Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... molecular equations and as ionic equations. We shall only consider molecular equations in this exercise. ...
... molecular equations and as ionic equations. We shall only consider molecular equations in this exercise. ...
The Periodic Law (Unit #5) Study Guide 1. Who is credited with
... 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge or _atomic number______. 4. The _periodic_______ law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their _ato ...
... 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge or _atomic number______. 4. The _periodic_______ law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their _ato ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... • The higher elements in the group are metallic and lose electrons to form cations. • Oxides change from acidic to amphoteric to basic as you move down the group. • All Group 5A(15) elements form gaseous hydrides with the formula EH3. – All except NH3 are extremely reactive and toxic. ...
... • The higher elements in the group are metallic and lose electrons to form cations. • Oxides change from acidic to amphoteric to basic as you move down the group. • All Group 5A(15) elements form gaseous hydrides with the formula EH3. – All except NH3 are extremely reactive and toxic. ...
Periodic Table Notes
... The periodic table as we have it today has not always existed; it developed much in the same way as atomic theory did. In the early 1800’s scientists began looking for ways to classify the elements that had been discovered. ...
... The periodic table as we have it today has not always existed; it developed much in the same way as atomic theory did. In the early 1800’s scientists began looking for ways to classify the elements that had been discovered. ...
4.IonicCompounds - Gleneaglesunit1and2chemistry2012
... state they are not free to move. – When an ionic compound melts, however, the particles are free to move and the compound will conduct electricity. ...
... state they are not free to move. – When an ionic compound melts, however, the particles are free to move and the compound will conduct electricity. ...
Naming Compounds Essential Question
... In order to write a formula or name a compound, you need to understand relationships among the elements as shown by their position on the Periodic Table. 1. Metals are on the __________ and have the following characteristics: a. __________ oxidation numbers (the apparent charge on an atom in a compo ...
... In order to write a formula or name a compound, you need to understand relationships among the elements as shown by their position on the Periodic Table. 1. Metals are on the __________ and have the following characteristics: a. __________ oxidation numbers (the apparent charge on an atom in a compo ...
Atoms, elements and compounds
... Are these statements true or false? 1. There are 1000 elements 2. All substances are made from atoms 3. Compounds are listed on the periodic table 4. Sulfur is a compound 5. Sodium is an element 6. An element contains only one type of atom ...
... Are these statements true or false? 1. There are 1000 elements 2. All substances are made from atoms 3. Compounds are listed on the periodic table 4. Sulfur is a compound 5. Sodium is an element 6. An element contains only one type of atom ...
File
... eg. state at room temperature, boiling and melting points, color, solubility, mass, electrical conductivity 2. Physical Change: a change in the size or form of a substance that does not change its composition eg. cutting, bending, changes in state: boiling, melting, condensing, and solidifying 3. Ch ...
... eg. state at room temperature, boiling and melting points, color, solubility, mass, electrical conductivity 2. Physical Change: a change in the size or form of a substance that does not change its composition eg. cutting, bending, changes in state: boiling, melting, condensing, and solidifying 3. Ch ...
Chemistry Ch. 5
... One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, ...
... One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, ...
Chapter 2
... The salt calcium fluoride is an ionic substance with formula CaF2, meaning that, while the atoms of Ca and F are in a 1-to-2 ratio, it does not exist as molecules of CaF2, but as a crystal lattice containing 1 Ca for every 2 F atoms. ...
... The salt calcium fluoride is an ionic substance with formula CaF2, meaning that, while the atoms of Ca and F are in a 1-to-2 ratio, it does not exist as molecules of CaF2, but as a crystal lattice containing 1 Ca for every 2 F atoms. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 6. What is a binary compound? 7. What is a ternary compound? 8. What is a polyatomic ion? 9. What is a molecular compound? 10. What is a compound? 11. What is an ionic compound? 12. What must be true about al ionic compounds? 13. What charge does each element in a group on the periodic table form? 1 ...
... 6. What is a binary compound? 7. What is a ternary compound? 8. What is a polyatomic ion? 9. What is a molecular compound? 10. What is a compound? 11. What is an ionic compound? 12. What must be true about al ionic compounds? 13. What charge does each element in a group on the periodic table form? 1 ...
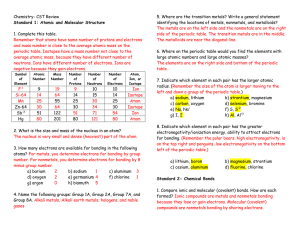
Chemistry- CST Review
... 4. What atoms does carbon commonly form bonds with? Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and another carbon commonly form bonds with carbon. Standard 11- Nuclear Processes 1. What elements have radioactive isotopes? Elements with atomic number 84 and above are radioisotopes. There are more like carbon which ...
... 4. What atoms does carbon commonly form bonds with? Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and another carbon commonly form bonds with carbon. Standard 11- Nuclear Processes 1. What elements have radioactive isotopes? Elements with atomic number 84 and above are radioisotopes. There are more like carbon which ...
TRENDS in the PERIODIC TABLE
... a whole orbital when they form. • Anions are bigger than the atoms they started as, because by adding electrons into the outer orbital, they must stretch a bit larger to accommodate those extra negative charges that push against each other. ...
... a whole orbital when they form. • Anions are bigger than the atoms they started as, because by adding electrons into the outer orbital, they must stretch a bit larger to accommodate those extra negative charges that push against each other. ...
Topic 4 Chemistry of the Elements of the Main Group
... electricity. Metals make crystal lattice structures in which electrons can flow freely. Metalloids or semi-metals show intermediate conduction properties (they are semiconductors). Their electronegativity values are close to 2. The valence electrons of metalloids are localised around the nucleus but ...
... electricity. Metals make crystal lattice structures in which electrons can flow freely. Metalloids or semi-metals show intermediate conduction properties (they are semiconductors). Their electronegativity values are close to 2. The valence electrons of metalloids are localised around the nucleus but ...
Chapter 5 - Geocities
... Alkali metals: Group 1 of the Periodic Table Alkaline-earth metals: Group 2 Transition elements: d-block elements with typical metallic properties Main-Group elements: p-block elements and s-block elements Halogens: Group 17 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties Atomic radius: ½ ...
... Alkali metals: Group 1 of the Periodic Table Alkaline-earth metals: Group 2 Transition elements: d-block elements with typical metallic properties Main-Group elements: p-block elements and s-block elements Halogens: Group 17 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties Atomic radius: ½ ...
Chapter 6 Studyguide: The Periodic Table
... 12.What does each period in the periodic table corresponds to? 13.The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic ____. 14.Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to predict the properties of missing elements? 15.What general category classifie ...
... 12.What does each period in the periodic table corresponds to? 13.The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic ____. 14.Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to predict the properties of missing elements? 15.What general category classifie ...
Periodic Table Cloze - Science
... Fill in the blanks with words from the box. atom gold nonmetals ...
... Fill in the blanks with words from the box. atom gold nonmetals ...
File
... Elements in the same family have the same characteristics (except for Hydrogen , it doesn’t fit into a family) The first column are called the alkali metals They react most strongly with other elements and are so reactive they EXPLODE! when put in water Column 2 are the Alkaline Earth Metals that a ...
... Elements in the same family have the same characteristics (except for Hydrogen , it doesn’t fit into a family) The first column are called the alkali metals They react most strongly with other elements and are so reactive they EXPLODE! when put in water Column 2 are the Alkaline Earth Metals that a ...
Alkaline Earth Metals
... What’s the formula for the maximum number of electrons allowed in a certain PEL? List the elements that exist as diatomics. What are the trends in atomic radius as you go down and across the periodic table? ...
... What’s the formula for the maximum number of electrons allowed in a certain PEL? List the elements that exist as diatomics. What are the trends in atomic radius as you go down and across the periodic table? ...
Grouping of Elements in the Periodic Table
... 7. Which elements are most likely to lose electrons and form cations? a) transition metals b) noble gases c) elements in the last two periods d) metals in the first two periods 8. What is another name for semimetals? a) alkaline earth metals b) alkali metals c) transition metals d) metalloids 9. How ...
... 7. Which elements are most likely to lose electrons and form cations? a) transition metals b) noble gases c) elements in the last two periods d) metals in the first two periods 8. What is another name for semimetals? a) alkaline earth metals b) alkali metals c) transition metals d) metalloids 9. How ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... Noble Gases - Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are all noble gases. They are unique in that the outer shell of their atoms is full of electrons. This means they don't react much with other elements. They are often used in signs as they glow in bright colors when an electrical current i ...
... Noble Gases - Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are all noble gases. They are unique in that the outer shell of their atoms is full of electrons. This means they don't react much with other elements. They are often used in signs as they glow in bright colors when an electrical current i ...
File
... Noble gases are [inert, very reactive, only react with certain elements]. [Potassium, Calcium, Sulfur, Neon] has properties most similar to oxygen. [Calcium, Potassium, Chlorine, Sodium] has two valence electrons. Periods form [horizontal, vertical] rows on the periodic table and show the number of ...
... Noble gases are [inert, very reactive, only react with certain elements]. [Potassium, Calcium, Sulfur, Neon] has properties most similar to oxygen. [Calcium, Potassium, Chlorine, Sodium] has two valence electrons. Periods form [horizontal, vertical] rows on the periodic table and show the number of ...
C3 Revision Question Booklet
... Fluorine reacts in the dark, explosively, at very low temperatures. Chlorine reacts explosively in sunlight, at room temperature. Bromine, in light, only reacts if heated to about 200°C. Suggest the conditions needed for hydrogen and iodine to react. ...
... Fluorine reacts in the dark, explosively, at very low temperatures. Chlorine reacts explosively in sunlight, at room temperature. Bromine, in light, only reacts if heated to about 200°C. Suggest the conditions needed for hydrogen and iodine to react. ...