Periodic Trends Studyguide with Questions and Answers
... 1. Properties of the Modern Periodic Table Concept Facts: Study to remember the followings about the Periodic Table. . Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers . Chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers . The elements on the Periodic Table ...
... 1. Properties of the Modern Periodic Table Concept Facts: Study to remember the followings about the Periodic Table. . Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers . Chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers . The elements on the Periodic Table ...
Lab Manual Yr 1 organic
... existence of elements other than carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Elements such as nitrogen, sulphur, iodine, chlorine and bromine in organic compounds can easily be detected by means of straightforward chemical tests. J.L. Lassaigne has developed a method used for the quantitative determination of elem ...
... existence of elements other than carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Elements such as nitrogen, sulphur, iodine, chlorine and bromine in organic compounds can easily be detected by means of straightforward chemical tests. J.L. Lassaigne has developed a method used for the quantitative determination of elem ...
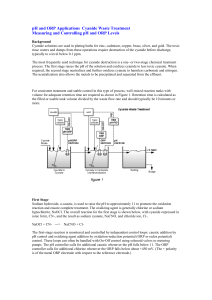
pH and ORP Applications Cyanide Waste Treatment
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
Increasing Radii
... poor conductors of heat and electricity brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, A ...
... poor conductors of heat and electricity brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, A ...
Unit 3.pmd
... Thus process of formation of O in gas phase is unfavourable even though O 2– is isoelectronic with neon. It is due to the fact that, (i) ...
... Thus process of formation of O in gas phase is unfavourable even though O 2– is isoelectronic with neon. It is due to the fact that, (i) ...
Chapter 2 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Every orbital can hold up to two electrons. The two electrons are designated as having one spin up ↑ and one spin down ↓ The number of orbitals per n level is given by n2. The maximum number of electrons per n level is 2n2. The value is 2n2 because of the two paired electrons. ...
... Every orbital can hold up to two electrons. The two electrons are designated as having one spin up ↑ and one spin down ↓ The number of orbitals per n level is given by n2. The maximum number of electrons per n level is 2n2. The value is 2n2 because of the two paired electrons. ...
Stoichiometry worksheet KEY
... e) Use the answers from questions b, c, and d above to show that this equation obeys the law of conservation of mass. Mass of reactants = mass of products (52.0 g C2H2 + 160 g O2) = (176 g CO2 + 36.0 g H2O) 212 g reactants = 212 g products ...
... e) Use the answers from questions b, c, and d above to show that this equation obeys the law of conservation of mass. Mass of reactants = mass of products (52.0 g C2H2 + 160 g O2) = (176 g CO2 + 36.0 g H2O) 212 g reactants = 212 g products ...
Periodic Table Element Pattern
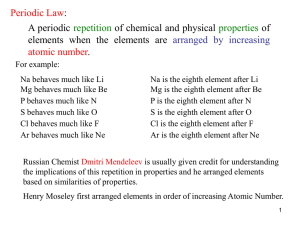
... sole credit for development of the actual periodic table itself. The table itself is a visual representation of the periodic law which states that certain properties of elements repeat periodically when arranged by atomic number. The table arranges elements into vertical columns (Groups) and horizon ...
... sole credit for development of the actual periodic table itself. The table itself is a visual representation of the periodic law which states that certain properties of elements repeat periodically when arranged by atomic number. The table arranges elements into vertical columns (Groups) and horizon ...
Periodicity of Elements and Periodic Table CHAPTER – 4
... 1. Some are mono atomic and some are di-atomic. 2. Some of them exist in gaseous and some are in solid state. 3. Elements of this group have quite tendency to form compounds. 4. The tendency of forming covalent bond decreases from oxygen to polonium. 5. There is a gradual decrease in the ionization ...
... 1. Some are mono atomic and some are di-atomic. 2. Some of them exist in gaseous and some are in solid state. 3. Elements of this group have quite tendency to form compounds. 4. The tendency of forming covalent bond decreases from oxygen to polonium. 5. There is a gradual decrease in the ionization ...
Unit 7 Homework and Lab Packet
... 3. Add 50.0 ml of distilled water to the beaker. Swirl the beaker around to dissolve all of the copper(II)sulfate crystals. 4. Obtain two clean, dry iron nails from your teacher. If the nails are not clean, use a piece of sand paper or steel wool to make the surface of the nail shiny. Find the mass ...
... 3. Add 50.0 ml of distilled water to the beaker. Swirl the beaker around to dissolve all of the copper(II)sulfate crystals. 4. Obtain two clean, dry iron nails from your teacher. If the nails are not clean, use a piece of sand paper or steel wool to make the surface of the nail shiny. Find the mass ...
3.5 Empirical Formulas - Mayfield City Schools
... MgSO4•xH2O, where x indicates the number of moles of H2O per mole of MgSO4. When 5.061 g of this hydrate is heated to 250oC, all the water of hydration is lost, leaving 2.472 g of MgSO4. What is the value of x? Follow ALL math work rules! ...
... MgSO4•xH2O, where x indicates the number of moles of H2O per mole of MgSO4. When 5.061 g of this hydrate is heated to 250oC, all the water of hydration is lost, leaving 2.472 g of MgSO4. What is the value of x? Follow ALL math work rules! ...
KD 1
... Atomic Number Atoms are composed of identical protons, neutrons, and electrons How then are atoms of one element different from another element? Elements are different because they contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Atomic Number Atoms are composed of identical protons, neutrons, and electrons How then are atoms of one element different from another element? Elements are different because they contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
chemistry module p
... Molecules Molecules are formed in many substances when small groups of atoms join together with a unique structural conformation. The atoms can be all the same or there can be several different types. A chemical formula gives information about the types and numbers of atoms present in each of these ...
... Molecules Molecules are formed in many substances when small groups of atoms join together with a unique structural conformation. The atoms can be all the same or there can be several different types. A chemical formula gives information about the types and numbers of atoms present in each of these ...
2 Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table
... or they may be shared between the atoms. In either case, the change results in a chemical reaction—that is, new substances form. Later in this chapter, you will learn which elements are likely to gain electrons, which are likely to give up electrons, and which are likely to share electrons. You will ...
... or they may be shared between the atoms. In either case, the change results in a chemical reaction—that is, new substances form. Later in this chapter, you will learn which elements are likely to gain electrons, which are likely to give up electrons, and which are likely to share electrons. You will ...
CH 151 Companion
... Safety is of utmost importance. Work in the laboratory should be a safe experience. It will be safe, however, only if certain safety precautions are followed without exception. Safety is up to you. Everyone working in the chemistry laboratories must follow the following rules. Your instructor will d ...
... Safety is of utmost importance. Work in the laboratory should be a safe experience. It will be safe, however, only if certain safety precautions are followed without exception. Safety is up to you. Everyone working in the chemistry laboratories must follow the following rules. Your instructor will d ...
chem - CBSE Guess
... Rancidity: The oily and fatty food oxidizes and give bad smell and test is called rancidity.Preventatioin:By adding antioxidant which slow down the process of oxidation.2. Vaccum packing,3Flusing N2 gas in chips packets.3.Refrigeration. Q.Explain the various types of reactions with one example of ea ...
... Rancidity: The oily and fatty food oxidizes and give bad smell and test is called rancidity.Preventatioin:By adding antioxidant which slow down the process of oxidation.2. Vaccum packing,3Flusing N2 gas in chips packets.3.Refrigeration. Q.Explain the various types of reactions with one example of ea ...
Practical Assessment of Sanitizers Steve Gray November
... circulation techniques as appropriate to the equipment. All surfaces should be exposed to sanitizing solution for a period of at least 60 seconds or more if specified by a governing code. Allow to free Drain. Do not rinse. Internal ...
... circulation techniques as appropriate to the equipment. All surfaces should be exposed to sanitizing solution for a period of at least 60 seconds or more if specified by a governing code. Allow to free Drain. Do not rinse. Internal ...
Stoichiometry: Predicting Amounts in Reactions
... Stoichiometry is the process of determining how much product is made or how much reactant is needed during a chemical reaction. As we know, in chemical reactions atoms are conserved. We show thi ...
... Stoichiometry is the process of determining how much product is made or how much reactant is needed during a chemical reaction. As we know, in chemical reactions atoms are conserved. We show thi ...
3.0 Properties of Phosgene
... start reacting with steel, weakening the piping and vessels. At 483oF, chlorine will ignite iron and produce a fire. Detection of these impurity generated reactions can be noticed by a rapid rise in the temperature of the feed gas after the carbon monoxide and chlorine mixing point. The use of high ...
... start reacting with steel, weakening the piping and vessels. At 483oF, chlorine will ignite iron and produce a fire. Detection of these impurity generated reactions can be noticed by a rapid rise in the temperature of the feed gas after the carbon monoxide and chlorine mixing point. The use of high ...
Chemistry - Set as Home Page
... (one which occurs between a metal and oxygen, one which takes in heat, one which occurs between metals and non-metals, one which gives out heat) ...
... (one which occurs between a metal and oxygen, one which takes in heat, one which occurs between metals and non-metals, one which gives out heat) ...
practical identification of organic compounds.docx
... the nitrogen and sulphur present ) , add an excess of silver nitrate solution. Precipitate silver halides to indicates the present of halogen. If the precipitate is white , chlorine is present ; if it is pale yellow , bromine is present ; if it is yellow , iodine is present. ...
... the nitrogen and sulphur present ) , add an excess of silver nitrate solution. Precipitate silver halides to indicates the present of halogen. If the precipitate is white , chlorine is present ; if it is pale yellow , bromine is present ; if it is yellow , iodine is present. ...
Chapter 5
... • An ion is an atom or group of bonded atoms that has a positive or negative charge. ...
... • An ion is an atom or group of bonded atoms that has a positive or negative charge. ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
... many chemicals. Methanol is made by reacting carbon monoxide and hydrogen at high temperature and pressure. CO(g) ⫹ 2H2(g) ¡ CH3OH(g) a. How many moles of each reactant are needed ...
... many chemicals. Methanol is made by reacting carbon monoxide and hydrogen at high temperature and pressure. CO(g) ⫹ 2H2(g) ¡ CH3OH(g) a. How many moles of each reactant are needed ...
Chemical Bonding
... These formations are made of crystals of calcium carbonate, CaCO3(s), also known as limestone. Calcium carbonate, as its name and formula suggest, is a compound made up of three different elements. In addition to its crystalline structure, calcium carbonate has high melting and boiling points and di ...
... These formations are made of crystals of calcium carbonate, CaCO3(s), also known as limestone. Calcium carbonate, as its name and formula suggest, is a compound made up of three different elements. In addition to its crystalline structure, calcium carbonate has high melting and boiling points and di ...
IGCSE® Chemistry - Hodder Plus Home
... (iii) the gas in older style (non-fluorescent) electric light bulbs [1] ...
... (iii) the gas in older style (non-fluorescent) electric light bulbs [1] ...