Parts of Speech cheat sheet
... In order to speak and write properly, students must know the eight parts of speech, their definitions, and how to use them correctly. Here is a guide of the parts of speech to assist you and your child. ...
... In order to speak and write properly, students must know the eight parts of speech, their definitions, and how to use them correctly. Here is a guide of the parts of speech to assist you and your child. ...
6th Grade Parts of Speech packet
... Directions: Use this handout and the grammar section of BrainPop to review the basic parts of speech. Use the login, adamerritt, and the password, brainpop to access BrainPop. Be prepared for a quiz during the first week of the 2014-2015 school year. Nouns ...
... Directions: Use this handout and the grammar section of BrainPop to review the basic parts of speech. Use the login, adamerritt, and the password, brainpop to access BrainPop. Be prepared for a quiz during the first week of the 2014-2015 school year. Nouns ...
Arabic Parts of Speech: A Brief Overview
... verb, e.g. saufa ta‘lamûna “Very soon they will come to know.” (5) 3. Particle (harf): The particle in Arabic is such a word that which is dependent on a noun or a verb in order to convey a complete or useful meaning. Its meaning will be complete when it is used along with the noun or verb in a sent ...
... verb, e.g. saufa ta‘lamûna “Very soon they will come to know.” (5) 3. Particle (harf): The particle in Arabic is such a word that which is dependent on a noun or a verb in order to convey a complete or useful meaning. Its meaning will be complete when it is used along with the noun or verb in a sent ...
GMAS Crash Couse
... or to whom something was done. I read the class the entire book. Object of a preposition – answers the question whom or what after the preposition. ...
... or to whom something was done. I read the class the entire book. Object of a preposition – answers the question whom or what after the preposition. ...
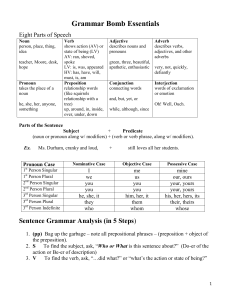
Grammar Bomb Essentials
... b. LV What word describes or renames the subject? PA Describes = adjective = Predicate Adjective PN Renames = noun = Predicate Nominative ...
... b. LV What word describes or renames the subject? PA Describes = adjective = Predicate Adjective PN Renames = noun = Predicate Nominative ...
1. Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing
... Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. ...
... Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. ...
condensed grammar review
... A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or a pronoun that is the object of the preposition. Common Prepositions aboard ...
... A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or a pronoun that is the object of the preposition. Common Prepositions aboard ...
Parts of Speech
... considering, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, next, of, off, on, onto, opposite, out, outside, over, past, plus, regarding, respecting, round, since, than, through, throughout, till, to, toward, under, underneath, unlike, until, unto, up, upon, with, within, wi ...
... considering, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, next, of, off, on, onto, opposite, out, outside, over, past, plus, regarding, respecting, round, since, than, through, throughout, till, to, toward, under, underneath, unlike, until, unto, up, upon, with, within, wi ...
English Grammar - HCC Learning Web
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
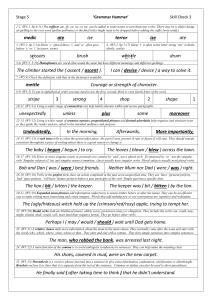
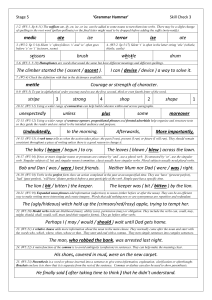
Stage 5 Check 3 – Answers
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
medic ate ize terror ize ate scissors brush whistle drum The climber
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
Polyptoton 1
... H. It means a change of course; a different arrangement of the same word, a leading of the same word through different inflections. I. In Latin is called casum varietas, “a variety of cases.” J. This figure, therefore, is a repetition of the same word in the same sense, but not in the same form: fro ...
... H. It means a change of course; a different arrangement of the same word, a leading of the same word through different inflections. I. In Latin is called casum varietas, “a variety of cases.” J. This figure, therefore, is a repetition of the same word in the same sense, but not in the same form: fro ...
English Grammar
... and spoken formats. The student a. Identifies and uses the eight basic parts of speech and demonstrates that words can be different parts of speech within a ...
... and spoken formats. The student a. Identifies and uses the eight basic parts of speech and demonstrates that words can be different parts of speech within a ...
English Grammar
... as a noun. The word or word group that the preposition introduces is its object. They received a postcard from Bobby telling about his trip to Canada. ...
... as a noun. The word or word group that the preposition introduces is its object. They received a postcard from Bobby telling about his trip to Canada. ...
Parts of Speech
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
English Grammar
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
Parts of Speech
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
Parts of Speech - Capital Community College
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
Parts of Speech - Capital Community College
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
... The pronoun is a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea. ...
Accusative Case
... O Just like English, German has prepositions. O When a noun follows a preposition, in is ...
... O Just like English, German has prepositions. O When a noun follows a preposition, in is ...
Arabic grammar

Arabic grammar (Arabic: النحو العربي An-naḥw al-‘arabiyy or قواعد اللغة العربية qawā‘id al-lughah al-‘arabīyyah) is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the grammar of other Semitic languages.The article focuses both on the grammar of Literary Arabic (i.e. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic, which have largely the same grammar) and of the colloquial spoken varieties of Arabic. The grammar of the two types is largely similar in its particulars. Generally, the grammar of Classical Arabic is described first, followed by the areas in which the colloquial variants tend to differ (note that not all colloquial variants have the same grammar). The largest differences between the two systems are the loss of grammatical case; the loss of the previous system of grammatical mood, along with the evolution of a new system; the loss of the inflected passive voice, except in a few relic varieties; and restriction in the use of the dual number.