* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4: Measuring economic performance
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
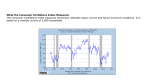
Unit 4: Measuring economic performance What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics is the study of the large economy as a whole. It is the study of the big picture. • • Instead of analyzing one consumer, we analyze everyone. Instead of one business we study all businesses. Why study the whole economy? • Macro was created to: 1. Measure the health of the whole economy. 2. Guide government policies to fix problems. 2 For all countries there are three major economic goals: 1. Promote Economic Growth 2. Keep Prices Stable (Limit Inflation) 3. Limit unemployment In this unit we will analyze how each of these are measured. 3 Stats used to measure economic performance: • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Gross domestic product productivity inflation unemployment Gross Domestic Product Most important stat used to measure 5 ECONOMC GROWTH!!! GDP • GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUT (GDP) = dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders in one year. World GDP Distribution 2010 Nominal GDP 7 GDP expenditure approach • Adds up the value of spending in an economy in one year *1. Consumer Spending/consumption (C) Goods and services purchased by consumers (durable and nondurable goods) *largest category of GDP 2. Investment (I) spending • When businesses put money back into their own business Includes spending on: Capital resources Construction Inventory Capital resources Equipment, machinery, factories etc Construction Inventory • Unsold merchandise 3. Government Spending (G) Any good or service the government purchases (military, education, roads etc) Infrastructure: roads bridges 4. Net Exports (Xn) spending Spending on TOTAL exports Exports vs. Imports • Exports items made in the US and sold to another country • Imports items made in another country and sold to the US Imports are counted in The GDP, but NEGATIVELY!! Formula for GDP (expenditure approach) GDP = C + I + G + XN For each situation, identify if it is included in GDP the identify the category C, I, G, or Xn 1 You spend $10.00 for movie tickets 2 The Government spends $5M Increase in defense spedning 3 Ford builds a new $2M factory 4 You buy $20,000 Toyota that was produced in Japan 5 A Canadian purchases a U.S. produced car 6 You spend $10,000 Tuition to attend college 18 7 A Farmer purchases new $100K tractor Things excluded in expenditure approach: 1. intermediate goods Item that goes into making a final product 2. Transfer payments • Money is transferred from person or government to another person • example: social security, welfare, tax refund etc. 3. donations and gifts 4. Financial transactions Include things like: Buying and selling of stock One business buying another 5. used items 6. illegal sales *Anything in which a record is not kept is NOT counted in the GDP Example: A man builds a deck on his own house; he does not pay himself to do this You baby sit your neighbor and are paid“under the table” Counted or Not Counted in the GDP???? 1. Sam buys an outfit from Plato’s closet, a resale clothing store 2. Sue buys a new outfit from Macy’s 3. Bill gets new brakes installed on his car 4. Ford purchases steel from Germany to build a car 5. France buys computers from the United States 6. Michael buys stock in Disney Shortcomings of GDP 1. Non-market (production occurs but no $ is exchanged) transactions not counted 2. Does not look at quality 3. Tells nothing about who gets goods 4. Does not account for population Per Capita GDP • Looks at the GDP per person total GDP/population ** Better indication of a country’s standard of living!!! World GDP Distribution 2010 Nominal GDP 30 Topic 2: Interpreting GDP Statistics GDP measures growth or lack of growth of an economy Business Cycle Calculating GDP over several years results in a Business Cycle = ups and downs of the economy THE BUSINESS CYCLE The national economy fluctuates resulting in periods of boom and bust. Recession: decline in GDP for 6 months or more 34 Blue line NOT trend line; Above 0% = growth Under 0% = decline U.S. Business Cycle 36 Predicting Business Cycles • Economists use Index of Leading Economic Indicators (ILEI) to predict future of the economy ILEI includes stats such as: stock prices, unemployment claims building permits Pizza Making Factory Materials: 1 black marker, 1 red marker, scissors, sheets of paper, round template Procedures: 1. Trace the pizza template onto a piece of paper 2. Cut out the circle 3. Draw 5 colored in (size of a quarter)pepperoni pieces on the circle using the RED marker 4. Draw 5 colored in (size of a dime) black olives on the circle using the BLACK marker Circles must be traced and then CUT using scissors, no tearing!!!! Cut 1 pizza at a time! Pizza Making Factory 1. What happened to productivity (line 10) from round 1 to round 3? Why? 2. What happened to the quality of the pizzas from round 1 to 3? Why? 3. What effect did productivity have on the average cost of a pizza (line 8)? Why is this important??? Topic 3: Productivity Number of goods/ services that a worker can produce for each hour of work Productivity and economic growth Things that increase a country’s productivity: 1. Improvement in capital resources 2. Improvement in labor resources more training/education Specialization incentives 3. better technology Topic 4: Inflation Increase in the economy’s overall price level (does not mean all prices are rising, prices rise unevenly) What is Inflation? Inflation reduces the “purchasing power” of money •When inflation occurs, each dollar of income will buy fewer goods than before. Degrees of Inflation: 1. Creeping inflation Prices grow up to 4% a year Prices “creep” up 2. Galloping Price level DOUBLES in a year 3. Hyperinflation Prices increase 500% a year or more “Ducktales – inflation” Inflation types: consider a Polar Pop ($.74) Next year’s price Creeping inflation $.76 (3%) Galloping inflation $1.48 (double) Hyperinflation $3.70 (500%) Measuring Inflation 1. Consumer Price Index (CPI) Index used to measure INFLATION CPI looks at a consumer market basket of goods such as food, clothing, transportation, entertainment & medical care CPI formula CPI = Current price/base price X 100 CPI example Year Price of bread 2000 $1.19 2002 $1.32 2006 $1.49 CPI - using 2000 as base Year Price of bread CPI - using 2000 as base 2000 $1.19 1.19/1.19 X 100 = 100 2002 $1.32 1.32/1.19 X 100 = 110.9 2006 $1.49 1.49/1.19 X 100 = 125.2 CPI info. • To find % rate of change in inflation, take the CPI and subtract 100 from it • Base year will always have a CPI of 100 Adjusting numbers for inflation • To be able to compare the value of items or statistics, they must be adjusted for inflation – WHY?? Prices increases over the years; a 2012 statistic would always be more than a 2011, 2005 1990 etc. statistic because prices have increased during that time period Example of adjusting for inflation (highest grossing movies in U.S. history) How can you figure out which is the most popular movie of all time? What is the problem with this method? Nominal Box Office Receipts 63 How can you figure out which is the most popular movie of all time? Real Box Office Receipts (adjusted for inflation) Did the economy below actually grow??? If apples are the only thing being produced Year 1: 10 apples at $1 each; GDP = $10 Year 2: 10 apples x $2.00; GDP = $20 65 • Real GDP - GDP adjusted for price increases • best indicator of economic growth, uses a BASE year to make comparisons • More accurate statistic when trying to determine growth of an economy • GDP deflator removes the effects of inflation from the GDP REAL GDP = Nominial GDP GDP deflator X 100 Did this economy really grow? Year GDP GDP deflator Real GDP 1 $450 100 450/100 X 100 = 2 $452 106 452/106 X 100 = Example of Real GDP Year GDP GDP Real deflator GDP 1 $450 100 $450 2 $452 106 $426 Once real GDP is calculated it shows the economy did not really grow from year 1 Rule of 70 Can find the # of years it will take for prices to double Take % increase in prices and divide into 70 How long will it take for prices to double if prices increase by 3% a year: 70/3 = 23 years Does GDP accurately measure standard of living? Real GDP per capita is the best measure of a nation’s standard of living. Real GDP per capita is real GDP divided by the total population. 73 4. Real Income Income adjusted for inflation; DETERMINES PURCHASING POWER Purchasing Power = how much stuff $ will buy Cost of Living in U.S. Highest cost of living New York, NY Honolulu, Hawaii San Francisco, CA San Jose, CA Stamford, Conn. Washington DC Fairbanks, AL Boston, Mass San Diego, CA LA, CA Lowest cost of living Brownsville, TX Pueblo, Co Ft. Hood, TX Fort Smith, Ark Sherman, TX Springfield, Ill Waco, TX Fayetteville, Ark Austin, TX Springfield, MO Formula for Real income Real income = nominal income/ CPI X 100 * Shows purchasing power Example of real income Year Income CPI Real income 1 $30,000 100 30,000/100 x 100 = ?? 2 $30,900 105 (3%raise) 30,900/105 X 100 = ??? Example of real income Year Income CPI 1 $30,000 100 2 $30,900 105 (3%raise) Real income $30,000 $29,428.57 Person made more $ But ….. purchasing power actually went down Reasons for Inflation 1. Cost push inflation IT COST COMPANIES MORE TO PRODUCE - They PUSH this price increase on to consumers Example: the price of beef goes up, so McDonalds raises the price of their hamburgers 2. Demand Pull inflation Caused by demand exceeding supply or a rapid increase in the money supply spending PULLS price level up Zimbabwe 2008 Inflation rate 79,600,000,000% Amount of time for price to double: 24.7 hours Inflation practice Item Year 1 Year 2 Food $5000 $5400 Clothing $2250 $2700 Gas $3200 $3000 CPI = Current price/ Base price X 100 What is the CPI for food in year 2 using year 1 as a base? What is the CPI for gas in year 2 using year 1 as a base? • Food CPI = 108 • Gas CPI = 93.8 Did the economy in the chart below grow from year 1 to year 2? Why or why not? Year Nominal GDP GDP deflator 1 $5,000 100 2 $6,600 125 Find REAL GDP for each year and compare Real GDP = actual GDP/GDP deflator X 100 • Real GDP year 1 = $5,000 • Real GDP year 2 = $5,280 – YES economy did grow In which of the cities below will you earn the MOST REAL income? Real income = Actual income/ CPI X 100 City Income CPI Cleveland $30,000 101 Atlanta $30,000 103 Chicago $30,000 110 • You receive a 2% raise at your job. Inflation increases by 3%. Does your purchasing power increase, decrease or stay the same? _______________________ • You receive a 4% raise at your job. Inflation increases by 2%. Does your purchasing power increase, decrease or stay the same? _______________________ write CP is the statement refers to cost push inflation and DP if the statement refers to DP inflation. ____The price of sugar increases. As a result, bakeries charge more for a cake. ____ Americans have more money. As a result their demand for items is higher which causes prices to go up ____ The auto workers union is successful in negotiating pay raises – as a result, the price of cars go up Effects of Inflation • Anticipated inflation • inflation that is expected • Able to plan for • Unanticipated Inflation • Inflation whose full extent was not expected; not planned for 1. Fixed Income Groups - elderly living on fixed retirement funds - landlords receiving fixed payments - minimum wage workers * are hurt by inflation because the amount of $ being received is FIXED for a number of years. Prices go up, but income stays the same = decrease in purchasing power 2. Savers • *depends on interest rate given and what happens to price level. • For example: if you earn 1% interest on a savings account but inflation goes up 1.5%, your $ will buy less; If you earn more interest than the inflation rate purchasing power will go up 3. Lenders • * depends on interest rate charged and what happens to price level. • For example: if a bank charges a 6% interest rate and inflation goes up 7%, the $, once it is paid back will be worth less than when it was borrowed 4. Borrowers * Depends on interest rate charged and what happens to price level. Helped or hurt by inflation?? • 1. A man lends $100 to his friend in 2010. The friend pays him back today. • 2. A tenant signs a one year lease to rent an apartment for $800 a month? • 3. An elderly couple lives off fixed retirements payments $2,000 a month • 4. A woman who is saving money in a savings account earning 1% a year. Inflation is going up by 3% a year. Topic 5: Unemployment The % of people who are not working, but actively seeking employment Unemployment rates Highest rates: Lowest rates: Yuma, AR 27.5% Bismark, ND 2.6% El Centro, CA 26.6% Fargo, ND 3% Yuba City CA 15.8% Lincoln, Neb 3% Merced, CA 15.7% Midland, TX 3% Ocean City, NJ 14.5% Ames, Iowa 3.1% Lafayette, LA 3.1% Modesto, CA 14.5% Types of Unemployment 99 1. Frictional Unemployment “Temporarily unemployed” Skills are present • Results from “normal” changes in the labor market Reasons for frictional unemployment •Graduating from school •In between jobs •Re-enter workforce 100 2. Seasonal Unemployment •Due to time of year and the nature of the job. •These jobs will come back Examples: Life Guards 101 3. Structural Unemployment •Changes in the organization of the labor force or the structure of a company •Workers DO NOT have skills needed and these jobs will not come back OR skill of worker is obsolete •Workers must learn new skills to get a job. Examples: •VCR repairmen •Carriage makers 102 Reasons why structural unemployment occurs: Change in technology Company relocates Merger takes place 103 4 Cyclical Unemployment •Unemployment that results from a RECESSION - the company doesn’t have $ to keep the worker Examples: •Steel workers laid off during recessions. •workers laid off due to people not spending $ 104 Practice 1. Joe just graduated from school and is looking for his first management job 2. Sally lost her job at Sears due to declining sales 3. Tim was replaced by a robot on the assembly line 4. Kim just graduated from school and cannot find a job in her field so she is working as a waitress 5. Jim lost his job when his company consolidated and moved to another state Video clip • “unemployment benefits - the 99ers” The Natural Rate of Unemployment •This is the normal amount of unemployment that we SHOULD have. 108 Full employment means NO Cyclical unemployment! Unemployment rate of around 4-6% = FULL EMPLOYMENT 109 Criticisms of the Unemployment Rate What is wrong with the unemployment rate? It can misdiagnose the actual unemployment rate because of the following: Discouraged workers- • Some people are no longer looking for a job because they have given up. Part-Time Workers- • Someone who wants more shifts but can’t get them is still considered employed. 110 Cost of Unemployment GDP GAP - potential production is lost Okun’s Law • For every 1% point by which the actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural rate, a GDP gap of about 2% occurs • Example: The unemployment rate is 8% (2% over acceptable) GDP gap 2 X 2 = 4 Tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. In general, there is an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation 114 • When UNEMPLOYMENT is low (more $ circulating in the economy) the value of the dollar goes down INFLATION is higher • When UNEMPLOYMENT is high (less $ circulating in economy) INFALTION is lower