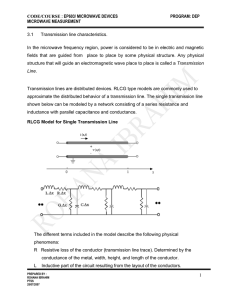
Fundamentals Of Electricity
... A motor with a slip of 5% or less is known as a normal-slip motor. A normal-slip motor is sometimes referred to as a 'constant speed' motor because the speed changes very little from no-load to full-load conditions. A common four-pole motor with a synchronous speed of 1,800 rpm may have a no-load ...
... A motor with a slip of 5% or less is known as a normal-slip motor. A normal-slip motor is sometimes referred to as a 'constant speed' motor because the speed changes very little from no-load to full-load conditions. A common four-pole motor with a synchronous speed of 1,800 rpm may have a no-load ...
A 256×256 CMOS active pixel sensor camera-on-a
... where v, is the voltage noise, A,f is the gain of the pixel source follower, Ch and Ccolare the sample-and-hold capacitor and the column capacitance, respectively. The factor of two represents the effect of double sampling. The noise expression shown above indicates that the APS noise is governed by ...
... where v, is the voltage noise, A,f is the gain of the pixel source follower, Ch and Ccolare the sample-and-hold capacitor and the column capacitance, respectively. The factor of two represents the effect of double sampling. The noise expression shown above indicates that the APS noise is governed by ...
2x1.2W stereo audio power amplifier with dedicated standby pins
... 2. All PSRR data limits are guaranteed by production sampling tests. Dynamic measurements - 20*log(rms(Vout)/rms(Vripple)). Vripple is the sinusoidal signal superimposed upon ...
... 2. All PSRR data limits are guaranteed by production sampling tests. Dynamic measurements - 20*log(rms(Vout)/rms(Vripple)). Vripple is the sinusoidal signal superimposed upon ...
MAX4361/MAX4362/MAX4363 ADSL Drivers/Receivers for Customer Premise Equipment General Description
... +12.5dBm and maintain the best SFDR. High-quality capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) such as multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) should be used to minimize supply voltage ripple and power dissipation. A larger capacitor located in proximity to the MAX4361/MAX4362/MAX4363 improv ...
... +12.5dBm and maintain the best SFDR. High-quality capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) such as multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) should be used to minimize supply voltage ripple and power dissipation. A larger capacitor located in proximity to the MAX4361/MAX4362/MAX4363 improv ...
average power - Department of Electrical Engineering
... The Power Superposition Principle (cont.) The superposition of average power The average power delivered to a circuit by several sinusoidal sources, acting together, is equal to the sum of the average power delivered to the circuit by each source acting alone, if and only if, no two of the source h ...
... The Power Superposition Principle (cont.) The superposition of average power The average power delivered to a circuit by several sinusoidal sources, acting together, is equal to the sum of the average power delivered to the circuit by each source acting alone, if and only if, no two of the source h ...
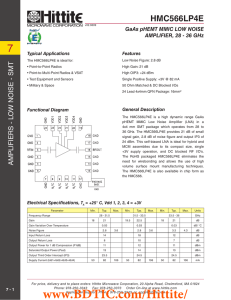
HMC566LP4E 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The HMC566LP4E is a high dynamic range GaAs pHEMT MMIC Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) in a 4x4 mm SMT package which operates from 28 to 36 GHz. The HMC566LP4E provides 21 dB of small signal gain, 2.8 dB of noise figure and output IP3 of 24 dBm. This self-biased LNA is ideal for hybrid and MCM assemblies ...
... The HMC566LP4E is a high dynamic range GaAs pHEMT MMIC Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) in a 4x4 mm SMT package which operates from 28 to 36 GHz. The HMC566LP4E provides 21 dB of small signal gain, 2.8 dB of noise figure and output IP3 of 24 dBm. This self-biased LNA is ideal for hybrid and MCM assemblies ...
TechTopics No. 20 - Power factor correction capacitor
... motor. This arrangement minimizes the switching costs, as an additional switching device is not needed. This also provides a path for the capacitor to discharge quickly when the contactor is opened. More importantly, it automatically adds capacitance to the system only when the load with the poor po ...
... motor. This arrangement minimizes the switching costs, as an additional switching device is not needed. This also provides a path for the capacitor to discharge quickly when the contactor is opened. More importantly, it automatically adds capacitance to the system only when the load with the poor po ...
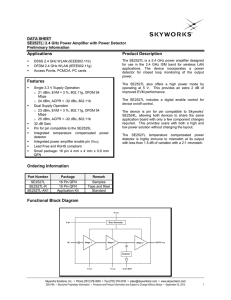
SE2527L 数据资料DataSheet下载
... are provided by Skyworks as a service to its customers and may be used for informational purposes only by the customer. Skyworks assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in these materials or the information contained herein. Skyworks may change its documentation, products, services, specif ...
... are provided by Skyworks as a service to its customers and may be used for informational purposes only by the customer. Skyworks assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in these materials or the information contained herein. Skyworks may change its documentation, products, services, specif ...