Cornell Notes Template
... All lava is not the same; the viscosity of lava varies Viscosity- the inability for a liquid to flow ↑ viscosity=↓ ability to flow/move Lava that has more silica is more viscous, lava that has less silica is less viscous The ingredients (composition) of the lava determines if a volcano will have a v ...
... All lava is not the same; the viscosity of lava varies Viscosity- the inability for a liquid to flow ↑ viscosity=↓ ability to flow/move Lava that has more silica is more viscous, lava that has less silica is less viscous The ingredients (composition) of the lava determines if a volcano will have a v ...
Classifying Volcanoes
... a. Plate tectonics; colliding plates produce excess magma which rises to the surface, after coming to the surface it cools and hardens forming the sides of the volcano 2. Parts of a volcano (draw diagram into notebooks) a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being rel ...
... a. Plate tectonics; colliding plates produce excess magma which rises to the surface, after coming to the surface it cools and hardens forming the sides of the volcano 2. Parts of a volcano (draw diagram into notebooks) a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being rel ...
Volcanoes
... moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface 3. Vent – the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano 4. Lava flow – the area cover by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent 5. Crater – a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening ...
... moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface 3. Vent – the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano 4. Lava flow – the area cover by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent 5. Crater – a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
What is like living near a volcano?
... • People live close to volcanoes because they felt that the advantages outweighed the disadvantages. • Most volcanoes are perfectly safe for long periods in between eruptions • Today, about 500 million people live on or close to volcanoes. • We even have major cities close to active volcanoes. Popo ...
... • People live close to volcanoes because they felt that the advantages outweighed the disadvantages. • Most volcanoes are perfectly safe for long periods in between eruptions • Today, about 500 million people live on or close to volcanoes. • We even have major cities close to active volcanoes. Popo ...
Volcanoes - BrainPOP
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
Chapter 9 - Volcanoes
... • Caldera – A large depression formed after the eruption and much larger than the crater. A crater with collapsed walls. • Lava Plateaus – Formed by repeated eruptions with massive outpourings of lava spreading out over a large area. These are usually formed by rift zones (huge cracks in the surface ...
... • Caldera – A large depression formed after the eruption and much larger than the crater. A crater with collapsed walls. • Lava Plateaus – Formed by repeated eruptions with massive outpourings of lava spreading out over a large area. These are usually formed by rift zones (huge cracks in the surface ...
2. Volcanoes
... steep-sided; alternating layers of pyroclastics and lava from ash falls and lava flows Where do they occur? At subduction zones examples: Mt. Pinatubo, Philippines; Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Rainier, Mt. Fuji, Mt. Hood explosive eruption due to type of magma: higher viscosity, 700 C; contains gases; from ...
... steep-sided; alternating layers of pyroclastics and lava from ash falls and lava flows Where do they occur? At subduction zones examples: Mt. Pinatubo, Philippines; Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Rainier, Mt. Fuji, Mt. Hood explosive eruption due to type of magma: higher viscosity, 700 C; contains gases; from ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropped from the air. Volcanic Dust – Is fragments of rock that are blown into the air during a volcanic eruption. (very small particles) ...
... Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropped from the air. Volcanic Dust – Is fragments of rock that are blown into the air during a volcanic eruption. (very small particles) ...
File
... F.3.4.1. List the landforms that lava and ash create. F.3.4.2. Explain how magma that hardens beneath Earth’s surface creates landforms. F.3.4.3. Analyze other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
... F.3.4.1. List the landforms that lava and ash create. F.3.4.2. Explain how magma that hardens beneath Earth’s surface creates landforms. F.3.4.3. Analyze other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
Ch. 4 Volcanism and Extrusive Ignous Rocks
... water vapor • Biosphere both positively and negatively influenced by volcanism – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – Violent eruptions can destroy nearly all life in their paths – Large amounts of ash and volcanic gases in atmosphere can trigger rapid climate changes and contribute ...
... water vapor • Biosphere both positively and negatively influenced by volcanism – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – Violent eruptions can destroy nearly all life in their paths – Large amounts of ash and volcanic gases in atmosphere can trigger rapid climate changes and contribute ...
Volcanoes
... 2) What is the difference between magma and lava? 3) Why are so many volcanoes found on the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean? 4) What do you know about Magma? 5) List magma types in order of increasing viscosity (least viscous first). 6) Which magma types will flow the fastest? 7) Which type of mag ...
... 2) What is the difference between magma and lava? 3) Why are so many volcanoes found on the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean? 4) What do you know about Magma? 5) List magma types in order of increasing viscosity (least viscous first). 6) Which magma types will flow the fastest? 7) Which type of mag ...
File
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
Earth Science - Mr.E Science
... Largest volcanoes in the world An example: Hawaiian Islands Gentle slopes & domed shaped ...
... Largest volcanoes in the world An example: Hawaiian Islands Gentle slopes & domed shaped ...
Volcanoes - Tanque Verde Unified School District
... Where is the nearest volcano to Tucson located? ___________________________________ 2. Features of a volcano include: ________________ – melted rock/molten material ______________________________________________. ___________ – Opening in Earth’s surface where ________________________________________ ...
... Where is the nearest volcano to Tucson located? ___________________________________ 2. Features of a volcano include: ________________ – melted rock/molten material ______________________________________________. ___________ – Opening in Earth’s surface where ________________________________________ ...
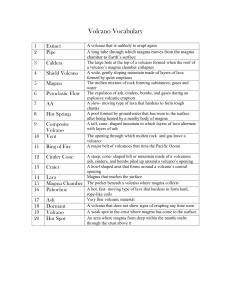
Volcano Vocabulary
... A major belt of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean A steep, cone- shaped hill or mountain made of a volcanoes ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening A bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening Magma that reaches the surface The pocket beneath a volcano wh ...
... A major belt of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean A steep, cone- shaped hill or mountain made of a volcanoes ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening A bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening Magma that reaches the surface The pocket beneath a volcano wh ...
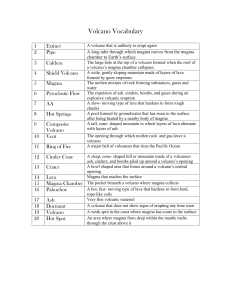
Volcano Vocabulary
... A major belt of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean A steep, cone- shaped hill or mountain made of a volcanoes ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening A bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening Magma that reaches the surface The pocket beneath a volcano wh ...
... A major belt of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean A steep, cone- shaped hill or mountain made of a volcanoes ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening A bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening Magma that reaches the surface The pocket beneath a volcano wh ...
Volcanoes: The Fire Within
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava (molten rock on the surface) and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kila ...
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava (molten rock on the surface) and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kila ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volcanic debris mixed with water/melting ice or snow Pyroclastic Fall Deposits – material falls from vertical eruption, well sorted, bla ...
... Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volcanic debris mixed with water/melting ice or snow Pyroclastic Fall Deposits – material falls from vertical eruption, well sorted, bla ...
Chapter 12
... That makes it 3 times the height of Mt. Everest. Unlike Everest, Olympus Mons has a very gentle slope. It is up to 550 km at its base. ...
... That makes it 3 times the height of Mt. Everest. Unlike Everest, Olympus Mons has a very gentle slope. It is up to 550 km at its base. ...
why live enar a volcano-1
... • People live close to volcanoes because they felt that the advantages outweighed the disadvantages. • Most volcanoes are perfectly safe for long periods in between eruptions • Today, about 500 million people live on or close to volcanoes. • We even have major cities close to active volcanoes. Popo ...
... • People live close to volcanoes because they felt that the advantages outweighed the disadvantages. • Most volcanoes are perfectly safe for long periods in between eruptions • Today, about 500 million people live on or close to volcanoes. • We even have major cities close to active volcanoes. Popo ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... (also the largest volcano on earth) ...
... (also the largest volcano on earth) ...
Llullaillaco

Llullaillaco is a potentially active stratovolcano at the border of Argentina (Salta Province) and Chile. It lies in the Puna de Atacama, a region of very high volcanic peaks on a high plateau within the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places in the world. It is the fourth highest volcano in the world, and it is also the seventh highest mountain of the Andes.Llullaillaco follows the typical Puna de Atacama volcano pattern: it is surrounded by large debris fields and is perpetually capped by small snow patches, though there are no true glaciers due to the extreme aridity. The snow line in this region is the highest in the world, at around 6,500 metres (21,300 ft), which is around 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) higher than in the Himalayas and 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) higher than in the Andes of Colombia and Ecuador.The peak's name comes from the Aymara for ""murky water"": llulla= dirty and yacu= water. Other sources propose it to have originated from Quechua Lullac= lie, Yacu= water: ""lying (or treacherous) water"".It has been confirmed that Incas climbed Llullaillaco in the pre-Columbian period. Artifacts on the summit constitute the highest evidence of human presence worldwide before the late nineteenth century. Also, the huáqueros may have also reached its summit and those of other mountains in the region during their searches. The first recorded ascent was on December 1, 1952, by Bión González and Juan Harseim.