* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viscosity Activity
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
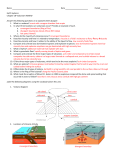
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ________ Period: _____ Viscosity Activity Background: Viscosity is a liquid’s “resistance to flow”. All Lava is made out of rock, but flows differently depending on silica content, amount of water, gas content and temperature. When lava erupts from a vent in the Earth’s crust it spreads out in all directions and eventually cools and becomes a solid. Volcanoes may erupt many times or only a couple of times. The repeated eruptions and lava flows are what build the different landforms we see on earth’s surface. Purpose: To investigate how the viscosity of lava will affect the type of volcanic landform that is created. Materials: 3 paper plates 3 paper cups, with a ¼ cup of flour in each 1 Plastic spoon ruler Procedure: 1. Label each plate; one is High Viscosity, one is Medium viscosity, the last is Low Viscosity. 2. Next label the three cups, high, medium and low. 3. In the cup marked high, pour 30ml (about 2 Tablespoons) of water in to the cup and mix well. 4. Slowly, pour the mixture on to the middle of the plate marked high viscosity and make observations of how fast the mixture pours. When the flow stops measure its diameter, in metric units. 5. In the medium cup slowly, pour 37ml (2 ½ tablespoon) water and mix. Pour slowly onto the plate marked medium and record your observations. 6. In the cup marked low viscosity slowly, pour 52 ml. (3 ½ Tablespoons) water and mix. Pour slowly onto the plate marked low viscosity and record your observations. Data Chart A: Viscosity Describe how it poured, speed, time, etc. Diameter of the lava flow What type of landform will this lava create. High Med Low Analysis: 1. How does viscosity affect the shape of volcanoes? Be specific, using information from the activity. 2. What do you think would happen to the flow rate of the liquids if a solid such as sand was added before pouring? 3. How would this relate to a composite volcano? 4. Describe the 3 main types of volcanoes based upon the viscosity of the eruption. Conclusion: Sum up the learning of this unit experience. Explain viscosity. How is this related to volcanoes? How are the 3 types of volcanoes formed with regards to viscosity?