* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
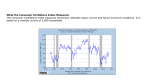
Chapter 5 Macroeconomics the Big Picture Hossain: MSMC Gross Domestic Product In simple terms, GDP is the total output produced in an economy It is often used to measure: USA: 14.59 trillion The size of an economy Japan: 4.91 trillion The performance of an economy GDP shrunk USStandard of by 4% in the 3rd quarter of 2009 Germany: 3.65 trillion US GDP grew by living in an economy 2% in the 1st quarter of 2010 Commonly measured by per capital GDP Hossain: MSMC 2 2008 GDPs Hossain: MSMC 3 Gross Domestic Product Formal definition: Nominal GDP value of andand services finalgoods Total value of all allfinal final goods services produced in an an economy economy in given given year yearvalued valued at the current current price current price price Real GDP Total value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in given year adjusted adjusted to to eliminate eliminate the the effect effect of of price price change change Hossain: MSMC 4 Nominal and Real GDP Consider the following table Goods and Services 2008 2009 P Q Text Book 100 500 Hair Cuts 10 400 P Q Nominal GDP in 2008 100 X 500 + 10 X 400 Hossain: MSMC = 54,000 5 Nominal and Real GDP Goods and Services 2008 2009 P Q P Q Text Book 100 500 150 400 Hair Cuts 10 400 15 300 Nominal GDP in 2008 100 X 500 + 10 X 400 = 54,000 = 64,500 Nominal GDP in 2009 150 X 400 + 15 X 300 Hossain: MSMC 6 Nominal and Real GDP Goods and Services Text Book Hair Cuts 2008 2009 P Q P Q 1985 P 100 10 500 400 150 15 400 300 75 5 Real GDP in 2008 75 X 500 + 5 X 400 = 39,500 = 31,500 Real GDP in 2009 75 X 400 + 5 X 300 Hossain: MSMC 7 Business Cycle Economy does not grow at a constant rate Rather, it has a cyclical pattern, which can be described by following components: Expansion Recession Peak Trough Hossain: MSMC 8 Business Cycle An expansion is a sustained period in which real GDP is rising. A recession is a sustained period in which real GDP is falling. A peak is the point of the business cycle at which an expansion ends and a recession begins. A trough is the point of the business cycle at which a recession ends and an expansion begins. Business Cycle Hossain: MSMC 10 U.S. Real GDP Hossain: MSMC 11 Changes in Price Level Price Levels are different from Price we learned in chapter 3 It is NOT the price of apple, orange or banana It is the average price of all goods and services in an economy Usually, measured by a basket of representative goods and services Hossain: MSMC 12 Changes in Price Level For example CPI or Consumer Price Index tracks the prices of goods and services purchased by a typical urban family of four. When price level rises, we call this Inflation When price level falls, we call this deflation Hossain: MSMC 13 Inflation in the U.S. Hossain: MSMC 14 Impacts of Inflation Unanticipated inflation has following adverse impacts: Fall of purchasing power Redistributes wealth Creates uncertainty Hurts lenders and benefits borrowers Hossain: MSMC 15 Impacts of deflation Unanticipated deflation has following adverse impacts: Redistributes wealth Creates uncertainty Hurts borrowers and benefits lenders Hossain: MSMC 16 Computation of CPI Price Index is a number whose movement reflects the changes in average price level In any index system, we select a base period and compare the changes in price levels from the base period Typically, indexing is done in such a way that, Price Index for the Base Period= 100 Hossain: MSMC 17 Computation of CPI Lets assume that Base period is 1985. So, CPI1985 = 100 Now, if I tell you that CPI2000 = 150 What can we say about price level in 2000? Clearly, price level has increased from 1985 Therefore, economy observed inflation By how much? It is 50% compared to the base year This is the advantage of indexing to 100 Hossain: MSMC 18 Another Example Lets assume again, CPI1985 = 100 Now, if I tell you that CPI2005 = 160 What can we say about price level in 2005? Again, price level has increased from 1985 Therefore, economy observed inflation By how much? It is 60% compared to the base year Can we say anything about inflation compared to 2000 (CPI2000=150)? Hossain: MSMC 19 Another Example To compute inflation compared to non-base years, we need some simple computations Note we have, CPI1985 = 100 CPI2000 = 150 CPI2005 = 160 We like to know how price level had changed form 2000 to 2005 Again looks like its an inflation. But how much? We want to know, 150 to 160 is an increase of how many percentage points? Hossain: MSMC 20 Percentage Computation All percentage computations, use the same formula: NEW OLD X 100 OLD So, computing percentage change in CPI from 2000 (150) to 2005 (165) 160 – 150 X 100 = 6.67% 150 Hossain: MSMC 21 In class Exercise Assume, CPI1985 = 100 CPI1975 = 88 CPI2002 = 138 Compute the inflation rate in 1975 compared to the base year Compute the inflation rate in 2002 compared to the base year Compute the inflation rate in 2002 compared to 1975 Note inflation rate means percentage change in CPI Hossain: MSMC 22 Construction of CPI BLS surveys, computes and publishes CPI Price Data Goods and Services Market Basket 2000 Price 1985 Price Apple 10 pounds $4.00 $2.00 Banana 15 pounds $1.00 $0.50 $3.00 $0.25 Cat food 2 bags To compute CPI, we first compute the Cost of basket (COB) Here, COB2000 =10x4 + 15x1 + 2x3 = 61 Hossain: MSMC 23 Construction of CPI Price Data Goods and Services Market Basket 2000 Price 1985 Price Apple 10 pounds $4.00 $2.00 Banana 15 pounds $1.00 $0.50 $3.00 $0.25 Cat food 2 bags Here, COB2000 =10x4 + 15x1 + 2x3 = 61 Here, COB1985 =10x2 + 15x.50 + 2x.25 = 28 Hossain: MSMC 24 Formula for CPI Use COB numbers to the formula for CPI CPI xxxx = COBxxxx X 100 COBBaseYear Using this formula compute CPI of 1985 (the base year) CPI of 2000 Hossain: MSMC 25