Volcanoes Week 2
... Ash Ash is the most common pyroclastic rock material ejected during an eruption. Volcanic ash is so fine that it can be blown into the atmosphere and picked up by the jet stream where it can circle the Earth for several years. Lapilli Lapilli are pea-size to walnut-sized pieces of volcanic rock. All ...
... Ash Ash is the most common pyroclastic rock material ejected during an eruption. Volcanic ash is so fine that it can be blown into the atmosphere and picked up by the jet stream where it can circle the Earth for several years. Lapilli Lapilli are pea-size to walnut-sized pieces of volcanic rock. All ...
Chapter 10
... 2. Vent= A opening in the surface of earth through which molten rock and gases are released 3. Pyroclastic Material= Volcanic rock during an eruption, including ash, bombs, and blocks 4. Volcano= A mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic Material 5. Crater= The depression at the summit of a volca ...
... 2. Vent= A opening in the surface of earth through which molten rock and gases are released 3. Pyroclastic Material= Volcanic rock during an eruption, including ash, bombs, and blocks 4. Volcano= A mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic Material 5. Crater= The depression at the summit of a volca ...
Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Mountains
... Magma rises upward because it is less dense than the surrounding rock It does not always reach the surface before it turns to rock again If it does reach the surface, it forms a volcano ...
... Magma rises upward because it is less dense than the surrounding rock It does not always reach the surface before it turns to rock again If it does reach the surface, it forms a volcano ...
S05_4359_L24
... Four requirements for large-scale operation: Magmatic heat source (active volcano); hot water or steam (above heat source); highly permeable rocks (to allow water flow); nearly impermeable cap rock (to maintain pressure). Hot, dry steam is best; wet acidic steam corrodes pipes and makes development ...
... Four requirements for large-scale operation: Magmatic heat source (active volcano); hot water or steam (above heat source); highly permeable rocks (to allow water flow); nearly impermeable cap rock (to maintain pressure). Hot, dry steam is best; wet acidic steam corrodes pipes and makes development ...
Explosive and Non - Saint Peter School | Danbury, CT
... • Rock fragments shoot in the air • Ash from this type of eruption can enter the earths atmosphere and stay there for years • Magma in these eruptions contain a lot of water • Water turns into gas and expands which caused explosion • Magma is packed with silica which causes it to move slow and cause ...
... • Rock fragments shoot in the air • Ash from this type of eruption can enter the earths atmosphere and stay there for years • Magma in these eruptions contain a lot of water • Water turns into gas and expands which caused explosion • Magma is packed with silica which causes it to move slow and cause ...
VOLCANOES MR.OCHOA CHAPTER 6
... Many volcanoes form near converging plate boundaries where oceanic crust returns to the mantle. Slabs of oceanic crust sink through a deep ocean trench into the mantle, where it forms magma that rises back toward the surface. ...
... Many volcanoes form near converging plate boundaries where oceanic crust returns to the mantle. Slabs of oceanic crust sink through a deep ocean trench into the mantle, where it forms magma that rises back toward the surface. ...
Volcanic Activity
... • Mostly along plate boundaries; 80% in the "ring of fire“. • Molten rock, including small components of dissolved gases, produced where lithospheric plates interact with other earth materials is called MAGMA • Lava- magma from a volcano Typically produce composite volcanoes, whose magma is high in ...
... • Mostly along plate boundaries; 80% in the "ring of fire“. • Molten rock, including small components of dissolved gases, produced where lithospheric plates interact with other earth materials is called MAGMA • Lava- magma from a volcano Typically produce composite volcanoes, whose magma is high in ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Directed Reading
... surrounds the volcano are called ____________________________. 13. Pyroclastic particles less than 0.25 mm in diameter that are so small they might travel around Earth in the upper atmosphere are called ________________________________. 14. The largest pyroclastic particles, which form from solid ro ...
... surrounds the volcano are called ____________________________. 13. Pyroclastic particles less than 0.25 mm in diameter that are so small they might travel around Earth in the upper atmosphere are called ________________________________. 14. The largest pyroclastic particles, which form from solid ro ...
Volcanoes - City of Redwood City
... A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth’s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive products—layers of lava, ashflows, and ash. When pressure from gases within the molten rock becomes too ...
... A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth’s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive products—layers of lava, ashflows, and ash. When pressure from gases within the molten rock becomes too ...
the free PDF resource
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
DStroupTalk3
... - very young channels and debris aprons found on many north-facing slopes at high latitudes are speculated to have formed when liquid water seeped out of the subsurface ...
... - very young channels and debris aprons found on many north-facing slopes at high latitudes are speculated to have formed when liquid water seeped out of the subsurface ...
iss__st4_files/Comenius Volcanoes
... gas that is released. These clouds of gas and ash can rise up to kilometers in height, sometimes rising up so high that air traffic is influenced. These gases can so be extremely hot that they can destroy the engines of planes, meaning that planes cannot fly in the close proximity of these gas clouds. ...
... gas that is released. These clouds of gas and ash can rise up to kilometers in height, sometimes rising up so high that air traffic is influenced. These gases can so be extremely hot that they can destroy the engines of planes, meaning that planes cannot fly in the close proximity of these gas clouds. ...
Chapter 11 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Outline
... a. Composed of alternating layers of rock particles and lava b. Forms from violent eruption first c. Quiet eruption follows d. Large cone-shaped mountain forms D. Volcanic activity 1. Active a. Erupts continually or periodically b. Several active ones in U.S. ...
... a. Composed of alternating layers of rock particles and lava b. Forms from violent eruption first c. Quiet eruption follows d. Large cone-shaped mountain forms D. Volcanic activity 1. Active a. Erupts continually or periodically b. Several active ones in U.S. ...
Volcanoes/REVIEW
... watch the powerpoints you have been working on. Notebooks will also be due on Friday, April 24 (there will be no portfolio page for this unit. PART A – Review pages 204-229 in your textbook and use your notebook 1. What is a volcano? __________________________________________________________________ ...
... watch the powerpoints you have been working on. Notebooks will also be due on Friday, April 24 (there will be no portfolio page for this unit. PART A – Review pages 204-229 in your textbook and use your notebook 1. What is a volcano? __________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... The belt around the rim of the Pacific Ocean is called ___________. Thicker magma contains more ______________________. What is a wide gently sloping mountain made of hardened layers of low silica lava know as? _____________________. What forms when magma hardens in a volcano’s pipe and is later exp ...
... The belt around the rim of the Pacific Ocean is called ___________. Thicker magma contains more ______________________. What is a wide gently sloping mountain made of hardened layers of low silica lava know as? _____________________. What forms when magma hardens in a volcano’s pipe and is later exp ...
Lecture 04 Volcanic Activity g
... –Produced by mild eruptions of large volumes of lava –Mauna Loa on Hawaii is a good example ...
... –Produced by mild eruptions of large volumes of lava –Mauna Loa on Hawaii is a good example ...
Classifying Volcanoes
... g. Layers- alternating layers of lava and debris, these create the volcano h. Dike- old lava that has hardened and crosses layers of debris i. Lava tube- channels of hardened lava that form in old lava flows and allow the lava to move far away from the vent 3. Classifying Volcanoes a. How often they ...
... g. Layers- alternating layers of lava and debris, these create the volcano h. Dike- old lava that has hardened and crosses layers of debris i. Lava tube- channels of hardened lava that form in old lava flows and allow the lava to move far away from the vent 3. Classifying Volcanoes a. How often they ...
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... What important function do volcanoes perform for the Earth? (Volcanoes act like cooling vents by releasing heat from Earth's core.) ...
... What important function do volcanoes perform for the Earth? (Volcanoes act like cooling vents by releasing heat from Earth's core.) ...
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
3-2 Notes: Volcanoes Eruptions • Volcano
... Volcanoes Form Along Plate Boundaries • Volcanoes are common along tectonic plate boundaries at subduction zones and _________________ boundaries. • Volcanoes can also form over _____________________. • There are ~1500 potentially active volcanoes in the world, _________ of which we know have erupte ...
... Volcanoes Form Along Plate Boundaries • Volcanoes are common along tectonic plate boundaries at subduction zones and _________________ boundaries. • Volcanoes can also form over _____________________. • There are ~1500 potentially active volcanoes in the world, _________ of which we know have erupte ...
Document
... All volcanoes are formed by the accumulation of magma; molten rock that forms below the earth's surface. Magma can erupt through one or more volcanic vents, which can be a single opening, a cluster of openings, or a long crack, It forms deep within the earth, generally within the upper part of the m ...
... All volcanoes are formed by the accumulation of magma; molten rock that forms below the earth's surface. Magma can erupt through one or more volcanic vents, which can be a single opening, a cluster of openings, or a long crack, It forms deep within the earth, generally within the upper part of the m ...
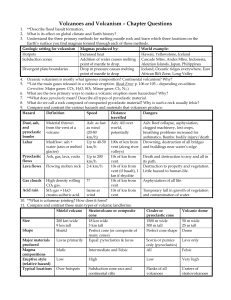
Volcanoes and Volcanism – Chapter Questions
... **Describe flood basalt formation. What is its effect on global climate and Earth history? Understand the three primary methods for melting mantle rock and learn which three locations on the Earth’s surface you find magmas formed through each of those methods. Geologic setting for volcanism Magmas p ...
... **Describe flood basalt formation. What is its effect on global climate and Earth history? Understand the three primary methods for melting mantle rock and learn which three locations on the Earth’s surface you find magmas formed through each of those methods. Geologic setting for volcanism Magmas p ...
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.