Object Recognition and Learning using the BioRC Biomimetic Real
... This requires 104 synapse circuits and about 104 2-input adder circuits, to sum the inputs. We need one axon hillock to perform the thresholding/spiking function. ...
... This requires 104 synapse circuits and about 104 2-input adder circuits, to sum the inputs. We need one axon hillock to perform the thresholding/spiking function. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neurotransmitter released from the varicosities diffuses to ____________ on the target tissue to produce a response c. The response ceases as the neurotransmitter diffuses _______ ...
... a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neurotransmitter released from the varicosities diffuses to ____________ on the target tissue to produce a response c. The response ceases as the neurotransmitter diffuses _______ ...
Chapter 16
... • Ach on the muscarinic receptors modulate G-proteins and the response could be either excitatory or inhibitory. Examples, – Ach + muscarine receptor of cardiac muscle is inhibitory. – Ach + muscarine receptor of smooth muscle is excitatory. ...
... • Ach on the muscarinic receptors modulate G-proteins and the response could be either excitatory or inhibitory. Examples, – Ach + muscarine receptor of cardiac muscle is inhibitory. – Ach + muscarine receptor of smooth muscle is excitatory. ...
Paper - Revision Science
... Suggest what would happen in the body if the arterial blood pressure increased and the feedback system in the kidney described did not function. ...
... Suggest what would happen in the body if the arterial blood pressure increased and the feedback system in the kidney described did not function. ...
Neuron Anatomy
... • This suggests that astrocytes are excitable cells. • Yet, their excitability is not based on Vm as it is in neurons, but rather, on changes in [Ca2+]i. • Astrocytes, connected together by gap junctions, have been shown to signal each other (and neurons) via intercellular Ca2+ pulses. ...
... • This suggests that astrocytes are excitable cells. • Yet, their excitability is not based on Vm as it is in neurons, but rather, on changes in [Ca2+]i. • Astrocytes, connected together by gap junctions, have been shown to signal each other (and neurons) via intercellular Ca2+ pulses. ...
Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs: Introduction Drugs
... channel opens. Thus, there are two requirements for NMDA receptor channel opening: Glutamate must bind the receptor and the membrane must be depolarized. The rise in intracellular Ca2+ that accompanies channel opening results in a long-lasting enhancement in synaptic strength that is referred to as ...
... channel opens. Thus, there are two requirements for NMDA receptor channel opening: Glutamate must bind the receptor and the membrane must be depolarized. The rise in intracellular Ca2+ that accompanies channel opening results in a long-lasting enhancement in synaptic strength that is referred to as ...
Learning and Memory, Part I: Brain Regions Involved in Two Types
... neuron within the central nucleus of the amygdala. Before the fear-conditioning training, neurons within the central nucleus would not have been activated by the mouse hearing the tone alone. Subsequent to the training where multiple pairing of tone and shock occurs, the synaptic effects from the to ...
... neuron within the central nucleus of the amygdala. Before the fear-conditioning training, neurons within the central nucleus would not have been activated by the mouse hearing the tone alone. Subsequent to the training where multiple pairing of tone and shock occurs, the synaptic effects from the to ...
Learning, Memory and Amnesia
... anoxic ischemia of the hippocampus. – On autopsy, it was found that the CA1 region of the hippocampus was gone. – The CA1 region is especially rich in NMDA receptors (involved in learning). • If only CA1 damaged: anterograde amnesia only. • Anoxia causes NMDA receptors to allow excessive Ca++ influx ...
... anoxic ischemia of the hippocampus. – On autopsy, it was found that the CA1 region of the hippocampus was gone. – The CA1 region is especially rich in NMDA receptors (involved in learning). • If only CA1 damaged: anterograde amnesia only. • Anoxia causes NMDA receptors to allow excessive Ca++ influx ...
Forea Wang
... essential aspect of brain development and function. While work in this and other laboratories strives to understand how neuronal responses come to be shaped by patterned input from the environment, there remains no direct method for producing controlled input patterns to a neuron and measuring its f ...
... essential aspect of brain development and function. While work in this and other laboratories strives to understand how neuronal responses come to be shaped by patterned input from the environment, there remains no direct method for producing controlled input patterns to a neuron and measuring its f ...
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... portion of a signal, the inhibitory synapses damped down their response at the same time. When these two types of cells are wired together in a feed-forward loop, the researchers found that the excitatory and inhibitory synapses acted in concert, filtering out lowfrequency signals while amplifying hi ...
... portion of a signal, the inhibitory synapses damped down their response at the same time. When these two types of cells are wired together in a feed-forward loop, the researchers found that the excitatory and inhibitory synapses acted in concert, filtering out lowfrequency signals while amplifying hi ...
Chapter 27
... of the size of the stimulus - The size of the A P does not decrease as it is transmitted along the neuron but always remains the same ...
... of the size of the stimulus - The size of the A P does not decrease as it is transmitted along the neuron but always remains the same ...
Biopsychology 2012 – sec 002
... 3. Both small and large neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles (there is normally only one type of neurotransmitter that gets packaged into a single vesicle) ...
... 3. Both small and large neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles (there is normally only one type of neurotransmitter that gets packaged into a single vesicle) ...
Amsterdam Brn Adapt View P3
... There is one other interesting thing about these synapses—many of them involve additional postsynaptic spines contacting presynaptic varicosities on which one or more spines already exist (Federmeier et al., submitted). A similar result has recently been reported by [Geinisman/Disterhoft] in the ? c ...
... There is one other interesting thing about these synapses—many of them involve additional postsynaptic spines contacting presynaptic varicosities on which one or more spines already exist (Federmeier et al., submitted). A similar result has recently been reported by [Geinisman/Disterhoft] in the ? c ...
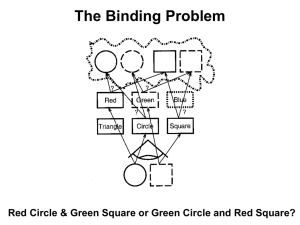
Optional extra slides on the Binding Problem
... of EPSPs and IPSPs, and thus increase the chance to depolarize post-synaptic cell. ...
... of EPSPs and IPSPs, and thus increase the chance to depolarize post-synaptic cell. ...
File
... the dendrites and only 5 to 20 percent on the soma The ends of the pre-synaptic fibers are generally enlarged to form (terminal buttons or synaptic knob) and it will synapse with: I. Axo-dendritic: In the cerebral and cerebellar cortex, ending are commonly located, on dendrites and frequently on (de ...
... the dendrites and only 5 to 20 percent on the soma The ends of the pre-synaptic fibers are generally enlarged to form (terminal buttons or synaptic knob) and it will synapse with: I. Axo-dendritic: In the cerebral and cerebellar cortex, ending are commonly located, on dendrites and frequently on (de ...
Poster
... According to the National Institutes of Health, 5.1 million Americans have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects memory and the ability to learn. In long-term potentiation (LTP), a correlate of learning and memory, the number of receptors at the synapse between neurons, increases. Calcium/calmodul ...
... According to the National Institutes of Health, 5.1 million Americans have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects memory and the ability to learn. In long-term potentiation (LTP), a correlate of learning and memory, the number of receptors at the synapse between neurons, increases. Calcium/calmodul ...
2. The Respiratory System
... Gas exchange can now take place more quickly meaning exercise can be maintained at a higher intensity for longer. 15 of 28 ...
... Gas exchange can now take place more quickly meaning exercise can be maintained at a higher intensity for longer. 15 of 28 ...
Adrenergic System
... 4) Binding by receptors: Noradrenaline released from synaptic vesicles diffuses across synaptic space and binds either to: Postsynaptic receptor on the effector organ or, Presynaptic receptor on the nerve endings ...
... 4) Binding by receptors: Noradrenaline released from synaptic vesicles diffuses across synaptic space and binds either to: Postsynaptic receptor on the effector organ or, Presynaptic receptor on the nerve endings ...
Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb
... Electrical synapses involve a neurotransmitter/chemical synapses Electrical synapses involve direct connection between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant ...
... Electrical synapses involve a neurotransmitter/chemical synapses Electrical synapses involve direct connection between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant ...
Synaptic Transmission and Neurotransmitters
... • Not all neurotransmitter is attached to postsynaptic receptor sites – Extra must be destroyed or repackaged – If not: could not limit effects – LSD is such a drug that does NOT degrade • Mimics the effects of a neurotransmitter • “wanders” around in the brain for up to 28 hours ...
... • Not all neurotransmitter is attached to postsynaptic receptor sites – Extra must be destroyed or repackaged – If not: could not limit effects – LSD is such a drug that does NOT degrade • Mimics the effects of a neurotransmitter • “wanders” around in the brain for up to 28 hours ...
Functional Human Physiology for the Exercise and Sport Sciences
... Post-synaptic neuron At a synapse, the neuron that receives signals from another neuron Post-synaptic membrane 1) Contains neurotransmitter receptors Specialized protein receptors that react with (or receive) a specified neurotransmitter ...
... Post-synaptic neuron At a synapse, the neuron that receives signals from another neuron Post-synaptic membrane 1) Contains neurotransmitter receptors Specialized protein receptors that react with (or receive) a specified neurotransmitter ...
The Nerve Impulse - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... causing an impulse to travel the membrane and the muscle cell to contract. Drugs and the Synapses Many poisons and drugs affect the activity of chemical neurotransmitters at the synapses. Nerve gas, curare, botulin toxin, and some poisonous insecticides can interfere with the functioning of acetylch ...
... causing an impulse to travel the membrane and the muscle cell to contract. Drugs and the Synapses Many poisons and drugs affect the activity of chemical neurotransmitters at the synapses. Nerve gas, curare, botulin toxin, and some poisonous insecticides can interfere with the functioning of acetylch ...
Text S1.
... associative plasticity, i.e. synaptic efficacies are modified by neural activity during a training process through long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). It is assumed that these synaptic weights have been set through repeated presentations of p different stimuli in random sequ ...
... associative plasticity, i.e. synaptic efficacies are modified by neural activity during a training process through long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). It is assumed that these synaptic weights have been set through repeated presentations of p different stimuli in random sequ ...