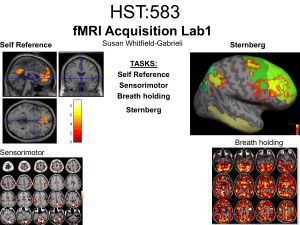
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
... activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
Document
... ◦ Researchers differ saying that without maintenance rehearsal something stays in STM for between 6-30 ...
... ◦ Researchers differ saying that without maintenance rehearsal something stays in STM for between 6-30 ...
Brain Teasers - Dartmouth Math Home
... suggesting that there is not much truth to the claim that cognitive performance is negatively affected by time constraints. On the other hand, no one was really invested in our little task, so who really knows what would happen under real pressure. ...
... suggesting that there is not much truth to the claim that cognitive performance is negatively affected by time constraints. On the other hand, no one was really invested in our little task, so who really knows what would happen under real pressure. ...
Stages of Memory
... • Q: Why are these explicit memories? • A: Because you can actively declare your answers to these questions ...
... • Q: Why are these explicit memories? • A: Because you can actively declare your answers to these questions ...
1 - contentextra
... Macrae et al. (1994) clearly demonstrated one of the most basic properties of schemas – that they can simplify information-processing and function as ‘energy-saving devices’. He asked participants to carry out two tasks at the same time. In the first, participants had to form impressions of a numbe ...
... Macrae et al. (1994) clearly demonstrated one of the most basic properties of schemas – that they can simplify information-processing and function as ‘energy-saving devices’. He asked participants to carry out two tasks at the same time. In the first, participants had to form impressions of a numbe ...
3 slides
... Z Distributed practice produces memories that are retained for long durations Z Massed practice produces memories that are retained well over short intervals (a few days) but are not retained well for longer durations Z Effects of massed vs. distributed practice depend on the timing of the retention ...
... Z Distributed practice produces memories that are retained for long durations Z Massed practice produces memories that are retained well over short intervals (a few days) but are not retained well for longer durations Z Effects of massed vs. distributed practice depend on the timing of the retention ...
-Louie Klaire Kat SAQ Outline Explain how biological factors may
... to localize the disorder with the left and right temporal lobes, as they can be involved in the formation of semantic and episodic memories. However, in a memory experiment involving the recall of previously presented numbers, ...
... to localize the disorder with the left and right temporal lobes, as they can be involved in the formation of semantic and episodic memories. However, in a memory experiment involving the recall of previously presented numbers, ...
Contemporary Issues - psychlotron.org.uk
... The resulting memory is real enough to cause trauma, even though it does not correspond to real events. Alien abduction experiences are an example of false memory syndrome ...
... The resulting memory is real enough to cause trauma, even though it does not correspond to real events. Alien abduction experiences are an example of false memory syndrome ...
AP PSYCHOLOGY OUTLINE Chapter 9: Memory
... c. Retrieval failure is what? i. What is proactive interference? Example? ii. What is retroactive interference? Example? d. Why would there be motivated forgetting? What are some items we might repress? VI. Memory Construction a. What is the misinformation effect? How does this work when a person wi ...
... c. Retrieval failure is what? i. What is proactive interference? Example? ii. What is retroactive interference? Example? d. Why would there be motivated forgetting? What are some items we might repress? VI. Memory Construction a. What is the misinformation effect? How does this work when a person wi ...
Chapter 7: Memory - Tipp City Schools
... • Answer just comes to us without working on it • Not consciously thinking about it ...
... • Answer just comes to us without working on it • Not consciously thinking about it ...
Working memory
... • If there is something called “working memory”, what is it? • How does it encode and manipulate information? • How does it transfer information to LTM? • What is the capacity? (128MB?) ...
... • If there is something called “working memory”, what is it? • How does it encode and manipulate information? • How does it transfer information to LTM? • What is the capacity? (128MB?) ...
2320Lecture22
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
The Aging Human Brain - San Diego State University
... largely intact in older adults, and can even improve with age, although processing time may be somewhat slower. Older adults have well structured, elaborate narratives and extensive vocabularies, and are usually judged as more interesting per se than younger people. But they can experience some text ...
... largely intact in older adults, and can even improve with age, although processing time may be somewhat slower. Older adults have well structured, elaborate narratives and extensive vocabularies, and are usually judged as more interesting per se than younger people. But they can experience some text ...