Natural disasters
... TSUNAMI IS A WAVE TRAIN GENERATED IN THE WATER BODY BY SOME DISTURBANCES THAT CAUSES WATER TO GET DISPLACED ...
... TSUNAMI IS A WAVE TRAIN GENERATED IN THE WATER BODY BY SOME DISTURBANCES THAT CAUSES WATER TO GET DISPLACED ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity - sir
... spreading centers the greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system mechanism of spreading lithosphere pulls apart ...
... spreading centers the greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system mechanism of spreading lithosphere pulls apart ...
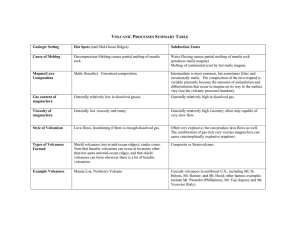
Volcanic Eruptions - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is
... - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is forced to the Earth’s surface - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano ...
... - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is forced to the Earth’s surface - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano ...
Volcanoes/REVIEW
... watch the powerpoints you have been working on. Notebooks will also be due on Friday, April 24 (there will be no portfolio page for this unit. PART A – Review pages 204-229 in your textbook and use your notebook 1. What is a volcano? __________________________________________________________________ ...
... watch the powerpoints you have been working on. Notebooks will also be due on Friday, April 24 (there will be no portfolio page for this unit. PART A – Review pages 204-229 in your textbook and use your notebook 1. What is a volcano? __________________________________________________________________ ...
the free PDF resource
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
Types of Volcanoes
... tall in just a few days. This volcano continued to erupt for 9 years and grew to be over 1,300 feet tall. ...
... tall in just a few days. This volcano continued to erupt for 9 years and grew to be over 1,300 feet tall. ...
5volcano notes chapter
... Composite volcano-tall cone shaped with layers of lava then layers of ash. Cinder cone volcano-high silica, explosive, steep cone shaped hill Lava plateau-lava runs out of several small cracks, flows and forms a high area. 2. Landforms created by magma include: Volcanic neck-magma hardens in volcano ...
... Composite volcano-tall cone shaped with layers of lava then layers of ash. Cinder cone volcano-high silica, explosive, steep cone shaped hill Lava plateau-lava runs out of several small cracks, flows and forms a high area. 2. Landforms created by magma include: Volcanic neck-magma hardens in volcano ...
VOLCANOES STUDY GUIDE Test 1/14/15 Key Words • Volcano
... Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava Need to know Most of Earth’s volcanoes are loca ...
... Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava Need to know Most of Earth’s volcanoes are loca ...
Chapter 6 study guide
... 9. If lava hardens quickly on the surface, what kind of texture will the igneous rock have? 10. If magma begins to harden slowly underground, then is forced up to the surface and continues to harden quickly, what kind of texture will the rock have? 11. Give an example of an igneous rock with fine te ...
... 9. If lava hardens quickly on the surface, what kind of texture will the igneous rock have? 10. If magma begins to harden slowly underground, then is forced up to the surface and continues to harden quickly, what kind of texture will the rock have? 11. Give an example of an igneous rock with fine te ...
Document
... 2. Magma temperature = hotter flows easier 3. Magma viscosity – determined by temp and ...
... 2. Magma temperature = hotter flows easier 3. Magma viscosity – determined by temp and ...
Inside Earth 3-2 Worksheets 2013
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
The Cascade Volcanoes - West Virginia University
... Subalkaline Flat trend on AFM diagram (no Fe-enrichment) Strongly plagioclase porphyritic Andesite-dominated strato-volcanoes Wider variety of rock types (basalt-andesite-dacite-rhyolite suite) than in tholeiitic suites ...
... Subalkaline Flat trend on AFM diagram (no Fe-enrichment) Strongly plagioclase porphyritic Andesite-dominated strato-volcanoes Wider variety of rock types (basalt-andesite-dacite-rhyolite suite) than in tholeiitic suites ...
Volcanoes SHOW
... the top of a volcano; formed by the explosion of the upper portion of the cone ...
... the top of a volcano; formed by the explosion of the upper portion of the cone ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
plosky tolbachik volcano in kamchatka erupts after 40 years
... expected to continue for some time, has not yet forced any changes in the airline flight patterns over this part of Russia. ...
... expected to continue for some time, has not yet forced any changes in the airline flight patterns over this part of Russia. ...
Document
... _____ 10. A wide, flat landform resulting from repeated nonexplosive eruptions of lava that spread over a large area is called a a. crater. b. caldera. c. lava plateau. d. rift. ...
... _____ 10. A wide, flat landform resulting from repeated nonexplosive eruptions of lava that spread over a large area is called a a. crater. b. caldera. c. lava plateau. d. rift. ...
chapter 9 vocabulary terms
... Mantle Plume (p. 279) – A mass of hotter than normal mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity. These plumes of solid yet mobile material may originate as deep as the core-mantle boundary. ...
... Mantle Plume (p. 279) – A mass of hotter than normal mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity. These plumes of solid yet mobile material may originate as deep as the core-mantle boundary. ...
Ch 8 Volcanoes Test – Study Guide
... 5. How do temperature, pressure, and fluid content affect the formation of magma? ...
... 5. How do temperature, pressure, and fluid content affect the formation of magma? ...
Volcanic and Plutonic
... Laccolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, exerting pressure upwards so as to cause a bulge. Lopolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, trapped from above by harder more resistant layer. The body then exerts a downward force resulting in a depre ...
... Laccolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, exerting pressure upwards so as to cause a bulge. Lopolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, trapped from above by harder more resistant layer. The body then exerts a downward force resulting in a depre ...
Llullaillaco

Llullaillaco is a potentially active stratovolcano at the border of Argentina (Salta Province) and Chile. It lies in the Puna de Atacama, a region of very high volcanic peaks on a high plateau within the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places in the world. It is the fourth highest volcano in the world, and it is also the seventh highest mountain of the Andes.Llullaillaco follows the typical Puna de Atacama volcano pattern: it is surrounded by large debris fields and is perpetually capped by small snow patches, though there are no true glaciers due to the extreme aridity. The snow line in this region is the highest in the world, at around 6,500 metres (21,300 ft), which is around 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) higher than in the Himalayas and 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) higher than in the Andes of Colombia and Ecuador.The peak's name comes from the Aymara for ""murky water"": llulla= dirty and yacu= water. Other sources propose it to have originated from Quechua Lullac= lie, Yacu= water: ""lying (or treacherous) water"".It has been confirmed that Incas climbed Llullaillaco in the pre-Columbian period. Artifacts on the summit constitute the highest evidence of human presence worldwide before the late nineteenth century. Also, the huáqueros may have also reached its summit and those of other mountains in the region during their searches. The first recorded ascent was on December 1, 1952, by Bión González and Juan Harseim.