VOLCANO CHAPARRASTIQUE ERUPTS IN EL SALVADOR
... the San Miguel municipality about 140 km (87 miles) east of San Salvador, the capital, spewed ash over a wide area known for its coffee plantations. ...
... the San Miguel municipality about 140 km (87 miles) east of San Salvador, the capital, spewed ash over a wide area known for its coffee plantations. ...
No Slide Title
... The area surrounding the Pacific Plate which contains almost 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. ...
... The area surrounding the Pacific Plate which contains almost 75% of the world’s active volcanoes. ...
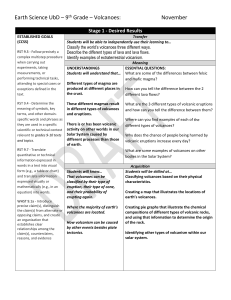
Earth Science UbD – 9th Grade – Volcanoes: November
... Create pie graphs of several volcanic rocks that show their chemical composition, then use the graphs to determine the type of lava from which they were produced. Given physical characteristics, correctly place various volcanoes in the right ...
... Create pie graphs of several volcanic rocks that show their chemical composition, then use the graphs to determine the type of lava from which they were produced. Given physical characteristics, correctly place various volcanoes in the right ...
Chapter 18 - Volcanoes
... eruptions Oceanic crust 2. Rhyolitic – high silica content; high water and gas content; explosive! Continental crust 3. Andesitic – mixture of basaltic & rhyolitic, found along continental margins ...
... eruptions Oceanic crust 2. Rhyolitic – high silica content; high water and gas content; explosive! Continental crust 3. Andesitic – mixture of basaltic & rhyolitic, found along continental margins ...
The Ring of Fire - American Red Cross
... The Ring of Fire Why are so many of the world’s volcanoes found along the edges of the Pacific Ocean in a region called The Ring of Fire? Scientists have discovered that the surface of the Earth is made up of tectonic plates — gigantic slabs of rock that fit together like the pieces of a puzzle. Som ...
... The Ring of Fire Why are so many of the world’s volcanoes found along the edges of the Pacific Ocean in a region called The Ring of Fire? Scientists have discovered that the surface of the Earth is made up of tectonic plates — gigantic slabs of rock that fit together like the pieces of a puzzle. Som ...
Cornell Notes Template
... All lava is not the same; the viscosity of lava varies Viscosity- the inability for a liquid to flow ↑ viscosity=↓ ability to flow/move Lava that has more silica is more viscous, lava that has less silica is less viscous The ingredients (composition) of the lava determines if a volcano will have a v ...
... All lava is not the same; the viscosity of lava varies Viscosity- the inability for a liquid to flow ↑ viscosity=↓ ability to flow/move Lava that has more silica is more viscous, lava that has less silica is less viscous The ingredients (composition) of the lava determines if a volcano will have a v ...
volcanoes - WISMYPScience
... leaves behind the solidified magma chamber It is the ancient crystallized core of a volcano ...
... leaves behind the solidified magma chamber It is the ancient crystallized core of a volcano ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
File
... Composite many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity Volcanoes lava, ash and rock debris. Mt. Rainier and Mount St. Helens are examples of this type of volcano. Shield Volcanoes ...
... Composite many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high-viscosity Volcanoes lava, ash and rock debris. Mt. Rainier and Mount St. Helens are examples of this type of volcano. Shield Volcanoes ...
Volcanoes
... • Lahars are mud flows that often occur after eruptions. • Nuée ardentes are mobile dense clouds of incandescent ash that can move downhill at speeds up to 100 ...
... • Lahars are mud flows that often occur after eruptions. • Nuée ardentes are mobile dense clouds of incandescent ash that can move downhill at speeds up to 100 ...
Active
... of differential change due to ground swelling upward. Maximum displacement is in center and pattern is concentric, suggesting a pending volcanic eruption ...
... of differential change due to ground swelling upward. Maximum displacement is in center and pattern is concentric, suggesting a pending volcanic eruption ...
Shield Volcano
... Cinder Cone Volcano • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate arou ...
... Cinder Cone Volcano • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate arou ...
volcanoes - an-0001
... • Gases spewed out from volcanic eruptions such as carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide, are more deadly. • Devastating mudflows, known as lahars, are caused by ashes, soil and rock combining on volcanic slopes. ...
... • Gases spewed out from volcanic eruptions such as carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide, are more deadly. • Devastating mudflows, known as lahars, are caused by ashes, soil and rock combining on volcanic slopes. ...
Chapter 4 volcanoes powerpoint notes
... Lava Types: • Pahoehoe (i.e. ropy): Basaltic lava that has a smooth, billowy, undulating, or ropy surface. • Aa (i.e. jagged, angular): Basaltic lava characterized by a rough or rubbly surface composed of broken lava blocks ...
... Lava Types: • Pahoehoe (i.e. ropy): Basaltic lava that has a smooth, billowy, undulating, or ropy surface. • Aa (i.e. jagged, angular): Basaltic lava characterized by a rough or rubbly surface composed of broken lava blocks ...
Student Science Volcano Project
... volcanoes erupt only once, but others erupt repeatedly. Volcanoes have not only destroyed but have also created many thousands of square miles of land surface, both as oceanic islands and on some continents. ...
... volcanoes erupt only once, but others erupt repeatedly. Volcanoes have not only destroyed but have also created many thousands of square miles of land surface, both as oceanic islands and on some continents. ...
Volcano Lesson Plan - Disaster Resilience Education For Schools
... volcanic eruptions occur and how to stay safe during an eruption. ...
... volcanic eruptions occur and how to stay safe during an eruption. ...
Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive
... Cinder cone volcanoes are formed from explosive eruptions (Jensen 34). Because the materials are ejected high into the air from the violent eruption, they cool before they hit the ground. Any tiny, fine-grained rock is then blown away by winds. The coarser rock fragments are left behind in a cone sh ...
... Cinder cone volcanoes are formed from explosive eruptions (Jensen 34). Because the materials are ejected high into the air from the violent eruption, they cool before they hit the ground. Any tiny, fine-grained rock is then blown away by winds. The coarser rock fragments are left behind in a cone sh ...
chapter 4 volcanoes
... Cinder cone volcanoes are formed from explosive eruptions. (Jensen34) Because the materials are ejected high into the air from the violent eruption, they cool before they hit the ground. Any tiny, fine-grained rock is then blown away by winds. The coarser rock fragments are left behind in a cone sha ...
... Cinder cone volcanoes are formed from explosive eruptions. (Jensen34) Because the materials are ejected high into the air from the violent eruption, they cool before they hit the ground. Any tiny, fine-grained rock is then blown away by winds. The coarser rock fragments are left behind in a cone sha ...
Chapter 13 Study Notes Volcanoes
... • A _______ cone is rarely more than a few hundred meters high, with slope angles up to 40°, and formed from ______ eruptions. – cinder – explosive ...
... • A _______ cone is rarely more than a few hundred meters high, with slope angles up to 40°, and formed from ______ eruptions. – cinder – explosive ...
Chapter 13 Study Notes Volcanoes
... • A _______ cone is rarely more than a few hundred meters high, with slope angles up to 40°, and formed from ______ eruptions. – cinder – explosive ...
... • A _______ cone is rarely more than a few hundred meters high, with slope angles up to 40°, and formed from ______ eruptions. – cinder – explosive ...
Volcanoes
... Composite or Stratovolcano • Form from alternating eruptions of quiet lava and explosive ash. The layers build up and make a moderate-sized volcano. –Most common kind of volcano –Made of layers of ash/tephra and lava. ...
... Composite or Stratovolcano • Form from alternating eruptions of quiet lava and explosive ash. The layers build up and make a moderate-sized volcano. –Most common kind of volcano –Made of layers of ash/tephra and lava. ...
Volcanoes Lesson
... Composite or Stratovolcano • Form from alternating eruptions of quiet lava and explosive ash. The layers build up and make a moderate-sized volcano. –Most common kind of volcano –Made of layers of ash/tephra and lava. ...
... Composite or Stratovolcano • Form from alternating eruptions of quiet lava and explosive ash. The layers build up and make a moderate-sized volcano. –Most common kind of volcano –Made of layers of ash/tephra and lava. ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... • As the temperature of lava increases, the viscocity decreases. • Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have magma with high silica, high viscosity, and higher gas content. • The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called pyroclastic material. • Pyroclastic materials include ash, cinders and ...
... • As the temperature of lava increases, the viscocity decreases. • Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have magma with high silica, high viscosity, and higher gas content. • The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called pyroclastic material. • Pyroclastic materials include ash, cinders and ...
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.