Quiz Chapter 2: Theories of Development (10 points)
... 10. Piaget used the term ____________ to describe the guidelines individuals use to organize and adapt to their environments. a. cognitive structures b. defense mechanisms c. formal concepts d. life structures 11. Piaget argued that a baby’s concept of the world is based on a. what makes them feel t ...
... 10. Piaget used the term ____________ to describe the guidelines individuals use to organize and adapt to their environments. a. cognitive structures b. defense mechanisms c. formal concepts d. life structures 11. Piaget argued that a baby’s concept of the world is based on a. what makes them feel t ...
6AnimalBehavior
... Niko Tinbergen animal behavior Q’s: 1. What stimulus elicits the behavior, and what physiological mechanisms mediate the response? (proximate) 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproductio ...
... Niko Tinbergen animal behavior Q’s: 1. What stimulus elicits the behavior, and what physiological mechanisms mediate the response? (proximate) 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproductio ...
Chapter 14 pp
... Day 8 – Units 12 & 13 TEST + Unit 13 Focus Objectives DUE TODAY + Mood Memory Repair activity DUE “Tomorrow” ...
... Day 8 – Units 12 & 13 TEST + Unit 13 Focus Objectives DUE TODAY + Mood Memory Repair activity DUE “Tomorrow” ...
View PDF
... Object permanence is the awareness that objects continue to exist when not perceived. For example, a child may look for a toy hidden under a blanket Conservation is the principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the form of objects. For example, a c ...
... Object permanence is the awareness that objects continue to exist when not perceived. For example, a child may look for a toy hidden under a blanket Conservation is the principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the form of objects. For example, a c ...
chapter 17
... caretakers; learn what not to do by being disciplined (not physically punished) for their wrong actions – children learn through watching successful parents • multiple models - learning more difficult when models are performing behaviors that conflict with one another. – children eventually learn to ...
... caretakers; learn what not to do by being disciplined (not physically punished) for their wrong actions – children learn through watching successful parents • multiple models - learning more difficult when models are performing behaviors that conflict with one another. – children eventually learn to ...
Sigmund Freud
... Catharsis: Expression of emotions that is expected to lead to the reduction of disturbing symptoms ...
... Catharsis: Expression of emotions that is expected to lead to the reduction of disturbing symptoms ...
Animal Behavior
... • Migrates upward during the day and descends at night • Also migrate from the west to the east during the day and return in the evening ...
... • Migrates upward during the day and descends at night • Also migrate from the west to the east during the day and return in the evening ...
Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences 1
... Use of physical force with the intention to cause an individual to experience pain (not injury) for purposes of correction or control of the individual's behavior. ...
... Use of physical force with the intention to cause an individual to experience pain (not injury) for purposes of correction or control of the individual's behavior. ...
Chapter_2 - Forensic Consultation
... Withdrawing a positive (not using car) or aversive (jail) Reinforcement can be positive or negative Positive: reward Negative: taking away something the person does not like (aversive event) ...
... Withdrawing a positive (not using car) or aversive (jail) Reinforcement can be positive or negative Positive: reward Negative: taking away something the person does not like (aversive event) ...
Learning Theory Theorists (Alphabetical) Year Ideals Classroom
... (knowledge) does not work, and needs to be changed to deal with a new object or situation. Equilibration –This is the force, which moves development along. Piaget believed that cognitive development did not progress at a steady rate, but rather in leaps and bounds. Equilibrium occurs when a child's ...
... (knowledge) does not work, and needs to be changed to deal with a new object or situation. Equilibration –This is the force, which moves development along. Piaget believed that cognitive development did not progress at a steady rate, but rather in leaps and bounds. Equilibrium occurs when a child's ...
SR6e Chapter 2
... louder, that he wants them to turn off the television so he can play Nintendo games. If you were Moosie’s father, how would you react? Here are four possible consequences of Moosie’s behavior. Consider both the type of consequences – whether it is a pleasant or aversive stimulus – and whether it is ...
... louder, that he wants them to turn off the television so he can play Nintendo games. If you were Moosie’s father, how would you react? Here are four possible consequences of Moosie’s behavior. Consider both the type of consequences – whether it is a pleasant or aversive stimulus – and whether it is ...
latent
... Defense Mechanisms (cont) – Regression - fall back on childlike response patterns when under stress – Identification - try to become like someone else to deal with anxiety – Compensation - make up for inferiorities in one area by becoming superior in another area – Sublimation - channel socially un ...
... Defense Mechanisms (cont) – Regression - fall back on childlike response patterns when under stress – Identification - try to become like someone else to deal with anxiety – Compensation - make up for inferiorities in one area by becoming superior in another area – Sublimation - channel socially un ...
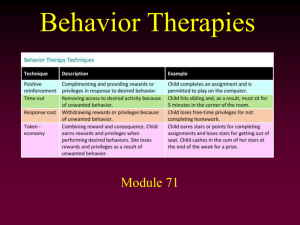
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • When moisture hits pad (bladder tension = NS) the Alarm sounds (US) waking the child (UR). • Eventually bladder tension (CR) causes the child to awaken (CR). • It is effective in about 75 percent of school-age children who have difficulties with bedwetting. ...
... • When moisture hits pad (bladder tension = NS) the Alarm sounds (US) waking the child (UR). • Eventually bladder tension (CR) causes the child to awaken (CR). • It is effective in about 75 percent of school-age children who have difficulties with bedwetting. ...
chapter - Human Kinetics
... • The teacher will record every demonstration of the student’s positive interactions as evidenced by the chart publicly displayed in the gym. The teacher will award points during class and supervise free time in the gym on Friday afternoons if the student earns the prescribed number of ...
... • The teacher will record every demonstration of the student’s positive interactions as evidenced by the chart publicly displayed in the gym. The teacher will award points during class and supervise free time in the gym on Friday afternoons if the student earns the prescribed number of ...
Practicum on Kohlberg`s Stages of Moral Development
... principles that may rise above government and laws. Example: “I don’t drive above the speed limit because I think by doing this I could save someone’s life.” Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Boston: Allyn and Bacon ...
... principles that may rise above government and laws. Example: “I don’t drive above the speed limit because I think by doing this I could save someone’s life.” Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Boston: Allyn and Bacon ...
Chapter 3 Socialization
... Preparatory Stage (up to age 3) Children prepare for role-taking by imitating the people around them. Play Stage (3 - 5) Children begin to see themselves in relation to others. ...
... Preparatory Stage (up to age 3) Children prepare for role-taking by imitating the people around them. Play Stage (3 - 5) Children begin to see themselves in relation to others. ...
Learning
... Positive reinforcement - consists of something that is desired: behavior is more likely to recur ...
... Positive reinforcement - consists of something that is desired: behavior is more likely to recur ...
pleasure principle”.
... Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense of self esteem will significantly affect interaction, resulting in the “self ...
... Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense of self esteem will significantly affect interaction, resulting in the “self ...
Behavioral Theory rev 2012
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
Chapter 3 Socialization
... 1. We imagine how our personality and appearance will look to other people. 2. We imagine how other people judge the appearance and personality that we think we present. 3. We develop a self-concept. ...
... 1. We imagine how our personality and appearance will look to other people. 2. We imagine how other people judge the appearance and personality that we think we present. 3. We develop a self-concept. ...
Pengelolaan Organisasi Entrepreneurial
... Learning Objectives – Explain differences between social learning theory and reinforcement theory – Discuss how self-managing can be useful in developing a motivation program – Describe how expectancy, equity, and goal-setting theories are used to motivate employees ...
... Learning Objectives – Explain differences between social learning theory and reinforcement theory – Discuss how self-managing can be useful in developing a motivation program – Describe how expectancy, equity, and goal-setting theories are used to motivate employees ...
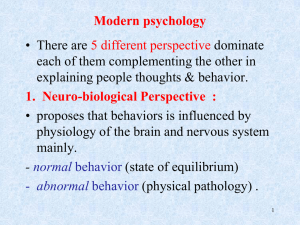
1. Neuro-biological Perspective
... • Albert Bandura states : that human behavior results from the interaction of environment with perception &thinking. ...
... • Albert Bandura states : that human behavior results from the interaction of environment with perception &thinking. ...
chapt43_image
... • Communication is an action by a sender that may influence the behavior of a receiver • Pheromones are chemical signals in low concentration that are passed between members of the same species • Moths, ants and termites, cheetahs and other cats • Humans have vomeronasal organ in the nose that can d ...
... • Communication is an action by a sender that may influence the behavior of a receiver • Pheromones are chemical signals in low concentration that are passed between members of the same species • Moths, ants and termites, cheetahs and other cats • Humans have vomeronasal organ in the nose that can d ...