Egypt - Issaquah Connect
... Polytheistic – believing in more than one god Practiced mummification to preserve the body for the after life Belief that there was life after death If you lived a good life in this world, you would have a good life in the next life Whatever the pharaoh believed and worshipped was done by the people ...
... Polytheistic – believing in more than one god Practiced mummification to preserve the body for the after life Belief that there was life after death If you lived a good life in this world, you would have a good life in the next life Whatever the pharaoh believed and worshipped was done by the people ...
History Study Guide Ch_ 4 _ 5
... 36. What did the delta of the Nile River provide Egyptians? protection from invaders 37. Who was responsible for uniting and governing Egypt? pharaohs ...
... 36. What did the delta of the Nile River provide Egyptians? protection from invaders 37. Who was responsible for uniting and governing Egypt? pharaohs ...
Ancient Egypt
... Each pyramid sits on a square base, with the entrance always facing north. Egyptians used astronomy to determine true north, also developed 365 day calendar grouped into 3 seasons. Farmers, surveyors, engineers, carpenters, and stone cutters were all used to build pyramids for the pharaoh. ...
... Each pyramid sits on a square base, with the entrance always facing north. Egyptians used astronomy to determine true north, also developed 365 day calendar grouped into 3 seasons. Farmers, surveyors, engineers, carpenters, and stone cutters were all used to build pyramids for the pharaoh. ...
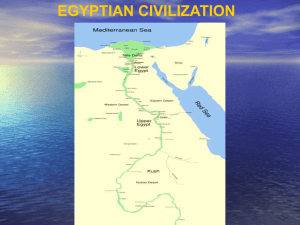
Geography and Early Egypt
... The decree appears in three scripts: the upper text is Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, the middle portion Demotic script, and the lowest Ancient Greek. Because it presents essentially the same text in all three scripts (with some minor differences among them), it provided the key to the modern underst ...
... The decree appears in three scripts: the upper text is Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, the middle portion Demotic script, and the lowest Ancient Greek. Because it presents essentially the same text in all three scripts (with some minor differences among them), it provided the key to the modern underst ...
Study Guide - Teachers.AUSD.NET
... Ramses II (pg.78) For each question below, record notes that prepare you to answer it. 1. What were the major accomplishments of the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms of ancient Egypt? ______________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ _______ ...
... Ramses II (pg.78) For each question below, record notes that prepare you to answer it. 1. What were the major accomplishments of the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms of ancient Egypt? ______________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ _______ ...
Impact of Geography
... ______________________ world order. 24. A ___________________________ in royal power could only mean that citizens were ______________________________ the gods and weakening that order. 25. Egyptian pharaohs possessed _________________________ power- that is, they had complete, _____________________ ...
... ______________________ world order. 24. A ___________________________ in royal power could only mean that citizens were ______________________________ the gods and weakening that order. 25. Egyptian pharaohs possessed _________________________ power- that is, they had complete, _____________________ ...
Document Practice Set #2 Early Civilizations
... The excerpt below describes farming in ancient Egypt. Farmers in ancient Egypt developed a system of watering their fields using the water from the Nile River. They built dams and dug ditches or canals to move the water into their fields. The farmers also built reservoirs in which they collected wa ...
... The excerpt below describes farming in ancient Egypt. Farmers in ancient Egypt developed a system of watering their fields using the water from the Nile River. They built dams and dug ditches or canals to move the water into their fields. The farmers also built reservoirs in which they collected wa ...
1 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 10. When the Theban kings rose to supremacy in the period now known as the Middle Kingdom the united Amon with this God to designate an Egyptian national God. a. Do b. Re c. Ra d. Hotep 11. In 1780 BCE a group of warlike people invaded Egypt and occupied her for 150 years. These people from present ...
... 10. When the Theban kings rose to supremacy in the period now known as the Middle Kingdom the united Amon with this God to designate an Egyptian national God. a. Do b. Re c. Ra d. Hotep 11. In 1780 BCE a group of warlike people invaded Egypt and occupied her for 150 years. These people from present ...
Sumerian, Egyptian, and Hebrew Literature
... (c.3100 BCE), though it was written on papyrus. Nobles (same social level as priests, but worked in government; had both privileges and money) Middle class – more numerous than above classes (artisans, merchants, physicians; served those above) Peasants and slaves – most numerous class. Had to ...
... (c.3100 BCE), though it was written on papyrus. Nobles (same social level as priests, but worked in government; had both privileges and money) Middle class – more numerous than above classes (artisans, merchants, physicians; served those above) Peasants and slaves – most numerous class. Had to ...
classroom tutorials
... But there was also a dark side—the life-giving Nile harbored dangerously swift currents in which a person could easily drown, and wild animals like crocodiles and hippopotami that could drag down a human. One could get lost forever in the great desert. Foreign invaders threatened attack. Illness was ...
... But there was also a dark side—the life-giving Nile harbored dangerously swift currents in which a person could easily drown, and wild animals like crocodiles and hippopotami that could drag down a human. One could get lost forever in the great desert. Foreign invaders threatened attack. Illness was ...
Essentials Nile River: The river that ran through Egypt. It allowed
... New Kingdom: Period of Egypt’s greatest strength and size. It lasted from 1539BC to 1075BC. It was also the period when Egypt most famous pharaohs ruled Pyramids: The Egyptians built pyramids during the Old Kingdom. They were believed to be a vehicle which took the pharaoh and workers to the aft ...
... New Kingdom: Period of Egypt’s greatest strength and size. It lasted from 1539BC to 1075BC. It was also the period when Egypt most famous pharaohs ruled Pyramids: The Egyptians built pyramids during the Old Kingdom. They were believed to be a vehicle which took the pharaoh and workers to the aft ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Egypt: Middle and New Kingdoms
... enlarged Egypt’s territory, expanded trade, and started massive building projects. Egyptian society was divided into different social classes. Most people worked as farmers and lived in rural areas. New Kingdom was a time of achievement in architecture, art and literature. ...
... enlarged Egypt’s territory, expanded trade, and started massive building projects. Egyptian society was divided into different social classes. Most people worked as farmers and lived in rural areas. New Kingdom was a time of achievement in architecture, art and literature. ...
Egyptian Society - Cherry Creek Academy
... Although the land was worked by the peasants, it was owned by the king, his officials and the temples. Farmers had to meet grain quotas, which were handed over to the owners as a form of taxation. They were allowed to keep a portion of the crops for their own benefit. If they did not produce the qua ...
... Although the land was worked by the peasants, it was owned by the king, his officials and the temples. Farmers had to meet grain quotas, which were handed over to the owners as a form of taxation. They were allowed to keep a portion of the crops for their own benefit. If they did not produce the qua ...
- SlideBoom
... anybody living there. There probably would not be an Egypt or any history about it. ...
... anybody living there. There probably would not be an Egypt or any history about it. ...
CHAPTER 5 STUDY GUIDE (Answers in bold) How religion affected
... fractures and wounds. Advanced mathematical principles, including geometry. 54. Amenhotep: changed his name to Akhenaton. 55. The Egyptian god responsible for life, death, and rebirth was? Osiris. 56. Which Continent is Egypt located on? Africa 57. What was not one of the three kingdoms of ancient E ...
... fractures and wounds. Advanced mathematical principles, including geometry. 54. Amenhotep: changed his name to Akhenaton. 55. The Egyptian god responsible for life, death, and rebirth was? Osiris. 56. Which Continent is Egypt located on? Africa 57. What was not one of the three kingdoms of ancient E ...
EgyptPPT
... The centers of the four sides are indented with an extraordinary degree of precision forming the only 8 sided pyramid; this effect is not visible from the ground or from a distance but only from the air, and then only under the proper lighting conditions. This phenomenon is only detectable from the ...
... The centers of the four sides are indented with an extraordinary degree of precision forming the only 8 sided pyramid; this effect is not visible from the ground or from a distance but only from the air, and then only under the proper lighting conditions. This phenomenon is only detectable from the ...
Night at the Museum Final
... Egypt is a country in North East Africa. The River Nile flows through the country and into the Mediterranean Sea. The River Nile was incredibly important for the Ancient Egyptians who lived along the riverbanks in Egypt. Farmers first settled in Egypt along the River Nile around 5000 B.C and about 9 ...
... Egypt is a country in North East Africa. The River Nile flows through the country and into the Mediterranean Sea. The River Nile was incredibly important for the Ancient Egyptians who lived along the riverbanks in Egypt. Farmers first settled in Egypt along the River Nile around 5000 B.C and about 9 ...
Section Summary Key Terms and People Academic Vocabulary
... afterlife life after death, a widely held ancient Egyptian belief mummies the Egyptian method of preserving dead bodies by wrapping them in ...
... afterlife life after death, a widely held ancient Egyptian belief mummies the Egyptian method of preserving dead bodies by wrapping them in ...
Egypt: A Moment in History - World Class Travel Leaders
... EGYPT: Splendors of the Nile Days 1-2: USA or Canada/ Cairo, Egypt Fly to Cairo, gateway to the land’s ancient wonders. Day 3: Cairo Begin your day at the pyramids of Cheops, Chephren and Mycerinus on the Giza Plateau. Cheops’, the largest of the three, dates back to about 2690 BC and is one of the ...
... EGYPT: Splendors of the Nile Days 1-2: USA or Canada/ Cairo, Egypt Fly to Cairo, gateway to the land’s ancient wonders. Day 3: Cairo Begin your day at the pyramids of Cheops, Chephren and Mycerinus on the Giza Plateau. Cheops’, the largest of the three, dates back to about 2690 BC and is one of the ...
Egypt Study Guide
... • Egyptian Obelisks What is an obelisk and what is its purpose? Obelisk Definition: An obelisk is a monumental tapering column carved from a single block of stone, with a square crosssection and capped with a pointed top called a pyramidion. Obelisks were set in pairs, at the entrances of temples, a ...
... • Egyptian Obelisks What is an obelisk and what is its purpose? Obelisk Definition: An obelisk is a monumental tapering column carved from a single block of stone, with a square crosssection and capped with a pointed top called a pyramidion. Obelisks were set in pairs, at the entrances of temples, a ...
Ancient Egyptian Art Where is Egypt?
... Ancient Egyptian Art is commonly divided up into three main periods/phases: ...
... Ancient Egyptian Art is commonly divided up into three main periods/phases: ...
Daily life in Ancient Egypt Family Life The only fertile land in Ancient
... The only fertile land in Ancient Egypt was next to the river Nile. Each year the river flooded its banks and the land around it was called “The Black Land”. The desert around the Nile valley was called “The Red Land”. It was here that the ancient Egyptians built their homes. Egyptian homes were made ...
... The only fertile land in Ancient Egypt was next to the river Nile. Each year the river flooded its banks and the land around it was called “The Black Land”. The desert around the Nile valley was called “The Red Land”. It was here that the ancient Egyptians built their homes. Egyptian homes were made ...
Ancient Egyptian technology

The characteristics of ancient Egyptian technology are indicated by a set of artifacts and customs that lasted for thousands of years. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam of ships. Egyptian paper, made from papyrus, and pottery were mass-produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean basin. The wheel, however, did not arrive until foreign influence introduced the chariot in the 16th century BCE. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology including ships and lighthouses.