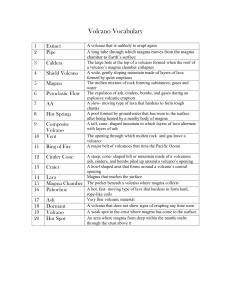
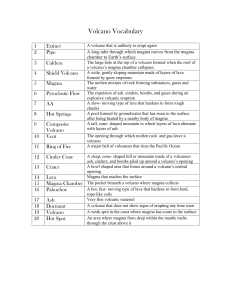
What IS A VOLCANO?
... Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks erupt through a volcano and come out as lava. The temperature of magma is extremely high while that of lava are lower as it cools down when it comes out under the ...
... Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks erupt through a volcano and come out as lava. The temperature of magma is extremely high while that of lava are lower as it cools down when it comes out under the ...
Study Guide: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
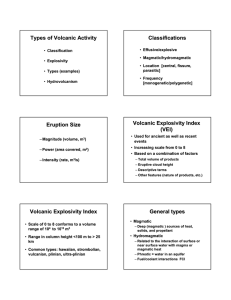
Types of Volcanic Activity Classifications Eruption Size Volcanic
... • Range in column height <100 m to > 25 km • Common types: hawaiian, hawaiian, strombolian, vulcanian, plinian, ultraultra-plinian ...
... • Range in column height <100 m to > 25 km • Common types: hawaiian, hawaiian, strombolian, vulcanian, plinian, ultraultra-plinian ...
notable events and disasters of 2014. highlights of volcanic eruptions
... HIKERS RETURNING: SATURDAY, SEPTEMBER 27, 2014 ...
... HIKERS RETURNING: SATURDAY, SEPTEMBER 27, 2014 ...
Chapter 29: Formation of Rocks
... Solid rock melts and becomes magma under certain conditions that lower the melting point of the material. ...
... Solid rock melts and becomes magma under certain conditions that lower the melting point of the material. ...
The Big Island
... • produced by current eruptive activity • covers the surface of most of the volcano ...
... • produced by current eruptive activity • covers the surface of most of the volcano ...
chapter 9 vocabulary terms
... Pyroclastic Flow (p. 255) – A highly heated mixture, largely of ash and pumice fragments, traveling down the flanks of a volcano or along the surface of the ground. ...
... Pyroclastic Flow (p. 255) – A highly heated mixture, largely of ash and pumice fragments, traveling down the flanks of a volcano or along the surface of the ground. ...
Chapter 13 Section 2
... expanding gases in the magma. • Other pyroclastic materials form when fragments of erupting lava cool and solidify as they fly through the air. • Scientists classify pyroclastic materials according to the sizes of the particles. ...
... expanding gases in the magma. • Other pyroclastic materials form when fragments of erupting lava cool and solidify as they fly through the air. • Scientists classify pyroclastic materials according to the sizes of the particles. ...
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... The Rock cycle was initially proposed by James Hutton Rocks are grouped into three main families based on their origin 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic. 1. IGNEOUS ROCKS: ...
... The Rock cycle was initially proposed by James Hutton Rocks are grouped into three main families based on their origin 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic. 1. IGNEOUS ROCKS: ...
volcanoes 1 - Earth Science Teachers` Association
... the sea but we cannot see them. The volcanoes under the sea erupt lava into very cold water which cools the lava down very quickly, forming into a dark dense rock consisting of very small crystals (basalt). Whereas, the lava from volcanoes erupting onto the land tends to cool more slowly which allow ...
... the sea but we cannot see them. The volcanoes under the sea erupt lava into very cold water which cools the lava down very quickly, forming into a dark dense rock consisting of very small crystals (basalt). Whereas, the lava from volcanoes erupting onto the land tends to cool more slowly which allow ...
science project 2012
... Plug Dome volcanoes spill loose fragments, (parts of the volcano) down its sides. Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, while others form short steep-sided lava flows known as “coulees.” ...
... Plug Dome volcanoes spill loose fragments, (parts of the volcano) down its sides. Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, while others form short steep-sided lava flows known as “coulees.” ...
Volcanoes
... Hazards Related to Volcanoes • Lava, the principal hazard? But not lifethreatening generally • Pyroclastics, more dangerous than lava flows ...
... Hazards Related to Volcanoes • Lava, the principal hazard? But not lifethreatening generally • Pyroclastics, more dangerous than lava flows ...
Directed Reading
... b. the nature of Earth’s tectonic plates. c. temperatures within Earth. d. the nature of Earth’s crust and mantle. ...
... b. the nature of Earth’s tectonic plates. c. temperatures within Earth. d. the nature of Earth’s crust and mantle. ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... volcanoes, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava dome volcanoes. A cinder cone volcano is the most simple type of volcano. They are blobs and particles of congealed lava that is ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and f ...
... volcanoes, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava dome volcanoes. A cinder cone volcano is the most simple type of volcano. They are blobs and particles of congealed lava that is ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and f ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
Chapter 7 - Florida Gateway College
... Match the type of lava (felsic/andesitic, mafic) with the type of viscosity (high or low viscosity) Pyroclastic flow (Definition, type of volcano that produces it) II - Volcanic activity relation to plate boundaries: Divergent plate boundaries (Type of volcano and volcanic activity) Convergent plate ...
... Match the type of lava (felsic/andesitic, mafic) with the type of viscosity (high or low viscosity) Pyroclastic flow (Definition, type of volcano that produces it) II - Volcanic activity relation to plate boundaries: Divergent plate boundaries (Type of volcano and volcanic activity) Convergent plate ...
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.