Memory following an Acquired Brain Injury
... injury has occurred, a person might have difficulties remembering either verbal (wordrelated) or non-verbal (pictorial) information. For example, damage to the left hand side of the brain can result in a difficulty with words and language and damage to the right hand side of the brain can affect rec ...
... injury has occurred, a person might have difficulties remembering either verbal (wordrelated) or non-verbal (pictorial) information. For example, damage to the left hand side of the brain can result in a difficulty with words and language and damage to the right hand side of the brain can affect rec ...
Memory
... - ability to identify _______________________________________________________________________ ...
... - ability to identify _______________________________________________________________________ ...
Unit 7A Guided Reading Questions
... 9. What is the author’s point to remember in regards to learning new subject material? 10. What is visual encoding? acoustic encoding? semantic encoding? a. Define imagery – b. What is rosy retrospection? c. What are mnemonics? Provide an example when you have used a mnemonic device. 11. What is chu ...
... 9. What is the author’s point to remember in regards to learning new subject material? 10. What is visual encoding? acoustic encoding? semantic encoding? a. Define imagery – b. What is rosy retrospection? c. What are mnemonics? Provide an example when you have used a mnemonic device. 11. What is chu ...
9.A.memoryintro
... Difficulty of Task • Was the exercise easy or difficult. It depends on what factors? ...
... Difficulty of Task • Was the exercise easy or difficult. It depends on what factors? ...
schema theory
... How have schemas been studied? • Serial reproduction-a participant reads a story then writes it down from memory and this version is read by another participant, who writes down what they recall. This version is then read and recalled by a third participant, and so on until 6-7 participants have re ...
... How have schemas been studied? • Serial reproduction-a participant reads a story then writes it down from memory and this version is read by another participant, who writes down what they recall. This version is then read and recalled by a third participant, and so on until 6-7 participants have re ...
Chapter 9 Packet
... T F 1. Memory storage is never automatic; it always takes effort. T F 2. When people go around a circle saying their names, their poorest memories are for what was said by the person just before them. T F 3. Memory aids (for example, those that use imagery and devices for organization) are no more u ...
... T F 1. Memory storage is never automatic; it always takes effort. T F 2. When people go around a circle saying their names, their poorest memories are for what was said by the person just before them. T F 3. Memory aids (for example, those that use imagery and devices for organization) are no more u ...
Chapter Eight - Kirkwood Community College
... hippocampus to the cortex, are brain replays the day’s experiences as it transfers them to the cortex for long term storage. ...
... hippocampus to the cortex, are brain replays the day’s experiences as it transfers them to the cortex for long term storage. ...
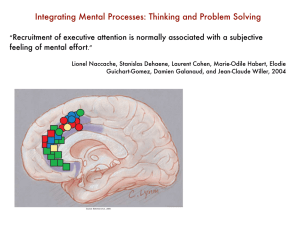
Integrating Mental Processes: Thinking and Problem Solving
... names, indicating that visual and sound representations of animals might be located in the same brain areas. The fact that her defcit was limited to the animal category indicates that different semantic categories -like animals and faces -- may be stored in differing brain regions. ...
... names, indicating that visual and sound representations of animals might be located in the same brain areas. The fact that her defcit was limited to the animal category indicates that different semantic categories -like animals and faces -- may be stored in differing brain regions. ...
HM Case Study
... though he could still remember events that happened more than 2 years before the surgery. • New experiences were quickly forgotten though he could remember a set of numbers or fact for short while. • The case of H.M. provided about memory impairment and amnesia, and allowed for better understanding ...
... though he could still remember events that happened more than 2 years before the surgery. • New experiences were quickly forgotten though he could remember a set of numbers or fact for short while. • The case of H.M. provided about memory impairment and amnesia, and allowed for better understanding ...
Chapter 7 Class Notes / Memory
... Duration: According to most memory theorists, the memories we process into our LTMs are relatively permanent. That is, most theorists believe once information is processed into LTM that it is, in some form, always there. Some question this asking, "then why do I forget things?" Memory theorists repl ...
... Duration: According to most memory theorists, the memories we process into our LTMs are relatively permanent. That is, most theorists believe once information is processed into LTM that it is, in some form, always there. Some question this asking, "then why do I forget things?" Memory theorists repl ...
Cognition: Memory
... conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited Intuition – effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit conscious reasoning See chart on p. 310 for its pros and cons ...
... conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited Intuition – effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit conscious reasoning See chart on p. 310 for its pros and cons ...
Brain Training Memory Three tasks/jobs: Encoding Select stimulus
... students who responded to the texts did much worse than the students who waited until the end of the lecture to respond. b. If learn while distracted – understand and remember less (shallower comprehension, not as able to transfer/extend knowledge). c. Mental exhaustion – each time you switch focus, ...
... students who responded to the texts did much worse than the students who waited until the end of the lecture to respond. b. If learn while distracted – understand and remember less (shallower comprehension, not as able to transfer/extend knowledge). c. Mental exhaustion – each time you switch focus, ...
Intelligence. Emotions. Memory. Temperament».
... probably take a variety of forms, depending on the nature of the material that needs to be tucked away in memory. For example, memories of visual scenes, of how to perform actions (such as typing or hitting a backhand stroke in tennis), and of factual information (such as definitions or dates in hi ...
... probably take a variety of forms, depending on the nature of the material that needs to be tucked away in memory. For example, memories of visual scenes, of how to perform actions (such as typing or hitting a backhand stroke in tennis), and of factual information (such as definitions or dates in hi ...
Does Sudafed® Improve Performance on
... dilation, and pupillary dilation. The significant difference in response time during the visual go/no-go task therefore can be attributed to having an increased heart rate and also having pupillary dilation. With increased heart rate, participants could have been more ready to respond to visual sti ...
... dilation, and pupillary dilation. The significant difference in response time during the visual go/no-go task therefore can be attributed to having an increased heart rate and also having pupillary dilation. With increased heart rate, participants could have been more ready to respond to visual sti ...