Macroeconomics 6
... theoretical, empirical, and historical perspectives. The issues of policy are highly controversial, and most of the material will be based on recent research, which is far from being the last word in the field. Hence, a great deal of creativity and open mindedness on the part of the course participa ...
... theoretical, empirical, and historical perspectives. The issues of policy are highly controversial, and most of the material will be based on recent research, which is far from being the last word in the field. Hence, a great deal of creativity and open mindedness on the part of the course participa ...
the role of monetary policy
... Despite the many challenges that we face as Europeans, we should never forget the significant achievements of European integration in providing peace, security and prosperity. The fact that the Treaty that gave birth to the euro was signed in this country symbolises the enduring role of the Netherla ...
... Despite the many challenges that we face as Europeans, we should never forget the significant achievements of European integration in providing peace, security and prosperity. The fact that the Treaty that gave birth to the euro was signed in this country symbolises the enduring role of the Netherla ...
State Bank of Pakistan’s Monetary Policy Statement June 2013 – SUMMARY
... business friendly and therefore reduction in the discount rate will foster the business growth and will have a positive impact on the country economy as it will support private business. Previous government raised the domestic borrowing to more than 60% of the GDP thereby showing that they were not ...
... business friendly and therefore reduction in the discount rate will foster the business growth and will have a positive impact on the country economy as it will support private business. Previous government raised the domestic borrowing to more than 60% of the GDP thereby showing that they were not ...
9708 ECONOMICS
... A maximum/minimum price intends to keep prices below/above the market level. The former would benefit consumers, the latter producers. Maximum prices will be ignored and ineffective if set above the market price and minimum will not work if below the market price. A maximum price will benefit those ...
... A maximum/minimum price intends to keep prices below/above the market level. The former would benefit consumers, the latter producers. Maximum prices will be ignored and ineffective if set above the market price and minimum will not work if below the market price. A maximum price will benefit those ...
3. Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand. Internal Balance
... 2. long-term wage and price contracts 3. and prices are sticky because of menu costs, money illusion, imperfect information and implicit price contracts. Menu costs: Firms change prices when the benefit of changing a price becomes larger than the menu cost of changing a price. Price changes may be b ...
... 2. long-term wage and price contracts 3. and prices are sticky because of menu costs, money illusion, imperfect information and implicit price contracts. Menu costs: Firms change prices when the benefit of changing a price becomes larger than the menu cost of changing a price. Price changes may be b ...
Money Supply and Demand - personal.kent.edu
... Then the demand for George’s picture will have doubled as well. This is the quantity theory of money. In its crudest form, it states that the price level changes in direct proportion to the supply of nominal money balances. Thus, if we were to burn a dollar bill and reduce the nominal money stock by ...
... Then the demand for George’s picture will have doubled as well. This is the quantity theory of money. In its crudest form, it states that the price level changes in direct proportion to the supply of nominal money balances. Thus, if we were to burn a dollar bill and reduce the nominal money stock by ...
fixed exchange rates
... Increased transparency: With 11 national markets and 11 different currencies, customers (firms or consumers) had imperfect information about prices across the whole area. A single currency makes it easier for customers to compare prices between different countries and buy from the cheapest source. ...
... Increased transparency: With 11 national markets and 11 different currencies, customers (firms or consumers) had imperfect information about prices across the whole area. A single currency makes it easier for customers to compare prices between different countries and buy from the cheapest source. ...
A Bit Longer Principles Review
... • “Natural” or normal rate of unemployment (NAIRU) Seasonal Unemployment Frictional Unemployment: searching for jobs Structural Unemployment: Imperfect match between employee skills and requirements of available jobs. • Cyclical Unemployment : Results from business cycle ...
... • “Natural” or normal rate of unemployment (NAIRU) Seasonal Unemployment Frictional Unemployment: searching for jobs Structural Unemployment: Imperfect match between employee skills and requirements of available jobs. • Cyclical Unemployment : Results from business cycle ...
short and long run Phillips curve
... Assume an economy in equilibrium at Y0 in diagram I (figure 54.6) where the natural rate of unemployment is U0 and yearly inflation is i0, diagram II. Aggregate demand increases from AD0 to AD1, and the economy moves from Y0 to Y1. In moving from Y0 to Y1, inflation is actually eroding real wages, s ...
... Assume an economy in equilibrium at Y0 in diagram I (figure 54.6) where the natural rate of unemployment is U0 and yearly inflation is i0, diagram II. Aggregate demand increases from AD0 to AD1, and the economy moves from Y0 to Y1. In moving from Y0 to Y1, inflation is actually eroding real wages, s ...
The Causes of Inflation and Deflation in Mainland China
... a linear combination of the world price level and unit labour cost, pursuant to the results of the co-integration analysis. The restriction c4 = 1-c3 is imposed to ensure dynamic homogeneity. To account for the endogeneity of future inflation, GMM is used to estimate the parameters. The point estima ...
... a linear combination of the world price level and unit labour cost, pursuant to the results of the co-integration analysis. The restriction c4 = 1-c3 is imposed to ensure dynamic homogeneity. To account for the endogeneity of future inflation, GMM is used to estimate the parameters. The point estima ...
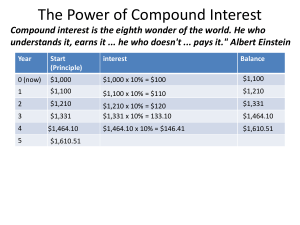
The Power of Compound Interest
... like inflation or interest: •If inflation rates go from 2% to 3%, your money will lose half its value in 24 years instead of 36. •If college tuition increases at 5% per year (which is faster than inflation), tuition costs will double in 72/5 or about 14.4 years. If you pay 15% interest on your credi ...
... like inflation or interest: •If inflation rates go from 2% to 3%, your money will lose half its value in 24 years instead of 36. •If college tuition increases at 5% per year (which is faster than inflation), tuition costs will double in 72/5 or about 14.4 years. If you pay 15% interest on your credi ...
ROMANIA – EUROPEAN UNION’S MEMBER MACROECONOMIC TENDENCIES AND PROGNOSIS
... the theory of GDP increasing of 6% for the year 2007. Tendencies of relaxing the monetary policy Disinflation process continued successfully in the first three months of the year 2007. Inflation rate recorded the level 3.66% in March, the disinflation tendency for the last months remaining so unmodi ...
... the theory of GDP increasing of 6% for the year 2007. Tendencies of relaxing the monetary policy Disinflation process continued successfully in the first three months of the year 2007. Inflation rate recorded the level 3.66% in March, the disinflation tendency for the last months remaining so unmodi ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... external debt in the course of sustaining failing financial institutions. In 1980 about half of the external debt was owed by the public sector; by 1985 that share had increased to 82 percent. 1.1.2 From Martinez de Hoz to Alfonsin (3/1981- 12/1983) The end to the military government did not come ea ...
... external debt in the course of sustaining failing financial institutions. In 1980 about half of the external debt was owed by the public sector; by 1985 that share had increased to 82 percent. 1.1.2 From Martinez de Hoz to Alfonsin (3/1981- 12/1983) The end to the military government did not come ea ...
Word Document
... Keynes: interest rates should be in a narrow band: when interest high, people expect it to fall. Keynes: If interest rates rise, then the price of a bond falls. So if ie↑, expect a capital loss from bonds. Baumol & Tobin showed transactions and precautionary demand are also sensitive to the in ...
... Keynes: interest rates should be in a narrow band: when interest high, people expect it to fall. Keynes: If interest rates rise, then the price of a bond falls. So if ie↑, expect a capital loss from bonds. Baumol & Tobin showed transactions and precautionary demand are also sensitive to the in ...
HOW THE FED CROWDED OUT REAGAN’S ECONOMIC POLICY Paul Craig Roberts
... can shift portions of your income from 1981 to 1982. Start arranging to do so now, and you will be able to cut your federal income taxes substantially.” On October 26, 1981 Business Week wrote about the “flood ofadvice on postponing income and accelerating deductions.” How were economists (and some ...
... can shift portions of your income from 1981 to 1982. Start arranging to do so now, and you will be able to cut your federal income taxes substantially.” On October 26, 1981 Business Week wrote about the “flood ofadvice on postponing income and accelerating deductions.” How were economists (and some ...
Introduction to Macroeconomics
... Short Run • Monetarists make a seemingly innocuous assumption that velocity is stable in the short run, or ...
... Short Run • Monetarists make a seemingly innocuous assumption that velocity is stable in the short run, or ...
Chapter 9
... investor expectations about future inflation rates LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE THEORY: Investors are willing to accept lower interest rates on short-term debt securities which provide greater liquidity and less interest rate risk ...
... investor expectations about future inflation rates LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE THEORY: Investors are willing to accept lower interest rates on short-term debt securities which provide greater liquidity and less interest rate risk ...
2010_Macro_FRQ_ans
... (i) On your graph in part (a), show how the government action affects AD. (ii) How will this government action affect the unemployment rate in the short run? Explain. Answer: 1. (b) (i) As can be seen on the graph, the increase in G would increase AD to AD2, increasing PL and Y. 1. (b) (II) The incr ...
... (i) On your graph in part (a), show how the government action affects AD. (ii) How will this government action affect the unemployment rate in the short run? Explain. Answer: 1. (b) (i) As can be seen on the graph, the increase in G would increase AD to AD2, increasing PL and Y. 1. (b) (II) The incr ...
2010 FRQ
... (i) On your graph in part (a), show how the government action affects AD. (ii) How will this government action affect the unemployment rate in the short run? Explain. Answer: 1. (b) (i) As can be seen on the graph, the increase in G would increase AD to AD2, increasing PL and Y. 1. (b) (II) The incr ...
... (i) On your graph in part (a), show how the government action affects AD. (ii) How will this government action affect the unemployment rate in the short run? Explain. Answer: 1. (b) (i) As can be seen on the graph, the increase in G would increase AD to AD2, increasing PL and Y. 1. (b) (II) The incr ...
Inflation Costs
... When past inflation is high and volatile: Argentina, Colombia, Uruguay and Venezuela ...
... When past inflation is high and volatile: Argentina, Colombia, Uruguay and Venezuela ...
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. A chief measure of price inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index (normally the consumer price index) over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.Inflation affects an economy in various ways, both positive and negative. Negative effects of inflation include an increase in the opportunity cost of holding money, uncertainty over future inflation which may discourage investment and savings, and if inflation were rapid enough, shortages of goods as consumers begin hoarding out of concern that prices will increase in the future.Inflation also has positive effects: Fundamentally, inflation gives everyone an incentive to spend and invest, because if they don't, their money will be worth less in the future. This increase in spending and investment can benefit the economy. However it may also lead to sub-optimal use of resources. Inflation reduces the real burden of debt, both public and private. If you have a fixed-rate mortgage on your house, your salary is likely to increase over time due to wage inflation, but your mortgage payment will stay the same. Over time, your mortgage payment will become a smaller percentage of your earnings, which means that you will have more money to spend. Inflation keeps nominal interest rates above zero, so that central banks can reduce interest rates, when necessary, to stimulate the economy. Inflation reduces unemployment to the extent that unemployment is caused by nominal wage rigidity. When demand for labor falls but nominal wages do not, as typically occurs during a recession, the supply and demand for labor cannot reach equilibrium, and unemployment results. By reducing the real value of a given nominal wage, inflation increases the demand for labor, and therefore reduces unemployment.Economists generally believe that high rates of inflation and hyperinflation are caused by an excessive growth of the money supply. However, money supply growth does not necessarily cause inflation. Some economists maintain that under the conditions of a liquidity trap, large monetary injections are like ""pushing on a string"". Views on which factors determine low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be attributed to fluctuations in real demand for goods and services, or changes in available supplies such as during scarcities. However, the consensus view is that a long sustained period of inflation is caused by money supply growing faster than the rate of economic growth.Today, most economists favor a low and steady rate of inflation. Low (as opposed to zero or negative) inflation reduces the severity of economic recessions by enabling the labor market to adjust more quickly in a downturn, and reduces the risk that a liquidity trap prevents monetary policy from stabilizing the economy. The task of keeping the rate of inflation low and stable is usually given to monetary authorities. Generally, these monetary authorities are the central banks that control monetary policy through the setting of interest rates, through open market operations, and through the setting of banking reserve requirements.