The World of Volcanoes
... How do volcanoes form? • Continental plates and oceanic plates collide • Subduction occurs • Melted rock becomes magma that forces its way up between the plates • Savage Earth Animation #2 ...
... How do volcanoes form? • Continental plates and oceanic plates collide • Subduction occurs • Melted rock becomes magma that forces its way up between the plates • Savage Earth Animation #2 ...
magma and lava
... 12.The depression that results when a volcanic cone collapses over an emptying magma chamber is called a caldera. 13.Why does magma rise to the surface? Magma rises because it is less dense than the surrounding material 14.What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is molten rock undergrou ...
... 12.The depression that results when a volcanic cone collapses over an emptying magma chamber is called a caldera. 13.Why does magma rise to the surface? Magma rises because it is less dense than the surrounding material 14.What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is molten rock undergrou ...
What mainly controls eruptive style? Viscosity in magma 2. Eruptive
... Tom Sisson of USGS estimates its age at ~100 ka ...
... Tom Sisson of USGS estimates its age at ~100 ka ...
Types of Volcanoes
... Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills out of a central vent or group of vents. A broad shaped, gently sloping cone is formed. This is caused by the very fluid, basaltic lava which can't be piled up into steep mounds Shield volcanoes may be ...
... Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills out of a central vent or group of vents. A broad shaped, gently sloping cone is formed. This is caused by the very fluid, basaltic lava which can't be piled up into steep mounds Shield volcanoes may be ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... _____ 5. made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions _____ 6. formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter flows of lava; also called stratovolcanoes ...
... _____ 5. made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions _____ 6. formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter flows of lava; also called stratovolcanoes ...
Ring of Fire – Around Pacific area, lots of volcanoes
... Pahoehoe – higher temperature, runnier, like honey, ropy texture at end ...
... Pahoehoe – higher temperature, runnier, like honey, ropy texture at end ...
Cascades?
... impending eruption, but together with other observations (deformation, gas emission, temperature changes) they provide one important and early clue when eruptions may be approaching. Volcano seismologists track not only earthquakes, but also various kinds of seismic signals with special characterist ...
... impending eruption, but together with other observations (deformation, gas emission, temperature changes) they provide one important and early clue when eruptions may be approaching. Volcano seismologists track not only earthquakes, but also various kinds of seismic signals with special characterist ...
PowerPoint explanation of volcanic impact on climate
... • As it rises, the pressure falls and the air cools • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic ...
... • As it rises, the pressure falls and the air cools • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic ...
Volcanic Landforms
... fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of flows of highly fluid ...
... fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of flows of highly fluid ...
Getting to Know: Effects of Volcanoes
... If a volcanic eruption is explosive, part or all of the volcano may blow up. For example, the Mt. St. Helens eruption left a huge crater in the side of the mountain. The mountain today looks much different than it did before the 1980 eruption. In contrast, a constructive eruption is one that helps b ...
... If a volcanic eruption is explosive, part or all of the volcano may blow up. For example, the Mt. St. Helens eruption left a huge crater in the side of the mountain. The mountain today looks much different than it did before the 1980 eruption. In contrast, a constructive eruption is one that helps b ...
VOLCANOES
... • Hawaiian volcanoes progress through pre-shield Lōʻihi, shield Mauna Loa and Kīlauea, post-shield Mauna Kea, Hualālai, and Haleakalā, erosional Kohala, Lāna‘i, and Wai‘anae, and rejuvenated Ko‘olau and West Maui stages. • As the islands age, they erode and subside, becoming atolls and seamounts. ...
... • Hawaiian volcanoes progress through pre-shield Lōʻihi, shield Mauna Loa and Kīlauea, post-shield Mauna Kea, Hualālai, and Haleakalā, erosional Kohala, Lāna‘i, and Wai‘anae, and rejuvenated Ko‘olau and West Maui stages. • As the islands age, they erode and subside, becoming atolls and seamounts. ...
Ch. 4 Volcanism and Extrusive Ignous Rocks
... – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – Violent eruptions can destroy nearly all life in their paths – Large amounts of ash and volcanic gases in atmosphere can trigger rapid climate changes and contribute to mass extinctions ...
... – Lava flows and ash weather to produce fertile soils – Violent eruptions can destroy nearly all life in their paths – Large amounts of ash and volcanic gases in atmosphere can trigger rapid climate changes and contribute to mass extinctions ...
Developing a Clincher Sentence
... 1. Although scientists now recognize that volcanoes are a natural part of how the earth changes over time, people have not always seen them that way. Many early cultures tried to understand volcanoes by linking them to supernatural forces. Some cultures believed that volcanic eruptions indicated tha ...
... 1. Although scientists now recognize that volcanoes are a natural part of how the earth changes over time, people have not always seen them that way. Many early cultures tried to understand volcanoes by linking them to supernatural forces. Some cultures believed that volcanic eruptions indicated tha ...
Directions: Read the information below. Use this information and
... volcanoes and shield volcanoes. Cinder cones are built from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. Cinder cones grow rapidly and soon approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height ...
... volcanoes and shield volcanoes. Cinder cones are built from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. Cinder cones grow rapidly and soon approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height ...
Typical shield volcano Mauna Loa, Hawaii
... Produced by mild eruptions of large volumes of lava primarily basaltic Example: Mauna Loa on Hawaii ...
... Produced by mild eruptions of large volumes of lava primarily basaltic Example: Mauna Loa on Hawaii ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park - Cook/Lowery15
... are accessible by tourists because the "Eruptions are much gentler" in this area. It is an area where people can walk on the hardened lava. Also, during volcano ...
... are accessible by tourists because the "Eruptions are much gentler" in this area. It is an area where people can walk on the hardened lava. Also, during volcano ...
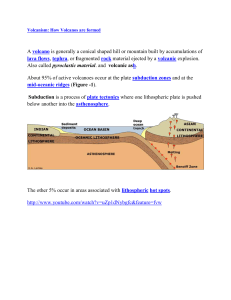
A volcano is generally a conical shaped hill or mountain built by
... Investigations have discovered that over the last 2 million years this volcano has exploded on a regular interval of about 700,000 years. The last eruption occurred 630,000 years ago and the next could take place anytime. When the Yellowstone caldera last erupted, it blasted 1,000 cubic kilometers o ...
... Investigations have discovered that over the last 2 million years this volcano has exploded on a regular interval of about 700,000 years. The last eruption occurred 630,000 years ago and the next could take place anytime. When the Yellowstone caldera last erupted, it blasted 1,000 cubic kilometers o ...
Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
... silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and ...
... silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and ...
Word format
... Sometimes, volcanic material can rush down the slopes of the volcano just like an avalanche, and is called a _________________________. It contains extremely hot bits of semi-molten rock, called ___________, as well as huge volumes of poisonous gases. What are the three types of tephra (from biggest ...
... Sometimes, volcanic material can rush down the slopes of the volcano just like an avalanche, and is called a _________________________. It contains extremely hot bits of semi-molten rock, called ___________, as well as huge volumes of poisonous gases. What are the three types of tephra (from biggest ...
Volcanoes - geographylyndon
... Despite the evacuations, 19 people were killed by the eruptions. This is because a small group of people chose to stay behind on the island and watch over their crops. Volcanic eruptions and lahars have destroyed large areas of Montserrat. The capital, Plymouth, has been covered in layers of ash and ...
... Despite the evacuations, 19 people were killed by the eruptions. This is because a small group of people chose to stay behind on the island and watch over their crops. Volcanic eruptions and lahars have destroyed large areas of Montserrat. The capital, Plymouth, has been covered in layers of ash and ...
here
... Hot ash clouds are denser than air and may collapse and rush down volcanic slopes at high speeds forming a nuee ardente (fiery cloud) or ash-flow. ...
... Hot ash clouds are denser than air and may collapse and rush down volcanic slopes at high speeds forming a nuee ardente (fiery cloud) or ash-flow. ...
Lecture 12
... Low silica, low gas magma originates in the mantle. Fluid, basaltic lava results in “Aa” and “Pahoehoe”. Low viscosity creates broad, gentle slopes. Phreatomagmatic eruptions occur when lava contacts water (rapid expansion of steam) . ...
... Low silica, low gas magma originates in the mantle. Fluid, basaltic lava results in “Aa” and “Pahoehoe”. Low viscosity creates broad, gentle slopes. Phreatomagmatic eruptions occur when lava contacts water (rapid expansion of steam) . ...
volcanoes-and-climate
... • As it rises, the pressure falls and the air cools • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic ...
... • As it rises, the pressure falls and the air cools • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic ...
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.