Volcano by jose angel garcia gomez and alejandro cuthy gomez
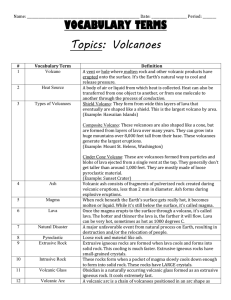
... Shield volcanoes • Quiet eruptions gradually build up gently sloping mountains ...
... Shield volcanoes • Quiet eruptions gradually build up gently sloping mountains ...
Three basic types of volcanoes
... the top of a volcano Vent—an opening at the surface of the Earth through which volcanic ...
... the top of a volcano Vent—an opening at the surface of the Earth through which volcanic ...
VOLCANO CHAPARRASTIQUE ERUPTS IN EL SALVADOR
... the San Miguel municipality about 140 km (87 miles) east of San Salvador, the capital, spewed ash over a wide area known for its coffee plantations. ...
... the San Miguel municipality about 140 km (87 miles) east of San Salvador, the capital, spewed ash over a wide area known for its coffee plantations. ...
Put your text here… - Social Circle City Schools
... earth’s surface was formed f. describe the effects of volcanic eruption on earth’s geological features ...
... earth’s surface was formed f. describe the effects of volcanic eruption on earth’s geological features ...
Volcanic hazards in Dante`s Peak
... Seismometer and seismogram Shallow earthquakes (<10-20 km) Precursor earthquakes "Harmonic tremors" — specific to magma moving around Composite volcano or stratovolcano Hot springs pH or acidity of water Volcanic gases (carbon dioxide [CO2], sulfur dioxide [SO2], etc.) Dead trees and animals from hi ...
... Seismometer and seismogram Shallow earthquakes (<10-20 km) Precursor earthquakes "Harmonic tremors" — specific to magma moving around Composite volcano or stratovolcano Hot springs pH or acidity of water Volcanic gases (carbon dioxide [CO2], sulfur dioxide [SO2], etc.) Dead trees and animals from hi ...
Click here for the "Dynamic Earth Vocabulary"
... A body of air or liquid from which heat is collected. Heat can also be transferred from one object to another, or from one molecule to another through the process of conduction. Shield Volcano: They form from wide thin layers of lava that eventually are shaped like a shield. This is the largest volc ...
... A body of air or liquid from which heat is collected. Heat can also be transferred from one object to another, or from one molecule to another through the process of conduction. Shield Volcano: They form from wide thin layers of lava that eventually are shaped like a shield. This is the largest volc ...
20150210090647
... Where are volcanoes located? • Volcanoes can be found: – Diverging Plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridge) – Converging plates with subduction zones • Oceanic plate vs. oceanic plate • Oceanic plate vs. continental plate ...
... Where are volcanoes located? • Volcanoes can be found: – Diverging Plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridge) – Converging plates with subduction zones • Oceanic plate vs. oceanic plate • Oceanic plate vs. continental plate ...
Chapter 10
... 8. Composite Cone= Volcano composed of both lava flow’s and pyroclastic material 9. Caldera= Large depression typically caused by collapse or ejection of the summit area of a volcano ...
... 8. Composite Cone= Volcano composed of both lava flow’s and pyroclastic material 9. Caldera= Large depression typically caused by collapse or ejection of the summit area of a volcano ...
What is Lava? - Princeton ISD
... Lava Plateau • Forms when lava erupts from long cracks, or fissures, and spreads out evenly (thousands of km) ...
... Lava Plateau • Forms when lava erupts from long cracks, or fissures, and spreads out evenly (thousands of km) ...
What is Lava?
... Lava Plateau • Forms when lava erupts from long cracks, or fissures, and spreads out evenly (thousands of km) ...
... Lava Plateau • Forms when lava erupts from long cracks, or fissures, and spreads out evenly (thousands of km) ...
QR-Volcanoes 59 points Using separate pieces of paper, answer
... difference in flow rates between each type of basaltic lava flow? 5. List the main gasses released during a volcanic eruption. 6. How do volcanic bombs differ from blocks of pyroclastic debris? 7. What is scoria? How is scoria different from pumice? 8. Compare and contrast the three main types of vo ...
... difference in flow rates between each type of basaltic lava flow? 5. List the main gasses released during a volcanic eruption. 6. How do volcanic bombs differ from blocks of pyroclastic debris? 7. What is scoria? How is scoria different from pumice? 8. Compare and contrast the three main types of vo ...
No Slide Title
... The area surrounding the Pacific Plate which contains almost 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. ...
... The area surrounding the Pacific Plate which contains almost 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. ...
File
... and solidification of magma) with a surface exposure of 100 square km (40 square miles) or larger. • Stock-is a discordant igneous intrusion having a surface exposure of less than 40 sq mi (100 km2), differing from batholiths only in ...
... and solidification of magma) with a surface exposure of 100 square km (40 square miles) or larger. • Stock-is a discordant igneous intrusion having a surface exposure of less than 40 sq mi (100 km2), differing from batholiths only in ...
Volcanoes - sabresocials.com
... Streaming gases carry liquid lava blombs into the atmosphere that rain back to earth around the vent to form a cone. ...
... Streaming gases carry liquid lava blombs into the atmosphere that rain back to earth around the vent to form a cone. ...
chapter_7_volcanoes
... Lava- magma (or hot, liquid rock) that reaches the surface Pyroclasts- hot rock fragments (from the Greek word “pyro” meaning fire and “clast” meaning broken) Pyroclastic flows- mixture of gases and pyroclastic debris. It is so dense that it hugs the ground ...
... Lava- magma (or hot, liquid rock) that reaches the surface Pyroclasts- hot rock fragments (from the Greek word “pyro” meaning fire and “clast” meaning broken) Pyroclastic flows- mixture of gases and pyroclastic debris. It is so dense that it hugs the ground ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... Viscosity is a measure of a material's resistance to flow ...
... Viscosity is a measure of a material's resistance to flow ...
Chapter 6 Volcanoes
... Four major kinds of pyroclastic materials &descriptions: 1.Volcanic blocks- largest pieces, of solid rock 2.Volcanic bombs- largest blobs of magma harden in the air, shape of bomb. 3.Lapilli- “little stone” little bits of magma become solid before hit the ground 4.Volcanic ash- forms when magma expa ...
... Four major kinds of pyroclastic materials &descriptions: 1.Volcanic blocks- largest pieces, of solid rock 2.Volcanic bombs- largest blobs of magma harden in the air, shape of bomb. 3.Lapilli- “little stone” little bits of magma become solid before hit the ground 4.Volcanic ash- forms when magma expa ...
Chapter 5: Volcanoes
... S Magma Chamber: Collection of magma under volcano S Pipe: Long tube connecting chamber to surface S Vent: Opening at top (or sides) where magma leaves ...
... S Magma Chamber: Collection of magma under volcano S Pipe: Long tube connecting chamber to surface S Vent: Opening at top (or sides) where magma leaves ...
volcanoreview
... composite cones, with explosive eruptions and erupted materials such as ash, bombs, and blocks. Mt St Helens ...
... composite cones, with explosive eruptions and erupted materials such as ash, bombs, and blocks. Mt St Helens ...
Ring of Fire – Around Pacific area, lots of volcanoes
... Pahoehoe – higher temperature, runnier, like honey, ropy texture at end ...
... Pahoehoe – higher temperature, runnier, like honey, ropy texture at end ...
Force of Volcanoes
... ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ___________________ magma is a mixture of basaltic and ...
... ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ___________________ magma is a mixture of basaltic and ...
Volcanoes - rialto.k12.ca.us
... Volcanoes * There are 2 (main) kinds of Volcanoes 1. Steep sloped with violent (explosive) eruptions 2. Gentle sloped with voluminous lava flows ...
... Volcanoes * There are 2 (main) kinds of Volcanoes 1. Steep sloped with violent (explosive) eruptions 2. Gentle sloped with voluminous lava flows ...
Llullaillaco

Llullaillaco is a potentially active stratovolcano at the border of Argentina (Salta Province) and Chile. It lies in the Puna de Atacama, a region of very high volcanic peaks on a high plateau within the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places in the world. It is the fourth highest volcano in the world, and it is also the seventh highest mountain of the Andes.Llullaillaco follows the typical Puna de Atacama volcano pattern: it is surrounded by large debris fields and is perpetually capped by small snow patches, though there are no true glaciers due to the extreme aridity. The snow line in this region is the highest in the world, at around 6,500 metres (21,300 ft), which is around 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) higher than in the Himalayas and 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) higher than in the Andes of Colombia and Ecuador.The peak's name comes from the Aymara for ""murky water"": llulla= dirty and yacu= water. Other sources propose it to have originated from Quechua Lullac= lie, Yacu= water: ""lying (or treacherous) water"".It has been confirmed that Incas climbed Llullaillaco in the pre-Columbian period. Artifacts on the summit constitute the highest evidence of human presence worldwide before the late nineteenth century. Also, the huáqueros may have also reached its summit and those of other mountains in the region during their searches. The first recorded ascent was on December 1, 1952, by Bión González and Juan Harseim.