Viscosity Activity
... Background: Viscosity is a liquid’s “resistance to flow”. All Lava is made out of rock, but flows differently depending on silica content, amount of water, gas content and temperature. When lava erupts from a vent in the Earth’s crust it spreads out in all directions and eventually cools and becomes ...
... Background: Viscosity is a liquid’s “resistance to flow”. All Lava is made out of rock, but flows differently depending on silica content, amount of water, gas content and temperature. When lava erupts from a vent in the Earth’s crust it spreads out in all directions and eventually cools and becomes ...
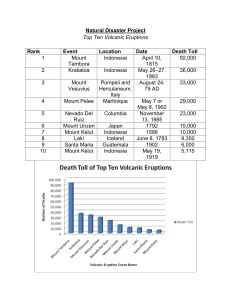
Natural Disaster Project Top Ten Volcanic Eruptions Rank Event
... city of Shimabaraon the island of Kyūshū, Japan’s southernmost main island.In 1792, the collapse of one of its several lava domes triggered a tsunami that killed about 15,000 people in Japan’s worst-ever volcanic-related disaster. The volcano was most recently active from 1990 to 1995, and a large e ...
... city of Shimabaraon the island of Kyūshū, Japan’s southernmost main island.In 1792, the collapse of one of its several lava domes triggered a tsunami that killed about 15,000 people in Japan’s worst-ever volcanic-related disaster. The volcano was most recently active from 1990 to 1995, and a large e ...
national geographic readings on volcanoes - Whitlock-Science
... What is the name of the tiny southernmost part of the Juan de Fuca plate subducting under northern California? 5. Whey is Glass Mountain in Lava Beds National Monument named as such? ...
... What is the name of the tiny southernmost part of the Juan de Fuca plate subducting under northern California? 5. Whey is Glass Mountain in Lava Beds National Monument named as such? ...
Volcanic Processes and Igneous Rocks
... The focus is the location in the crust where all of the seismic energy is released from. The epicenter is the location on the Earth’s surface and gives us coordinates and direction of where the center of the earthquake is located. 21. Describe how triangulation is used to locate the epicenter of an ...
... The focus is the location in the crust where all of the seismic energy is released from. The epicenter is the location on the Earth’s surface and gives us coordinates and direction of where the center of the earthquake is located. 21. Describe how triangulation is used to locate the epicenter of an ...
Lithosphere L > E Heat flowing in Earth`s core below the lithosphere
... When plates in the ocean shift (possibly due to the small earthquake that occurred in April 1990 prior to eruption), sulfur is spewed from the hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean. This sulfur in turn, feeds microbes. These microbes are at the bottom of the food chain. It all comes full cir ...
... When plates in the ocean shift (possibly due to the small earthquake that occurred in April 1990 prior to eruption), sulfur is spewed from the hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean. This sulfur in turn, feeds microbes. These microbes are at the bottom of the food chain. It all comes full cir ...
How Does Earth Work?
... Mt. Fuji, Japan – A classic example of a dacite to andesite composition composite volcano – often called a stratovolcano. These are built up from explosive and effusive eruptions producing alternating layers of pyroclastic rocks and lava flows. ...
... Mt. Fuji, Japan – A classic example of a dacite to andesite composition composite volcano – often called a stratovolcano. These are built up from explosive and effusive eruptions producing alternating layers of pyroclastic rocks and lava flows. ...
PowerPoint - Division for Planetary Sciences
... [email protected] - http://dps.aas.org/education/dpsdisc/ - Released 24 April 2009 ...
... [email protected] - http://dps.aas.org/education/dpsdisc/ - Released 24 April 2009 ...
CASCADES OF LAVA. 441 through these numerous craters into the
... through these numerous craters into the upper reservoir. The sides of the gulf, though composed of different strata of ancient lava, were perpendicular for about 400 feet, and rose from a wide horizontal ledge of solid black lava of irregular breadth, but extending completely round. Beneath this led ...
... through these numerous craters into the upper reservoir. The sides of the gulf, though composed of different strata of ancient lava, were perpendicular for about 400 feet, and rose from a wide horizontal ledge of solid black lava of irregular breadth, but extending completely round. Beneath this led ...
Ch 6 power point
... Volcanoes and volcanic hazards • Volcano – A vent through which lava, solid rock debris, volcanic ash, and gasses erupt from Earth’s crust to its surface – Can be explosive or nonexplosive ...
... Volcanoes and volcanic hazards • Volcano – A vent through which lava, solid rock debris, volcanic ash, and gasses erupt from Earth’s crust to its surface – Can be explosive or nonexplosive ...
Volcanic Landforms (pages 217*223)
... 2. Explain how the magma that hardens beneath the earth’s surface creates landforms. 3. Identify other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
... 2. Explain how the magma that hardens beneath the earth’s surface creates landforms. 3. Identify other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
Volcanoes - SPS186.org
... Sometimes a shield volcano contains hot gases or steam that sprays from the crater, creating a bright lava fountain. Since the paths of the lava flows are stable and predictable, scientists are often able to get very close to study them. Shield volcanoes can remain quietly active for long periods of ...
... Sometimes a shield volcano contains hot gases or steam that sprays from the crater, creating a bright lava fountain. Since the paths of the lava flows are stable and predictable, scientists are often able to get very close to study them. Shield volcanoes can remain quietly active for long periods of ...
Putting the Lava in the Lava Beds
... you may know, clear glass is nearly all silica. Rhyolite may contain as much as 77% silica and thus is responsible for the forming of obsidian, or "volcanic glass." Basalt, on the other hand, is less than one-half silica and is therefore less spectacular and looks more like what we might expect cool ...
... you may know, clear glass is nearly all silica. Rhyolite may contain as much as 77% silica and thus is responsible for the forming of obsidian, or "volcanic glass." Basalt, on the other hand, is less than one-half silica and is therefore less spectacular and looks more like what we might expect cool ...
Geology Library Notes Wk3.cwk (WP)
... As with more mafic volcanism, it is thought that the magma is created from melted mantle. What about the slope of the volcano? What makes it more felsic? Finally how would you expect the eruptive style to differ from more mafic volcanoes? ...
... As with more mafic volcanism, it is thought that the magma is created from melted mantle. What about the slope of the volcano? What makes it more felsic? Finally how would you expect the eruptive style to differ from more mafic volcanoes? ...
Erupting Volcano Model (916k PDF file)
... Cinders – Fragments of lava, commonly erupted in cinder cone volcanoes. Composite Volcano - A type of volcano in which the cone is very steep and built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a vo ...
... Cinders – Fragments of lava, commonly erupted in cinder cone volcanoes. Composite Volcano - A type of volcano in which the cone is very steep and built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a vo ...
2430 Volcano GUD v2 - Learning Resources
... Cinders – Fragments of lava, commonly erupted in cinder cone volcanoes. Composite Volcano - A type of volcano in which the cone is very steep and built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a vo ...
... Cinders – Fragments of lava, commonly erupted in cinder cone volcanoes. Composite Volcano - A type of volcano in which the cone is very steep and built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a vo ...
Volcanoes
... Eruptions of shield volcanoes are usually gentle rather than explosive, although the lava flows can still destroy roads, homes, and forests. Sometimes a shield volcano contains hot gases or steam that sprays from the crater, creating a bright lava fountain. Since the paths of the lava flows are stab ...
... Eruptions of shield volcanoes are usually gentle rather than explosive, although the lava flows can still destroy roads, homes, and forests. Sometimes a shield volcano contains hot gases or steam that sprays from the crater, creating a bright lava fountain. Since the paths of the lava flows are stab ...
Virtual Volcano
... Now go to the left hand side of the screen. Find the menu. Click on “volcano types.” How many common categories of volcanoes are there? ___________ Italy is home to what mountain that destroyed Pompeii in 79 ad? _____________ Now click on “cinder cone” in the bottom right hand side. Name two famous ...
... Now go to the left hand side of the screen. Find the menu. Click on “volcano types.” How many common categories of volcanoes are there? ___________ Italy is home to what mountain that destroyed Pompeii in 79 ad? _____________ Now click on “cinder cone” in the bottom right hand side. Name two famous ...
Lava and Volcanoes
... • Generally forms from a silica-rich magma • Such magmas typically are too viscous to flow far from the vent before cooling and crystallizing ...
... • Generally forms from a silica-rich magma • Such magmas typically are too viscous to flow far from the vent before cooling and crystallizing ...
5th Grade Chapter 1 “QUIZ ME” Questions
... 2. COMPARE What is the difference between magma and lava? 3. INFER Why does melted magma rise through the crust to the surface at convergent plate boundaries? 4. DESCRIBE What causes explosive volcanic eruptions? ...
... 2. COMPARE What is the difference between magma and lava? 3. INFER Why does melted magma rise through the crust to the surface at convergent plate boundaries? 4. DESCRIBE What causes explosive volcanic eruptions? ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawaiian Islands ...
... tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawaiian Islands ...
Forces of Nature Schools Synopsis.indd
... natural forces that helped create life on our green planet can also destroy it. With National Geographic’s trademark combination of scientific excellence, dramatic storytelling skill and human emotion, Forces of Nature will showcase the awesome spectacle of earthquakes, volcanoes and severe storms a ...
... natural forces that helped create life on our green planet can also destroy it. With National Geographic’s trademark combination of scientific excellence, dramatic storytelling skill and human emotion, Forces of Nature will showcase the awesome spectacle of earthquakes, volcanoes and severe storms a ...
Hot Spot Volcanoes
... In fact, the 7 main Hawaiian Islands are just the southern most portion of two great undersea mountain ranges, composed of hundreds of volcanoes, that runs for 6000 kilometers (4000 miles) across the floor of the Pacific Ocean ...
... In fact, the 7 main Hawaiian Islands are just the southern most portion of two great undersea mountain ranges, composed of hundreds of volcanoes, that runs for 6000 kilometers (4000 miles) across the floor of the Pacific Ocean ...
Volcano - The Disaster Center
... What are volcanoes, and what causes them to erupt? A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the earth’s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive products — layers of lava, ashflows, and ash. When pr ...
... What are volcanoes, and what causes them to erupt? A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the earth’s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive products — layers of lava, ashflows, and ash. When pr ...
Shield volcano

A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid magmaflows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes contain low-viscosity magma, which gives them flowing mafic lava.