Review for Unit 2 Exam KEY
... West = (35,903.3 – 35,231.8/35,903.3) x 100 = 0.19% growth Compute unemployment rates in the different regions of the country in March 2007 and March 2008. ...
... West = (35,903.3 – 35,231.8/35,903.3) x 100 = 0.19% growth Compute unemployment rates in the different regions of the country in March 2007 and March 2008. ...
AP Macro - Sect. 3 PP no bkgd
... Consumer Price Index - (CPI) Measure of the cost of the “market basket” of goods - Calculated each month by the Bureau of Labor Statistics ...
... Consumer Price Index - (CPI) Measure of the cost of the “market basket” of goods - Calculated each month by the Bureau of Labor Statistics ...
Macroeconomic Crises and the Social Order
... Encounters with younger colleagues in Europe or the United States often make me reflect on how the worldview of economists have changed over the last forty or fifty years. Back then, most believed that the private sector was unstable and riddled with market failures but that en enlightened and beenv ...
... Encounters with younger colleagues in Europe or the United States often make me reflect on how the worldview of economists have changed over the last forty or fifty years. Back then, most believed that the private sector was unstable and riddled with market failures but that en enlightened and beenv ...
INFLATION A TWO-WEEK UNIT OF STUDY Albert Goldsmith
... a. A definition of inflation can be written and learned. b. Effective control of inflation requires a cooperative relationship between the government and the people e. Inflation does affect me. d. The most important job of the government is to control and support our money system. e. Inflation is th ...
... a. A definition of inflation can be written and learned. b. Effective control of inflation requires a cooperative relationship between the government and the people e. Inflation does affect me. d. The most important job of the government is to control and support our money system. e. Inflation is th ...
Word Document
... Classicals and neoclassicals believed Say’s Law implies the economy must always be at full employment. Under new classical theory the economy is always at equilibrium: all unemployment is voluntary. Under real business cycle theory supply side shocks cause what appear to be business cycles. Th ...
... Classicals and neoclassicals believed Say’s Law implies the economy must always be at full employment. Under new classical theory the economy is always at equilibrium: all unemployment is voluntary. Under real business cycle theory supply side shocks cause what appear to be business cycles. Th ...
Chapter 12
... Central Bank Independence • Countries with Central Banks (the general name for institutions like the US Federal Reserve) that are more independent of political control have higher rates of economic growth. • This is because political influences tend to create inflationary tendencies which raises in ...
... Central Bank Independence • Countries with Central Banks (the general name for institutions like the US Federal Reserve) that are more independent of political control have higher rates of economic growth. • This is because political influences tend to create inflationary tendencies which raises in ...
Document
... 42. One implication of the Lucas critique is that a. It takes a long time for a reduction in money growth to reduce the inflation rate. b. Unemployment will always be above its natural rate in the short run. c. Unemployment is always at its natural rate in the short run. d. The sacrifice ratio shoul ...
... 42. One implication of the Lucas critique is that a. It takes a long time for a reduction in money growth to reduce the inflation rate. b. Unemployment will always be above its natural rate in the short run. c. Unemployment is always at its natural rate in the short run. d. The sacrifice ratio shoul ...
ECN 111 Chapter 13 Lecture Notes
... percent increase in the quantity of money demanded at each nominal interest rate. 2. Real GDP An increase in real GDP increases the demand for money. 3. Financial Technology Changes in financial technology can increase the demand for money (ATMs) or decrease the demand for money (credit cards). E. S ...
... percent increase in the quantity of money demanded at each nominal interest rate. 2. Real GDP An increase in real GDP increases the demand for money. 3. Financial Technology Changes in financial technology can increase the demand for money (ATMs) or decrease the demand for money (credit cards). E. S ...
UNDERLYING FACTORS OF PERSISTENT INFLATION IN ROMANIA
... generating higher wages and as a consequence the aggregate supply curve will quickly begin to shift leftward. As a result, a new equilibrium will occur with output returning at its natural level and prices being the only variable higher compared to the initial situation. Although the Keynesians do n ...
... generating higher wages and as a consequence the aggregate supply curve will quickly begin to shift leftward. As a result, a new equilibrium will occur with output returning at its natural level and prices being the only variable higher compared to the initial situation. Although the Keynesians do n ...
VII Neoclassical synthesis and economic policies of 1960s
... of original P.C. that shift for various πe (see graph slide) • Interpretation for monetary expansion – starting at natural rates: wage and price inflation and inflation expectations = 0 – Simplification: productivity growth = 0 ...
... of original P.C. that shift for various πe (see graph slide) • Interpretation for monetary expansion – starting at natural rates: wage and price inflation and inflation expectations = 0 – Simplification: productivity growth = 0 ...
Reconstructing Macroeconomics. Structuralist Proposals and Critiques of the Mainstream Brochure
... This book presents both a critique of mainstream macroeconomics from a structuralist perspective and an exposition of modern structuralist approaches. The fundamental assumption of structuralism is that it is impossible to understand a macroeconomy without understanding its major institutions and di ...
... This book presents both a critique of mainstream macroeconomics from a structuralist perspective and an exposition of modern structuralist approaches. The fundamental assumption of structuralism is that it is impossible to understand a macroeconomy without understanding its major institutions and di ...
Saturday S..
... – Correctness of data: Is the train driver seeing the tracks correctly? Or Does the government get the right data about where the economy is? – Timing of data: Is the train driver seeing the tracks with enough time to react? Or Does the government get the statistics quickly enough to do anything? – ...
... – Correctness of data: Is the train driver seeing the tracks correctly? Or Does the government get the right data about where the economy is? – Timing of data: Is the train driver seeing the tracks with enough time to react? Or Does the government get the statistics quickly enough to do anything? – ...
Inflation October 18
... Understanding the costs of inflation is not an easy task. There are a variety of myths about inflation. There are debates among economists about some of the more serious problems caused by inflation. A number of exercises in National Council on Economic Education publications, student workbooks, and ...
... Understanding the costs of inflation is not an easy task. There are a variety of myths about inflation. There are debates among economists about some of the more serious problems caused by inflation. A number of exercises in National Council on Economic Education publications, student workbooks, and ...
202 course paper: 2001
... (i) Explain the adaptive expectations hypothesis and comment on its major strengths and weaknesses. (ii) Explain the rational expectations hypothesis and comment on its major strengths and weaknesses. (iii) Compare the adaptive and rational expectations approaches to explaining the expected future v ...
... (i) Explain the adaptive expectations hypothesis and comment on its major strengths and weaknesses. (ii) Explain the rational expectations hypothesis and comment on its major strengths and weaknesses. (iii) Compare the adaptive and rational expectations approaches to explaining the expected future v ...
Chapter 22: Main Events of the Period 1970 to 1990
... What Phillips also discovered was that this trade-off was stable. His data extended back nearly 100 years. Whatever the relation had been in the 1950s, the same relation had existed in the 1920s, the 1890s, and even the 1870s. This was an amazing discovery. Relationships in Economics rarely stay the ...
... What Phillips also discovered was that this trade-off was stable. His data extended back nearly 100 years. Whatever the relation had been in the 1950s, the same relation had existed in the 1920s, the 1890s, and even the 1870s. This was an amazing discovery. Relationships in Economics rarely stay the ...
STRATEGY
... Yes, it is. We had the feeling it was for several months, and today this is definitely the case. All indicators are up, including the total consumer price index, the index ex-food and ex-energy, the PCE deflator (which is the Federal Reserve’s official objective) – all are accelerating. Some regiona ...
... Yes, it is. We had the feeling it was for several months, and today this is definitely the case. All indicators are up, including the total consumer price index, the index ex-food and ex-energy, the PCE deflator (which is the Federal Reserve’s official objective) – all are accelerating. Some regiona ...
Why Has Nominal Income Growth Been So Slow?
... First, the Fed implemented QE at the same time that it began paying interest to banks on their holdings of reserves. The quantitative analysis in Ireland (2014) shows that there can be an enormous expansion in banks’ demand for real excess reserves during the transition between an initial steady st ...
... First, the Fed implemented QE at the same time that it began paying interest to banks on their holdings of reserves. The quantitative analysis in Ireland (2014) shows that there can be an enormous expansion in banks’ demand for real excess reserves during the transition between an initial steady st ...
7. Medium-Term Projections
... of such a scenario may prompt the CBRT to lower short-term money market rates by easing liquidity conditions, while the adverse impact of rapid capital inflows on financial stability is alleviated through required reserves and the reserve options mechanism. Recently, the medium-term inflation expect ...
... of such a scenario may prompt the CBRT to lower short-term money market rates by easing liquidity conditions, while the adverse impact of rapid capital inflows on financial stability is alleviated through required reserves and the reserve options mechanism. Recently, the medium-term inflation expect ...
APE Macro Unit 3: Measurement of Economic Performance
... Students should be able to explain macroeconomics and how it differs from microeconomics AND answer the following question: Why is it that what is good for the part is not necessarily good for the whole? Explain why the business cycle is important and why policy makers seek to diminish the severity ...
... Students should be able to explain macroeconomics and how it differs from microeconomics AND answer the following question: Why is it that what is good for the part is not necessarily good for the whole? Explain why the business cycle is important and why policy makers seek to diminish the severity ...
Document
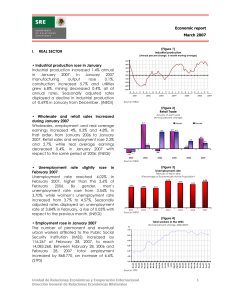
... the end of 2007 could reach 3.68% (this level is lower than their previous forecasts of 3.7%). The Banamex-Citigrup projection is 3.62%. Core inflation in 2007 will be 3.56%. • The Mexican economy will grow near 3.6% in 2007 BBVA-Bancomer.- Although it will depend in the performance in figures of co ...
... the end of 2007 could reach 3.68% (this level is lower than their previous forecasts of 3.7%). The Banamex-Citigrup projection is 3.62%. Core inflation in 2007 will be 3.56%. • The Mexican economy will grow near 3.6% in 2007 BBVA-Bancomer.- Although it will depend in the performance in figures of co ...
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. A chief measure of price inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index (normally the consumer price index) over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.Inflation affects an economy in various ways, both positive and negative. Negative effects of inflation include an increase in the opportunity cost of holding money, uncertainty over future inflation which may discourage investment and savings, and if inflation were rapid enough, shortages of goods as consumers begin hoarding out of concern that prices will increase in the future.Inflation also has positive effects: Fundamentally, inflation gives everyone an incentive to spend and invest, because if they don't, their money will be worth less in the future. This increase in spending and investment can benefit the economy. However it may also lead to sub-optimal use of resources. Inflation reduces the real burden of debt, both public and private. If you have a fixed-rate mortgage on your house, your salary is likely to increase over time due to wage inflation, but your mortgage payment will stay the same. Over time, your mortgage payment will become a smaller percentage of your earnings, which means that you will have more money to spend. Inflation keeps nominal interest rates above zero, so that central banks can reduce interest rates, when necessary, to stimulate the economy. Inflation reduces unemployment to the extent that unemployment is caused by nominal wage rigidity. When demand for labor falls but nominal wages do not, as typically occurs during a recession, the supply and demand for labor cannot reach equilibrium, and unemployment results. By reducing the real value of a given nominal wage, inflation increases the demand for labor, and therefore reduces unemployment.Economists generally believe that high rates of inflation and hyperinflation are caused by an excessive growth of the money supply. However, money supply growth does not necessarily cause inflation. Some economists maintain that under the conditions of a liquidity trap, large monetary injections are like ""pushing on a string"". Views on which factors determine low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be attributed to fluctuations in real demand for goods and services, or changes in available supplies such as during scarcities. However, the consensus view is that a long sustained period of inflation is caused by money supply growing faster than the rate of economic growth.Today, most economists favor a low and steady rate of inflation. Low (as opposed to zero or negative) inflation reduces the severity of economic recessions by enabling the labor market to adjust more quickly in a downturn, and reduces the risk that a liquidity trap prevents monetary policy from stabilizing the economy. The task of keeping the rate of inflation low and stable is usually given to monetary authorities. Generally, these monetary authorities are the central banks that control monetary policy through the setting of interest rates, through open market operations, and through the setting of banking reserve requirements.