance ...
... Water is a raw material, a necessity for all living things, a solvent, a transport medium and a thermal regulator. Surface tension is the resistance of a liquid to increase its surface area. Higher surface tension means it beads in a spherical drop rather than spread out. Viscosity is the resistance ...
The Periodic Table/Trends Chapter 5
... A.The Atomic Radius: The distance from the center of the nucleus to the valence electron. ...
... A.The Atomic Radius: The distance from the center of the nucleus to the valence electron. ...
MOLES, MASS, and VOLUME OF A GAS
... Consider the reaction: 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(g) Identify the limiting reagent in each of the reaction mixtures given below; a) 50 molecules of H2 and 50 molecules of O2. b) 100 molecules of H2 and 40 molecules of O2. c) 100 molecules of H2 and 60 molecules of O2. d) 0.50 moles of H2 and 0.75 moles ...
... Consider the reaction: 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(g) Identify the limiting reagent in each of the reaction mixtures given below; a) 50 molecules of H2 and 50 molecules of O2. b) 100 molecules of H2 and 40 molecules of O2. c) 100 molecules of H2 and 60 molecules of O2. d) 0.50 moles of H2 and 0.75 moles ...