Chapter 9 - Volcanoes
... • Caldera – A large depression formed after the eruption and much larger than the crater. A crater with collapsed walls. • Lava Plateaus – Formed by repeated eruptions with massive outpourings of lava spreading out over a large area. These are usually formed by rift zones (huge cracks in the surface ...
... • Caldera – A large depression formed after the eruption and much larger than the crater. A crater with collapsed walls. • Lava Plateaus – Formed by repeated eruptions with massive outpourings of lava spreading out over a large area. These are usually formed by rift zones (huge cracks in the surface ...
Chapter 5 lesson 2
... a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano the area covered by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent a bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening a material found in magma that i ...
... a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano the area covered by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent a bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening a material found in magma that i ...
Geoscenario Specialists: Yellowstone Hotspot
... waves through Earth’s crust. Sources of particular interest include volcanoes and tectonic boundaries. Recent equipment has allowed seismologists to create three-dimensional images of magma chambers that fuel hotspots. This seismologist carries equipment to set up a remote seismology station. ...
... waves through Earth’s crust. Sources of particular interest include volcanoes and tectonic boundaries. Recent equipment has allowed seismologists to create three-dimensional images of magma chambers that fuel hotspots. This seismologist carries equipment to set up a remote seismology station. ...
Volcano Lecture ppt
... • Earthquake activity commonly precedes an eruption – Result of magma pushing up towards the surface – Increase volume of material in the volcano shatters the rock – This causes earthquakes ...
... • Earthquake activity commonly precedes an eruption – Result of magma pushing up towards the surface – Increase volume of material in the volcano shatters the rock – This causes earthquakes ...
Lecture 14 Summary
... Tephra - a general term for fragments of volcanic rock and lava regardless of size that are blasted into the air by explosions or carried upward by hot gases in eruption columns or lava fountains. Includes large dense blocks and bombs, and small light rock debris such as scoria, pumice, reticulite, ...
... Tephra - a general term for fragments of volcanic rock and lava regardless of size that are blasted into the air by explosions or carried upward by hot gases in eruption columns or lava fountains. Includes large dense blocks and bombs, and small light rock debris such as scoria, pumice, reticulite, ...
F08 5 Emplacement
... Hey…it’s a rough world out there! Earth’s surface is dynamic Advantages: transfer of abundant energy ...
... Hey…it’s a rough world out there! Earth’s surface is dynamic Advantages: transfer of abundant energy ...
Earth Science - Mr.E Science
... Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano - a weak spot in the crust where molten material, or magma, comes to the surface. Ring of Fire - Major Volcanic Belt surrounding the Pacific Ocean Tectonic Plate Boundaries ...
... Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano - a weak spot in the crust where molten material, or magma, comes to the surface. Ring of Fire - Major Volcanic Belt surrounding the Pacific Ocean Tectonic Plate Boundaries ...
Chapter 6 study guide
... 19. If a volcano erupts explosively, what will it produce in addition to (sometimes) lava flows? 20. What type of volcano forms from quiet eruptions? 21. What type of volcano forms from an explosive eruption without any lava flows? 22. What type of volcano forms from an explosive eruption with lava ...
... 19. If a volcano erupts explosively, what will it produce in addition to (sometimes) lava flows? 20. What type of volcano forms from quiet eruptions? 21. What type of volcano forms from an explosive eruption without any lava flows? 22. What type of volcano forms from an explosive eruption with lava ...
5volcano notes chapter
... Key point: most volcanoes form along diverging plate boundaries. I. Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of earth’s plates. Volcano –a weak spot in crust where magma comes to the surface. Ring of fire-major volcanic belt around rim of Pacific Ocean. (90% of volcanoes) Key point: magma called lav ...
... Key point: most volcanoes form along diverging plate boundaries. I. Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of earth’s plates. Volcano –a weak spot in crust where magma comes to the surface. Ring of fire-major volcanic belt around rim of Pacific Ocean. (90% of volcanoes) Key point: magma called lav ...
File
... understand the terms magma, lava, vent, and crater. Then tell them that there are three different types of volcanoes, and they are going to make models of each type. 2. On the chalkboard, write the names of the three different types of volcanoes: shield volcano, cinder cone, and composite volcano. 3 ...
... understand the terms magma, lava, vent, and crater. Then tell them that there are three different types of volcanoes, and they are going to make models of each type. 2. On the chalkboard, write the names of the three different types of volcanoes: shield volcano, cinder cone, and composite volcano. 3 ...
Shifting Plates Projects
... Draw conclusions as to why the largest continental United States earthquakes have & are likely to occur in or around California? ...
... Draw conclusions as to why the largest continental United States earthquakes have & are likely to occur in or around California? ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park - Cook/Lowery15
... Pele’s tears is formed by small bits of molten Lava that soon solidifies and forms tiny glass particles called Pele’s tears. These are Igneous as well. ...
... Pele’s tears is formed by small bits of molten Lava that soon solidifies and forms tiny glass particles called Pele’s tears. These are Igneous as well. ...
Unit test review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Label a volcano Distribution of volcanoes Geologic formations (pillow basalt, columnar jointing, plateau basalt) What comes out of a volcano? How does it affect surrounding areas? Effects of ash fall? Viscosity of lava: Aa, pahoehoe, what changes it’s viscosity Pysroclastic flow: how is it formed Vo ...
... Label a volcano Distribution of volcanoes Geologic formations (pillow basalt, columnar jointing, plateau basalt) What comes out of a volcano? How does it affect surrounding areas? Effects of ash fall? Viscosity of lava: Aa, pahoehoe, what changes it’s viscosity Pysroclastic flow: how is it formed Vo ...
Volcanoes, Hotspots, and Earthquakes
... during the past 3 million years is 56 mm/yr (2 in/yr). This is about the same rate at which your fingernails grow. Assuming this rate continues, scientists project that Los Angeles and San Francisco will be adjacent to one another in approximately 15 million years. ...
... during the past 3 million years is 56 mm/yr (2 in/yr). This is about the same rate at which your fingernails grow. Assuming this rate continues, scientists project that Los Angeles and San Francisco will be adjacent to one another in approximately 15 million years. ...
Assignment #21 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2) Cinder Cone: builds up from pyroclastic debris, slopes about 30 degrees, most material lands near the volcano and this is how the sides build up, life span short, smaller in size compared to Shield volcanoes 3) Composite Volcano: (p.91 fig 4.21) - intermediate type of slopes, pyroclastic layers b ...
... 2) Cinder Cone: builds up from pyroclastic debris, slopes about 30 degrees, most material lands near the volcano and this is how the sides build up, life span short, smaller in size compared to Shield volcanoes 3) Composite Volcano: (p.91 fig 4.21) - intermediate type of slopes, pyroclastic layers b ...
Lesson 4: Volcanoes Lesson Title: Volcanoes Topic: Types of
... similar to the sticky magma that traps gases. The room-temperature sample would produce a Strombolian eruption. The molasses in this sample is similar to thick magma. It may stop up the vent, but pressure is released frequently. The heated sample would produce a Hawaiian eruption, because the heated ...
... similar to the sticky magma that traps gases. The room-temperature sample would produce a Strombolian eruption. The molasses in this sample is similar to thick magma. It may stop up the vent, but pressure is released frequently. The heated sample would produce a Hawaiian eruption, because the heated ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
Inside Earth 3.3 Volcanic Landforms
... • Massive eruption empties the main vent and magma chamber beneath the volcano • The hollow mountain then collapses inward due to lack of support • A Caldera is the large hole left behind • Fills with pieces of the volcano, ash and water – Crater Lake in Oregon ...
... • Massive eruption empties the main vent and magma chamber beneath the volcano • The hollow mountain then collapses inward due to lack of support • A Caldera is the large hole left behind • Fills with pieces of the volcano, ash and water – Crater Lake in Oregon ...
Unit 4 Chapter 13
... Formation of Magma Magma is molten rock under the earth’s surface It can form under 3 conditions: 1.Temperature of the rock rises above the melting point of the material. 2.If enough pressure is removed from the rock, the melting point will decrease and the rock will melt. 3.Addition of fluids such ...
... Formation of Magma Magma is molten rock under the earth’s surface It can form under 3 conditions: 1.Temperature of the rock rises above the melting point of the material. 2.If enough pressure is removed from the rock, the melting point will decrease and the rock will melt. 3.Addition of fluids such ...
Geology 101 Homework 4
... 4) Explain the three ways magma forms inside the Earth (p. 140). What is the relationship between plate tectonic setting and the way magma forms? (p. 156) Which magma formation process occurs most frequently inside the Earth? 5) What shapes do bodies of igneous rock form when they intrude the Earth? ...
... 4) Explain the three ways magma forms inside the Earth (p. 140). What is the relationship between plate tectonic setting and the way magma forms? (p. 156) Which magma formation process occurs most frequently inside the Earth? 5) What shapes do bodies of igneous rock form when they intrude the Earth? ...
Inside Earth 3-2 Worksheets 2013
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
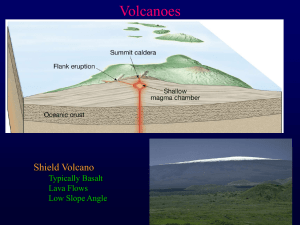
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.