Chapter 2 Section 2 Notes
... 2. If the Nile was just a few feet over normal mud brick villages could be destroyed along with granaries 3. The vast deserts on the sides did provide protection from invaders but also kept them from interaction with other peoples a. Thus Egypt was spared constant warfare that plagued the Fertile Cr ...
... 2. If the Nile was just a few feet over normal mud brick villages could be destroyed along with granaries 3. The vast deserts on the sides did provide protection from invaders but also kept them from interaction with other peoples a. Thus Egypt was spared constant warfare that plagued the Fertile Cr ...
Unit #3: Cradles of Civilization
... the capital in Memphis near the 1st cataract and establishes the 1st dynasty (sequence of rulers from the same family) • Ancient Egypt would go on to have nearly 30 different dynasties, spanning a period of over 2600 years. ...
... the capital in Memphis near the 1st cataract and establishes the 1st dynasty (sequence of rulers from the same family) • Ancient Egypt would go on to have nearly 30 different dynasties, spanning a period of over 2600 years. ...
The royal titulary
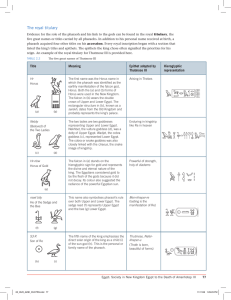
... Evidence for the role of the pharaoh and his link to the gods can be found in the royal titulary, the five great names or titles carried by all pharaohs. In addition to his personal name received at birth, a pharaoh acquired four other titles on his accession. Every royal inscription began with a se ...
... Evidence for the role of the pharaoh and his link to the gods can be found in the royal titulary, the five great names or titles carried by all pharaohs. In addition to his personal name received at birth, a pharaoh acquired four other titles on his accession. Every royal inscription began with a se ...
World History Exam Review Sheet
... Hereditary-passed down from parent to child Reform- change Culture-way of life Empire-group of states under one rule Reign- period of power Surplus-extra Artisan-skilled worker ...
... Hereditary-passed down from parent to child Reform- change Culture-way of life Empire-group of states under one rule Reign- period of power Surplus-extra Artisan-skilled worker ...
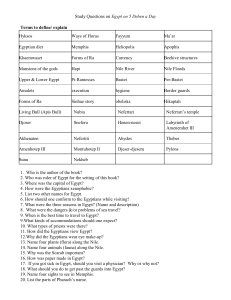
Study Questions on Egypt on 5 Deben a Day Terms to define
... 49. Why is Aketaten a ghost town and abandoned? 50. What was different about Aten? 51. How did Akhenaten attempt to change Egypt? How long did it last? 52. What happened toTutankhamun’s tomb? 53. Why was Abydos so sacred to the Egyptians? 54. Who drove out the Hyksos? 55. What were some of the main ...
... 49. Why is Aketaten a ghost town and abandoned? 50. What was different about Aten? 51. How did Akhenaten attempt to change Egypt? How long did it last? 52. What happened toTutankhamun’s tomb? 53. Why was Abydos so sacred to the Egyptians? 54. Who drove out the Hyksos? 55. What were some of the main ...
The Egyptian Empire
... control of new lands • Conquered peoples sent tribute to the Egyptian pharaoh enriching the kingdom. – forced payments ...
... control of new lands • Conquered peoples sent tribute to the Egyptian pharaoh enriching the kingdom. – forced payments ...
Chapter 5 Study Guide: Ancient Egypt Name Period ______
... Chapter 5 Study Guide: Ancient Egypt Name _________________________ Period ________ Directions: Answer the following questions on a separate piece of paper. No need to use complete sentences. Use this as a study tool for the chapter test. 1. What is the world’s longest river? 2. What did Egyptians m ...
... Chapter 5 Study Guide: Ancient Egypt Name _________________________ Period ________ Directions: Answer the following questions on a separate piece of paper. No need to use complete sentences. Use this as a study tool for the chapter test. 1. What is the world’s longest river? 2. What did Egyptians m ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Egypt: Middle and New Kingdoms
... Reign – time of rule Rural – country area ...
... Reign – time of rule Rural – country area ...
Ancient Egypt - Thomas County Schools
... of the Egyptian people, • Had two title: 'Lord of the Two Lands' and 'High Priest of Every Temple'. • ‘Lord of the Two Lands' meant he was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the land, made laws, collected taxes, and defended Egypt ...
... of the Egyptian people, • Had two title: 'Lord of the Two Lands' and 'High Priest of Every Temple'. • ‘Lord of the Two Lands' meant he was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the land, made laws, collected taxes, and defended Egypt ...
Ancient Egypt - Thomas County Schools
... of the Egyptian people. • Had two titles: 'Lord of the Two Lands' and 'High Priest of Every Temple'. • ‘Lord of the Two Lands' meant he was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the land, made laws, collected taxes, and defended Egypt. • As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh ...
... of the Egyptian people. • Had two titles: 'Lord of the Two Lands' and 'High Priest of Every Temple'. • ‘Lord of the Two Lands' meant he was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned all of the land, made laws, collected taxes, and defended Egypt. • As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh ...
Notes from sept 3 B
... – Nile River rose and spilled over its banks – Egyptians worshiped Nile River like a god ...
... – Nile River rose and spilled over its banks – Egyptians worshiped Nile River like a god ...
Kingdom of the NIle - Pleasantville High School
... “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile” – Herodotus Why is the river so important???? 1) Deposited rich layer of silt (soil) used for farming 2) Used for transportation 3) Trade routes ...
... “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile” – Herodotus Why is the river so important???? 1) Deposited rich layer of silt (soil) used for farming 2) Used for transportation 3) Trade routes ...
File - Mr. Butts World History
... Scholars divide the history of ancient Egypt into three main periods: the Old Kingdom (about 2575 B.C. to 2130 B.C.), the Middle Kingdom (about 1938 B.C. to 1630 B.C.), and the New Kingdom (about 1539 B.C. to 1075 B.C.). Although power passed from one dynasty, or ruling family, to another, the land ...
... Scholars divide the history of ancient Egypt into three main periods: the Old Kingdom (about 2575 B.C. to 2130 B.C.), the Middle Kingdom (about 1938 B.C. to 1630 B.C.), and the New Kingdom (about 1539 B.C. to 1075 B.C.). Although power passed from one dynasty, or ruling family, to another, the land ...
Name: Date: 6th Grade World History
... b. Queen Cleopatra kills herself before the New Kingdom began. c. Alexander the Great conquered Egypt after the first step pyramid was built. d. The New Kingdom began after the Egyptians joined Ra and Amun to make Amun-Ra the King of the Gods. 8. What is papyrus and what was it used for? How was thi ...
... b. Queen Cleopatra kills herself before the New Kingdom began. c. Alexander the Great conquered Egypt after the first step pyramid was built. d. The New Kingdom began after the Egyptians joined Ra and Amun to make Amun-Ra the King of the Gods. 8. What is papyrus and what was it used for? How was thi ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Egypt Multiple Choice – This section will be
... 11. This is the capital of Egypt’s Old Kingdom and is located on the Nile River. Memphis 12. This city became the capital of Egypt’s New Kingdom. Thebes 13. The world’s longest river, which flows northward through East Africa into the Mediterranean Sea is called the Nile River. 14. The Valley of the ...
... 11. This is the capital of Egypt’s Old Kingdom and is located on the Nile River. Memphis 12. This city became the capital of Egypt’s New Kingdom. Thebes 13. The world’s longest river, which flows northward through East Africa into the Mediterranean Sea is called the Nile River. 14. The Valley of the ...
EGYPTIAN CHRONOLOGY
... temples were abandoned and a new capital, Akhetaten, was established to the north. Attention to international affairs waned. Soon after the death of Akhenaten, his probable son - Tutankhaten - became pharaoh at about the age of nine. His was a short reign, but the old religious orders rose again an ...
... temples were abandoned and a new capital, Akhetaten, was established to the north. Attention to international affairs waned. Soon after the death of Akhenaten, his probable son - Tutankhaten - became pharaoh at about the age of nine. His was a short reign, but the old religious orders rose again an ...
Ancient Egypt WS.doc
... of Punt in East Africa. Her traders returned from Punt with frankincense, myrrh, and other luxury goods. She also commissioned major building projects throughout Egypt. Ramses II, a pharaoh that reigned about 200 years later, maintained Egyptian power through war. He is remembered as a great _______ ...
... of Punt in East Africa. Her traders returned from Punt with frankincense, myrrh, and other luxury goods. She also commissioned major building projects throughout Egypt. Ramses II, a pharaoh that reigned about 200 years later, maintained Egyptian power through war. He is remembered as a great _______ ...
Chapter 2 Section 2
... • Tutankhamen brought back the old Gods when Akhenaton died • Ramses II brought back some of the empire but the new kingdom collapsed in 1085 BC • Cleopatra VII tried to regain Egyptian independence but instead brought Roman rule over Egypt ...
... • Tutankhamen brought back the old Gods when Akhenaton died • Ramses II brought back some of the empire but the new kingdom collapsed in 1085 BC • Cleopatra VII tried to regain Egyptian independence but instead brought Roman rule over Egypt ...
Lesson 3
... Egyptians did not like the Hyksos. They resented paying taxes to foreign rulers. By the mid-‐1500s BC, Ahmose of Thebes drove the Hyksos out of Egypt and declared himself king of all Egypt. ...
... Egyptians did not like the Hyksos. They resented paying taxes to foreign rulers. By the mid-‐1500s BC, Ahmose of Thebes drove the Hyksos out of Egypt and declared himself king of all Egypt. ...
Egypt Ch.3 PPT
... Around 1480 B.C.E. Queen Hatshepsut carried out an extensive building program Thutomose III expanded empire ...
... Around 1480 B.C.E. Queen Hatshepsut carried out an extensive building program Thutomose III expanded empire ...
The Story of Ancient Egypt Study Guide Chapter 3 – complete
... Part 3: The New Kingdom (1500-1000 BCE) 1. What were five new weapons developed by the Egyptians after they were invaded by the Hyksos? Shields of bronze Battle axe and chain armor ...
... Part 3: The New Kingdom (1500-1000 BCE) 1. What were five new weapons developed by the Egyptians after they were invaded by the Hyksos? Shields of bronze Battle axe and chain armor ...
Egypt: The Middle Kingdom
... During this generally peaceful time trade picked up dramatically. Many resources which before had been unused were now being exploited such as the cultivation of crops, mines which produced gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects ...
... During this generally peaceful time trade picked up dramatically. Many resources which before had been unused were now being exploited such as the cultivation of crops, mines which produced gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects ...
Thebes, Egypt

Thebes (Ancient Greek: Θῆβαι, Thēbai), known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located east of the Nile about 800 kilometers (500 mi) south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Karnak and the necropolis of ancient Thebes lie nearby on the Nile's west bank.