Evolution by natural selection - BioGeoWiki-4ESO
... •Because of differences in their genes. •Genes are made up of DNA and are found in every cell of your body •The genetic code is a set of instructions for making an entire organism with each gene coding for a specific protein. ...
... •Because of differences in their genes. •Genes are made up of DNA and are found in every cell of your body •The genetic code is a set of instructions for making an entire organism with each gene coding for a specific protein. ...
B1.8_evolution_checklist
... Outline Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, which states that all species have evolved from life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Outline the process of evolution by natural selection: differences between genes causes variation within a species; some individual ...
... Outline Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, which states that all species have evolved from life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Outline the process of evolution by natural selection: differences between genes causes variation within a species; some individual ...
Evolution and Natural Selection Review
... • A change in the population because of a random event, such as a catastrophe • The smaller the population, the less genetic variety it has. traits can be lost from one generation to the next. ...
... • A change in the population because of a random event, such as a catastrophe • The smaller the population, the less genetic variety it has. traits can be lost from one generation to the next. ...
Evidence for Evolution
... Changes in metabolic processes.Direct evidence of evolution: Examples – 1. Bacteria acquiring antibiotic resistance 2. Insects & weeds becoming resistant to pesticides ...
... Changes in metabolic processes.Direct evidence of evolution: Examples – 1. Bacteria acquiring antibiotic resistance 2. Insects & weeds becoming resistant to pesticides ...
Research Abstract: The evolution of life has resulted
... discoideum. It is uniquely suitable for this work because transitions that are fixed in most organisms are still flexible. This amoeba preys on bacteria but, when starved, aggregates into a multicellular body that moves towards light, and then differentiates into 20% dead stalk cells that support 80 ...
... discoideum. It is uniquely suitable for this work because transitions that are fixed in most organisms are still flexible. This amoeba preys on bacteria but, when starved, aggregates into a multicellular body that moves towards light, and then differentiates into 20% dead stalk cells that support 80 ...
17-4 Patterns of Evolution
... nectar (see image at right). These hollow thorns are the exclusive nest-site of some species of ant that drink the nectar. But the ants are not just taking advantage of the ...
... nectar (see image at right). These hollow thorns are the exclusive nest-site of some species of ant that drink the nectar. But the ants are not just taking advantage of the ...
Darwin and Mechanisms of Evolution
... • Must STRUGGLE with environment also (disease, predators, temp changes etc) • Those that withstand will survive! ...
... • Must STRUGGLE with environment also (disease, predators, temp changes etc) • Those that withstand will survive! ...
HERE
... 2. Define “descent with modification” ______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... 2. Define “descent with modification” ______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
HBIO—Evolution II Notes
... iv. No immigration / emigration v. No Natural Selection b. If any of the above conditions are violated, evolution will occur. c. See Fishy Frequency Lab ...
... iv. No immigration / emigration v. No Natural Selection b. If any of the above conditions are violated, evolution will occur. c. See Fishy Frequency Lab ...
Ch 23 Notes
... Mutations Natural Selection Migration Non-Random Mating Genetic Drift (chance events that can change a population) Populations must be big Microevolution: Changes in the gene pool on the smallest scale. Genetic Drift can lead to microevolution. Examples: Accidents, part of the populatio ...
... Mutations Natural Selection Migration Non-Random Mating Genetic Drift (chance events that can change a population) Populations must be big Microevolution: Changes in the gene pool on the smallest scale. Genetic Drift can lead to microevolution. Examples: Accidents, part of the populatio ...
Spring Break Worksheet on Evolution
... 3) An adaptation is a physical trait that allows things not to become better suited for their environment. ...
... 3) An adaptation is a physical trait that allows things not to become better suited for their environment. ...
Biology Shaping Evolutionary Theory (15.3 Outline) AS YOU READ
... Genetic driftfounder effectbottleneckgradualismRespond to the prompts below: Explain what the Hardy-Weinberg principle is and the five major violations of the principle. ...
... Genetic driftfounder effectbottleneckgradualismRespond to the prompts below: Explain what the Hardy-Weinberg principle is and the five major violations of the principle. ...
Section 13.3 - CPO Science
... Chapter Thirteen: Evolution • 13.1 Evidence for Evolution • 13.2 How Evolution Works ...
... Chapter Thirteen: Evolution • 13.1 Evidence for Evolution • 13.2 How Evolution Works ...
How Evolution Works
... Variation and Selection Variation from two sources 1) New mutations = new allele types 2) Gene shuffling = new allele combinations Any change in allele frequency = Evolution Peppered Moth Simulation ...
... Variation and Selection Variation from two sources 1) New mutations = new allele types 2) Gene shuffling = new allele combinations Any change in allele frequency = Evolution Peppered Moth Simulation ...
Molecular Biology and Evidence for Evolution WebQuest
... DNA Agrees With all the Other Science: Darwin Was Right Evolution Makes Sense of Homologies Axing the Family Tree Chemical Clues to Darwin's Abominable Mystery Salvaged DNA Leads to Neanderthals' Mystique The New Shrew That's Not Genetic Similarities: Wilson, Sarich, Sibley, and Ahlquist Selection S ...
... DNA Agrees With all the Other Science: Darwin Was Right Evolution Makes Sense of Homologies Axing the Family Tree Chemical Clues to Darwin's Abominable Mystery Salvaged DNA Leads to Neanderthals' Mystique The New Shrew That's Not Genetic Similarities: Wilson, Sarich, Sibley, and Ahlquist Selection S ...
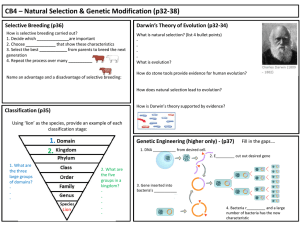
CB4 – Natural Selection and GM
... How is selective breeding carried out? 1. Decide which ______________are important 2. Choose _____________ that show these characteristics 3. Select the best ____________ from parents to breed the next generation 4. Repeat the process over many ___________ ...
... How is selective breeding carried out? 1. Decide which ______________are important 2. Choose _____________ that show these characteristics 3. Select the best ____________ from parents to breed the next generation 4. Repeat the process over many ___________ ...
Study Questions for Exam #1
... chromosomal bases for these principles specifically in terms of alleles, meiosis, and homologous chromosomes. Be able to identify the possible allele combinations in the gametes and the expected offspring genotypes for various genetic crosses, such as a dihybrid cross and test crosses. Use proba ...
... chromosomal bases for these principles specifically in terms of alleles, meiosis, and homologous chromosomes. Be able to identify the possible allele combinations in the gametes and the expected offspring genotypes for various genetic crosses, such as a dihybrid cross and test crosses. Use proba ...
Layout 4
... evolution, how DNA and genetic mutations create new species, and the fossil record of evolution: ● Principles of evolution - outline of evolution through natural selection, Darwin and Wallace ● DNA and cell division - mitosis and meiosis, how genetic information passes through generations ● Alleles ...
... evolution, how DNA and genetic mutations create new species, and the fossil record of evolution: ● Principles of evolution - outline of evolution through natural selection, Darwin and Wallace ● DNA and cell division - mitosis and meiosis, how genetic information passes through generations ● Alleles ...
The role of positive selection in molecular evolution
... evolution postulates that random genetic drift, not selection, is the major driving force behind evolution at the molecular level. Here, we address this question within a Poisson Random Field framework, based on aligned DNA sequence data from two closely related species. We investigate heavy-tailed ...
... evolution postulates that random genetic drift, not selection, is the major driving force behind evolution at the molecular level. Here, we address this question within a Poisson Random Field framework, based on aligned DNA sequence data from two closely related species. We investigate heavy-tailed ...
part - MOCKSTER.NET!
... one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally variety among individuals in a population Selection all species tend to produce more offspring th ...
... one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally variety among individuals in a population Selection all species tend to produce more offspring th ...
What you need to know for the Packet 11 test:
... What you need to know for the Packet 11 test: Prentice Hall Review Book pages 71-86 (all information) Textbook-You should refer to chapters 15, 16 and 17, however, you are not responsible for all information. You should have a clear understanding of: ...
... What you need to know for the Packet 11 test: Prentice Hall Review Book pages 71-86 (all information) Textbook-You should refer to chapters 15, 16 and 17, however, you are not responsible for all information. You should have a clear understanding of: ...
Patterns of - westbranch.k12.oh.us
... • More than 99% of species that have ever lived are now extinct -no longer exists on earth • Competition for resources/change in environments • Can be gradual for individuals or can be catastrophic mass extinctions that affect entire ecosystems ...
... • More than 99% of species that have ever lived are now extinct -no longer exists on earth • Competition for resources/change in environments • Can be gradual for individuals or can be catastrophic mass extinctions that affect entire ecosystems ...