VOLCANOES AND IGNEOUS ENVIRONMENTS
... a. basaltic – dark-colored fine-grained rock (basalt) formed from fast-moving lava containing dissolved gases such as H2O and CO2 b. rhyolitic – lighter-colored fine-grained rock (rhyolite) formed from slow-moving lava that does not contain much water; these types of flows are generally extremely vi ...
... a. basaltic – dark-colored fine-grained rock (basalt) formed from fast-moving lava containing dissolved gases such as H2O and CO2 b. rhyolitic – lighter-colored fine-grained rock (rhyolite) formed from slow-moving lava that does not contain much water; these types of flows are generally extremely vi ...
Geysers: Types: cone (has a cone of “geyserite” around a small vent
... many short explosions. Eruptive columns are typically larger than Stromb. columns, and they are mostly made up of ashy pyrocl. material. The explosions are initiated by hi-viscosity, hi-gas-content magma in which small amounts of gas pressure build up and thrust material into the air. In addition to ...
... many short explosions. Eruptive columns are typically larger than Stromb. columns, and they are mostly made up of ashy pyrocl. material. The explosions are initiated by hi-viscosity, hi-gas-content magma in which small amounts of gas pressure build up and thrust material into the air. In addition to ...
Forces in Earth
... • Seismic Waves- earthquake generated waves that travel through the ground as vibrations • Focus- the point in Earth’s interior where seismic waves originate • Epicenter- the point of earth’s surface directly above the focus • Seismograph- an instrument used by scientists to detect seismic waves as ...
... • Seismic Waves- earthquake generated waves that travel through the ground as vibrations • Focus- the point in Earth’s interior where seismic waves originate • Epicenter- the point of earth’s surface directly above the focus • Seismograph- an instrument used by scientists to detect seismic waves as ...
Slide 1 - Perry Local Schools
... that move over time in different directions and at different rates. Lithosphere-includes the crust and part of the mantle, this is what is divided into the tectonic plates. Asthenosphere- the layer under the lithosphere which allows the plates to slide, made up of mantle. ...
... that move over time in different directions and at different rates. Lithosphere-includes the crust and part of the mantle, this is what is divided into the tectonic plates. Asthenosphere- the layer under the lithosphere which allows the plates to slide, made up of mantle. ...
Volcanoes-Help of Hindrance
... Sometimes a volcano explodes sideways, shooting out ash and large pieces of rock that travel at very high speeds for several kilometers. These explosions can cause death by suffocation and knock down entire forests within seconds. Rivers of molten rock or hot fragments of rock from such eruptions c ...
... Sometimes a volcano explodes sideways, shooting out ash and large pieces of rock that travel at very high speeds for several kilometers. These explosions can cause death by suffocation and knock down entire forests within seconds. Rivers of molten rock or hot fragments of rock from such eruptions c ...
File
... Volcanoes Activity Objective In this activity, we are going to explore the two main volcano types: shield and composite. We will understand their connection to plate tectonics and learn more about hazards associated with each volcano type. Part 1: Volcanoes & Volcano Types Go to http://nationalgeogr ...
... Volcanoes Activity Objective In this activity, we are going to explore the two main volcano types: shield and composite. We will understand their connection to plate tectonics and learn more about hazards associated with each volcano type. Part 1: Volcanoes & Volcano Types Go to http://nationalgeogr ...
volcanism - Geophile.net
... • Current issues include: – desertification; depletion of underground water resources; lack of perennial rivers or permanent water ...
... • Current issues include: – desertification; depletion of underground water resources; lack of perennial rivers or permanent water ...
All About Volcanoes - Library Video Company
... from the chamber pushes on the crust above it, finding cracks and weak spots through which it can make its way to the surface.The main pathway through which the magma travels is called the central vent. Once magma reaches the Earth’s surface, it erupts as lava from a funnel-shaped opening at the top ...
... from the chamber pushes on the crust above it, finding cracks and weak spots through which it can make its way to the surface.The main pathway through which the magma travels is called the central vent. Once magma reaches the Earth’s surface, it erupts as lava from a funnel-shaped opening at the top ...
msword - rgs.org
... Lesson 5: Volcanoes: a suitable home? Factsheet for teachers Purpose of Lesson In the last lesson pupils understood that volcanoes are primarily (but not exclusively) located on the boundary between two tectonic plates. In its simplest terms a volcano is formed when magma penetrates the Earth’s crus ...
... Lesson 5: Volcanoes: a suitable home? Factsheet for teachers Purpose of Lesson In the last lesson pupils understood that volcanoes are primarily (but not exclusively) located on the boundary between two tectonic plates. In its simplest terms a volcano is formed when magma penetrates the Earth’s crus ...
Volcano Vocab.
... Intro to Topographic Maps: 1. Complete Intro. to Topographic Maps activity in packet (page 1 front & back) When you finish: Work on mountains & volcanoes vocabulary organizer ...
... Intro to Topographic Maps: 1. Complete Intro. to Topographic Maps activity in packet (page 1 front & back) When you finish: Work on mountains & volcanoes vocabulary organizer ...
Document
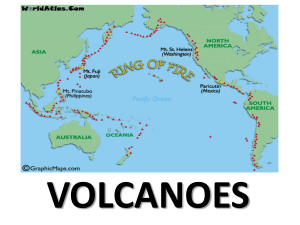
... Map of the world’s active volcanoes, showing that the majority of active volcanoes (about 66%) occur in the Pacific Ring of Fire. ...
... Map of the world’s active volcanoes, showing that the majority of active volcanoes (about 66%) occur in the Pacific Ring of Fire. ...
Take a `Chance` on the volcano erupting
... volcanologists were killed and injured by a small eruption of tephra whilst testing the use of micro-gravity changes to predict eruptions near the summit of Galeras volcano in Columbia in 1993. They thought the gravity meter was defective, when in fact the readings had gone off the scale, as rising ...
... volcanologists were killed and injured by a small eruption of tephra whilst testing the use of micro-gravity changes to predict eruptions near the summit of Galeras volcano in Columbia in 1993. They thought the gravity meter was defective, when in fact the readings had gone off the scale, as rising ...
Earthquake, Volcano and Mountain Review Sheet
... i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform boundary) c. Focus: the point underground where the rocks first begin to move d. Epicenter: the point on earth’s surface directly above the focus e. Stress: pressing, pulling or pushing of one object ag ...
... i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform boundary) c. Focus: the point underground where the rocks first begin to move d. Epicenter: the point on earth’s surface directly above the focus e. Stress: pressing, pulling or pushing of one object ag ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... volcano. They are blobs and particles of congealed lava that is ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. Composite volcanoes are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical con ...
... volcano. They are blobs and particles of congealed lava that is ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. Composite volcanoes are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical con ...
Volcanism in Iceland
... events occur offshore, too, especially off the southern coast. This kind of volcanism includes submarine volcanoes and newly formed volcanic islands such as the Jólnir Island. The plate tectonic theory says that the Earth’s surface is subdivided into a number of huge continental plates, which move e ...
... events occur offshore, too, especially off the southern coast. This kind of volcanism includes submarine volcanoes and newly formed volcanic islands such as the Jólnir Island. The plate tectonic theory says that the Earth’s surface is subdivided into a number of huge continental plates, which move e ...
Mount Kilauea, HI
... steep-sided slope. The eruption, in 1943, was made of ash and stones – loose pyroclastic material. The volcanic eruption lasted over a period of 8 years (which is a rare long period for this type of volcano, most last only a few months and rarely more than a few years). The volcano has been quiet si ...
... steep-sided slope. The eruption, in 1943, was made of ash and stones – loose pyroclastic material. The volcanic eruption lasted over a period of 8 years (which is a rare long period for this type of volcano, most last only a few months and rarely more than a few years). The volcano has been quiet si ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system. • Lithosphere pulls apart. • Less pressure on underlying rocks • Partial melting occurs • Large quantities of fluid basaltic magma are produced. ...
... volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system. • Lithosphere pulls apart. • Less pressure on underlying rocks • Partial melting occurs • Large quantities of fluid basaltic magma are produced. ...
ppt: volcano intro hook
... Why aren’t all volcanoes the same? Understanding why material comes out of a volcano explosively in one spot and not at another is related to what’s happening under the surface ...
... Why aren’t all volcanoes the same? Understanding why material comes out of a volcano explosively in one spot and not at another is related to what’s happening under the surface ...
Volcano Notes - MrTestaScienceClass
... Thicker, viscous Difficult for gases to escape, so pressure builds up ...
... Thicker, viscous Difficult for gases to escape, so pressure builds up ...
Section 6.1 Volcanic eruptions
... Thicker, viscous Difficult for gases to escape, so pressure builds up ...
... Thicker, viscous Difficult for gases to escape, so pressure builds up ...
The Origin and Petrogenesis of Mount Hasan (Small Mt. Hasan) and
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
Warm up question What hypothesis is Alfred Wegener known for
... volcanic vent. Become wider over time as materials fall back into the vent. Calderas – when a magma chamber is emptied the volcanic cone may collapse, forming a basin ...
... volcanic vent. Become wider over time as materials fall back into the vent. Calderas – when a magma chamber is emptied the volcanic cone may collapse, forming a basin ...
Volcano - Greenwich Central School
... A long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s ...
... A long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s ...
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.