27 - FacultyWeb Support Center
... the placenta takes over at about 3 months Establishing the Ovarian Cycle • During childhood, ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens that inhibit the hypothalamic release of GnRH • As puberty nears, GnRH is released; FSH and LH are released by the pituitary, and act on the ovaries • Thes ...
... the placenta takes over at about 3 months Establishing the Ovarian Cycle • During childhood, ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens that inhibit the hypothalamic release of GnRH • As puberty nears, GnRH is released; FSH and LH are released by the pituitary, and act on the ovaries • Thes ...
Reproduction notes
... stimulates the completion of meiosis, transforming the primary oocyte in the follicle into a secondary oocyte. it also signals enzymes to rupture the follicle, allowing ovulation to occur, and triggers the development of the corpus luteum from the ruptured follicle. it also promotes the secretio ...
... stimulates the completion of meiosis, transforming the primary oocyte in the follicle into a secondary oocyte. it also signals enzymes to rupture the follicle, allowing ovulation to occur, and triggers the development of the corpus luteum from the ruptured follicle. it also promotes the secretio ...
L05 and L06 - Superficial Back Muscles and Posterior Shoulder with
... Hypaxial differentiation Innervated by ventral motor roots which split into ventral rami – Deep muscles: intrinsic and move the head and the trunk, acting on the spine as principle extensors in lateral flexion and rotation spanning from the pelvis to the skull base Epaxial differentiation In ...
... Hypaxial differentiation Innervated by ventral motor roots which split into ventral rami – Deep muscles: intrinsic and move the head and the trunk, acting on the spine as principle extensors in lateral flexion and rotation spanning from the pelvis to the skull base Epaxial differentiation In ...
Yeasting 11-9
... down into inside of trophoblastic cells, forming an exoceolomic membrane (another layer now covers the original blastocele; 2 layers now exist—exocoelomic membrane of hypoblastic origin and trophoblastic cells). Hypoblastic cells migrate down on inside or trophoblasts and proliferate externally and ...
... down into inside of trophoblastic cells, forming an exoceolomic membrane (another layer now covers the original blastocele; 2 layers now exist—exocoelomic membrane of hypoblastic origin and trophoblastic cells). Hypoblastic cells migrate down on inside or trophoblasts and proliferate externally and ...
A Developmental Perspective: Changes in the Position of the
... dysozoan ancestor, one also needs to know what the common basis for the formation of these structures in all different metaancestor of the lophotrochozoan group (Figure 1), which gave zoan lineages is essential for understanding how molecular rise to animals as diverse as planarians, snails, and squ ...
... dysozoan ancestor, one also needs to know what the common basis for the formation of these structures in all different metaancestor of the lophotrochozoan group (Figure 1), which gave zoan lineages is essential for understanding how molecular rise to animals as diverse as planarians, snails, and squ ...
7.Mesoderm Derivatives
... the end of third week capillaries develop in the secondary chorionic villi ...
... the end of third week capillaries develop in the secondary chorionic villi ...
2nd week of developement
... maternal blood from ruptured endometrial capillaries and cellular debris from eroded uterine glands. The fluid in the lacunar spaces-embryotroph (Greek, trophe, nourishment)-passes to the embryonic disc by diffusion and provides nutritive material to the embryo. ...
... maternal blood from ruptured endometrial capillaries and cellular debris from eroded uterine glands. The fluid in the lacunar spaces-embryotroph (Greek, trophe, nourishment)-passes to the embryonic disc by diffusion and provides nutritive material to the embryo. ...
Animals File - Moodle
... – Associated with Bilateral symmetry – Puts sensory organs and mouth in the lead – Generally considered an adaptation for an active lifestyle – Contrast Porifera, Cnidaria, Echinodermata with Annelida and Arthropoda ...
... – Associated with Bilateral symmetry – Puts sensory organs and mouth in the lead – Generally considered an adaptation for an active lifestyle – Contrast Porifera, Cnidaria, Echinodermata with Annelida and Arthropoda ...
L8- Internal_Structures_of_Brainstem-2013
... nucleus of vagus, receive taste sensation from the tongue along the facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX) and vagus (X) cranial nerves ...
... nucleus of vagus, receive taste sensation from the tongue along the facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX) and vagus (X) cranial nerves ...
Thumb side = thenar - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... -ext rot/lat rot the arm Teres minor Subscapularis -the only rotator cuff muscle that medially rotates “The sub goes down.” Terrible triad of knee injury: -to tear MCL, ACL, and Medial menisci In fetus, blood bypasses the liver sinusoid through the ductus venosus What part of humerus articulates wit ...
... -ext rot/lat rot the arm Teres minor Subscapularis -the only rotator cuff muscle that medially rotates “The sub goes down.” Terrible triad of knee injury: -to tear MCL, ACL, and Medial menisci In fetus, blood bypasses the liver sinusoid through the ductus venosus What part of humerus articulates wit ...
ADDITIONALterms: • CLEARLY indicate all synapses involved like
... Unless a question asks only for a list or a diagram, answer all questions in complete sentences. Part of your grade depends upon your ability to communicate your ideas in a lucid manner. 1. Clearly diagram the structure and function of a Flexor (Withdrawal) Reflex. Include diagrammatic information s ...
... Unless a question asks only for a list or a diagram, answer all questions in complete sentences. Part of your grade depends upon your ability to communicate your ideas in a lucid manner. 1. Clearly diagram the structure and function of a Flexor (Withdrawal) Reflex. Include diagrammatic information s ...
Chapter 24 Development of digestive and respiratory system
... 2) development of esophagus and stomach ① development of esophagus ---derived from primitive gut extending from the laryngotracheal diverticulum to stomach ---with the descent of the heart and lungs, it lengthens rapidly ---muscular coat, formed by surrounding mesenchyme /striated in upper two-thir ...
... 2) development of esophagus and stomach ① development of esophagus ---derived from primitive gut extending from the laryngotracheal diverticulum to stomach ---with the descent of the heart and lungs, it lengthens rapidly ---muscular coat, formed by surrounding mesenchyme /striated in upper two-thir ...
Chapter 24 Development of digestive and respiratory system
... 2) development of esophagus and stomach ① development of esophagus ---derived from primitive gut extending from the laryngotracheal diverticulum to stomach ---with the descent of the heart and lungs, it lengthens rapidly ---muscular coat, formed by surrounding mesenchyme /striated in upper two-thir ...
... 2) development of esophagus and stomach ① development of esophagus ---derived from primitive gut extending from the laryngotracheal diverticulum to stomach ---with the descent of the heart and lungs, it lengthens rapidly ---muscular coat, formed by surrounding mesenchyme /striated in upper two-thir ...
Spinal Cord Structure
... anterior horn contains the cell bodies of somatic motor neurons, and it sends its axons out the anterior root of the spinal nerve to the muscle cells it innervates. The lateral horn is not found at all levels of the spinal cord, but is limited to thoracic and lumber segments of the cord. This is bec ...
... anterior horn contains the cell bodies of somatic motor neurons, and it sends its axons out the anterior root of the spinal nerve to the muscle cells it innervates. The lateral horn is not found at all levels of the spinal cord, but is limited to thoracic and lumber segments of the cord. This is bec ...
Chapter 1 study guide
... and lowest part of intestine ▪ Pelvic cavity contains reproductive organs, urinary bladder, pancreas, and spleen ...
... and lowest part of intestine ▪ Pelvic cavity contains reproductive organs, urinary bladder, pancreas, and spleen ...
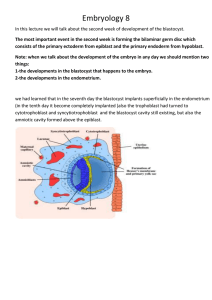
Embryology 8
... By the 13th day of development, the surface defect in the endometrium has usually healed. Occasionally, however, bleeding occurs at the implantation site as a result of increased blood flow into the lacunar spaces. Because this bleeding occurs near the 28th day of the menstrual cycle, it may be conf ...
... By the 13th day of development, the surface defect in the endometrium has usually healed. Occasionally, however, bleeding occurs at the implantation site as a result of increased blood flow into the lacunar spaces. Because this bleeding occurs near the 28th day of the menstrual cycle, it may be conf ...
protochordates
... environment. Most are colonial, and young bud from the parent to create colonies of organisms with colony members sharing things like excurrent siphons and the tunic, or body covering, that gives these animals their common name of tunicates. The tunic is composed of tunicin, a mixture of protein and ...
... environment. Most are colonial, and young bud from the parent to create colonies of organisms with colony members sharing things like excurrent siphons and the tunic, or body covering, that gives these animals their common name of tunicates. The tunic is composed of tunicin, a mixture of protein and ...
Animal Evolution Assignment File
... mostly motile/non-motile Two unique tissues found only in animals are: muscle/epithelial/connective/nervous Most animals reproduce sexually/asexually. The diploid/haploid stage is usually dominant in their life cycle. Reproduction and Development Fertilization occurs when a small flagellated sperm ...
... mostly motile/non-motile Two unique tissues found only in animals are: muscle/epithelial/connective/nervous Most animals reproduce sexually/asexually. The diploid/haploid stage is usually dominant in their life cycle. Reproduction and Development Fertilization occurs when a small flagellated sperm ...
Anatomy and Physiology of Balance
... inferior division: posterior part of saccule, and posterior canal • to vestibular nuclei • to cerebellum ...
... inferior division: posterior part of saccule, and posterior canal • to vestibular nuclei • to cerebellum ...
video slide - Course Notes
... • Development is determined by the zygote’s genome and molecules in the egg cytoplasm called Cytoplasmic determinants. • Cell differentiation is the specialization of cells in structure and function. ...
... • Development is determined by the zygote’s genome and molecules in the egg cytoplasm called Cytoplasmic determinants. • Cell differentiation is the specialization of cells in structure and function. ...
NEUROANATOMY 3
... • Anterior commisure (horizontal mass of white fibres) • Anterior perforated substance • Amygdala ...
... • Anterior commisure (horizontal mass of white fibres) • Anterior perforated substance • Amygdala ...
video slide - TeacherWeb
... • Development is determined by the zygote’s genome and molecules in the egg cytoplasm called Cytoplasmic determinants. • Cell differentiation is the specialization of cells in structure and function. ...
... • Development is determined by the zygote’s genome and molecules in the egg cytoplasm called Cytoplasmic determinants. • Cell differentiation is the specialization of cells in structure and function. ...
Show List of Dissection Steps
... ❏ On the cranial aspect of the limb, find the cranial tibial a. and trace its path as it continues distally down the hind limb. As the cranial tibial a. passes over the talocrural joint it becomes the dorsal pedal a. ...
... ❏ On the cranial aspect of the limb, find the cranial tibial a. and trace its path as it continues distally down the hind limb. As the cranial tibial a. passes over the talocrural joint it becomes the dorsal pedal a. ...
L10-Internal_Structures_of_Brainstem-20132014-08
... Through the whole length of the brain stem and into upper segments of spinal cord. It lies in all levels of M.O, medial to the spinal tract of the trigeminal. It receives pain and temperature from face, forehead. Its tract present in all levels of M.O. is formed of descending fibers that terminate i ...
... Through the whole length of the brain stem and into upper segments of spinal cord. It lies in all levels of M.O, medial to the spinal tract of the trigeminal. It receives pain and temperature from face, forehead. Its tract present in all levels of M.O. is formed of descending fibers that terminate i ...
Drosophila embryogenesis

Drosophila embryogenesis, the process by which Drosophila (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for geneticists and developmental biologists studying embryogenesis. The small size, short generation time, and large brood size make it ideal for genetic studies. Transparent embryos facilitate developmental studies. Drosophila melanogaster was introduced into the field of genetic experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1909.