Lithosphere L > E Heat flowing in Earth`s core below the lithosphere
... This also harmed the atmosphere due to evaporation. E > B > L > A > H Gases emitted from volcanoes can integrate with moisture in the air and become acid rain (furthering the damage done to the lithosphere and atmosphere). When plates in the ocean shift (possibly due to the small earthquake that occ ...
... This also harmed the atmosphere due to evaporation. E > B > L > A > H Gases emitted from volcanoes can integrate with moisture in the air and become acid rain (furthering the damage done to the lithosphere and atmosphere). When plates in the ocean shift (possibly due to the small earthquake that occ ...
Earth Science Chapter 6 Volcanoes
... – Vent - an opening through which the magma leaves the volcano – Crater - a bowl-shaped area around a volcano's central vent. – Pyroclastic Flow -an explosive fast-moving current of hot gas and rock (1800 0F) hurls out ash, cinders, and bombs. ...
... – Vent - an opening through which the magma leaves the volcano – Crater - a bowl-shaped area around a volcano's central vent. – Pyroclastic Flow -an explosive fast-moving current of hot gas and rock (1800 0F) hurls out ash, cinders, and bombs. ...
Volcanoes
... by the mud, rock hard by the time I saw it a few years later. However, if any good came from this event, it was that it opened many people's eyes around the world to the dangers posed by volcanoes and the relatively simple solutions to preventing tragedies like this. ...
... by the mud, rock hard by the time I saw it a few years later. However, if any good came from this event, it was that it opened many people's eyes around the world to the dangers posed by volcanoes and the relatively simple solutions to preventing tragedies like this. ...
Volcanoes Page 1 of 4 I. Introduction: two predominant types of lava
... c. Interbedded lavas and pyroclastics—andesitic magma 1) fluid lavas early 2) pyroclastics build steep upper slopes of coarse material, finer widespread 3) lavas stabilize this area—short central vent flows d. Most violent type of activity (e.g. Vesuvius) e. Often produce nuée ardente 1) Fiery pyroc ...
... c. Interbedded lavas and pyroclastics—andesitic magma 1) fluid lavas early 2) pyroclastics build steep upper slopes of coarse material, finer widespread 3) lavas stabilize this area—short central vent flows d. Most violent type of activity (e.g. Vesuvius) e. Often produce nuée ardente 1) Fiery pyroc ...
Volcanoes/REVIEW
... 5. What other eruption is there besides a quiet eruption and how is it different than a quiet eruption? _________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What are the three types of volcanoes? ________________________________________________ 7. H ...
... 5. What other eruption is there besides a quiet eruption and how is it different than a quiet eruption? _________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What are the three types of volcanoes? ________________________________________________ 7. H ...
Volcanology - Departments
... Types of Lava • Lava resulting from the process of subduction is described as ANDESITIC and occurs as/at: • Island arcs • Destructive plate boundaries where oceanic crust is being destroyed and gases are being added ...
... Types of Lava • Lava resulting from the process of subduction is described as ANDESITIC and occurs as/at: • Island arcs • Destructive plate boundaries where oceanic crust is being destroyed and gases are being added ...
VolcanicHazards2
... -change in heat output -change in the composition of gases -local seismic activity ...
... -change in heat output -change in the composition of gases -local seismic activity ...
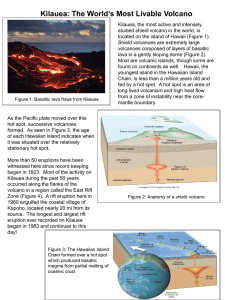
Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
... Kapoho, located nearly 20 mi from its source. The longest and largest rift eruption ever recorded on Kilauea began in 1983 and continues to this day! ...
... Kapoho, located nearly 20 mi from its source. The longest and largest rift eruption ever recorded on Kilauea began in 1983 and continues to this day! ...
Chapter 4 volcanoes powerpoint notes
... Volcanoes are conical or dome-shaped landforms built by the emission of lava and its contained gasses (or pyroclastics) from a constricted vent onto Earth’s surface. Lava rises in a narrow, pipe-like conduit (vent) from a magma chamber beneath. ...
... Volcanoes are conical or dome-shaped landforms built by the emission of lava and its contained gasses (or pyroclastics) from a constricted vent onto Earth’s surface. Lava rises in a narrow, pipe-like conduit (vent) from a magma chamber beneath. ...
Active
... There are 33 active volcanoes in the US Most are at convergent plate boundaries in Alaska and N. California, Oregon, and Washington. These are all stratovolcanoes, which are the most dangerous in terms of explosive activity. Some are on or near hotspots: Hawaii’s volcanoes, and Yellowstone Some are ...
... There are 33 active volcanoes in the US Most are at convergent plate boundaries in Alaska and N. California, Oregon, and Washington. These are all stratovolcanoes, which are the most dangerous in terms of explosive activity. Some are on or near hotspots: Hawaii’s volcanoes, and Yellowstone Some are ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... volcanic chain • The only active volcano is over the hot spot ...
... volcanic chain • The only active volcano is over the hot spot ...
Ice Core PowerPoint notes
... History – Ice Cores Why is ice key to our understanding of earth’s history? ...
... History – Ice Cores Why is ice key to our understanding of earth’s history? ...
THIS Volcano powerpoint
... There is a great range in the severity of volcanic eruptions. Many eruptions are relatively quiet and are characterized by the calm, nonviolent extrusion of lava flows on the earth's surface. If the material is fluid in nature (solid and semi-solid) this type of flow is called Pyroclastic Flow (the ...
... There is a great range in the severity of volcanic eruptions. Many eruptions are relatively quiet and are characterized by the calm, nonviolent extrusion of lava flows on the earth's surface. If the material is fluid in nature (solid and semi-solid) this type of flow is called Pyroclastic Flow (the ...
Volcanoes
... Plug: mass of solid lava that blocks a volcano’s vent. Geothermal energy: power made from heat within the Earth. Geyser: fountain of hot water and steam erupting from the ground in a volcanic area. ...
... Plug: mass of solid lava that blocks a volcano’s vent. Geothermal energy: power made from heat within the Earth. Geyser: fountain of hot water and steam erupting from the ground in a volcanic area. ...
3 types of Volcanoes Reading
... The lava and pyroclastic material that erupt from volcanoes create a variety of landforms. Perhaps the best known of all volcanic landforms are the volcanoes themselves. Volcanoes result from the buildup of rock around a vent. Three basic types of volcanoes are illustrated in Figure 4. Shield volcan ...
... The lava and pyroclastic material that erupt from volcanoes create a variety of landforms. Perhaps the best known of all volcanic landforms are the volcanoes themselves. Volcanoes result from the buildup of rock around a vent. Three basic types of volcanoes are illustrated in Figure 4. Shield volcan ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... Lassen Volcanic National Park is home to smoking fumaroles, meadows freckled with wildflowers, clear mountain lakes, and numerous volcanoes. Jagged peaks tell the story of its eruptive past while hot water continues to mold the land. Lassen Volcanic offers opportunities to discover the wonder and my ...
... Lassen Volcanic National Park is home to smoking fumaroles, meadows freckled with wildflowers, clear mountain lakes, and numerous volcanoes. Jagged peaks tell the story of its eruptive past while hot water continues to mold the land. Lassen Volcanic offers opportunities to discover the wonder and my ...
Introduction to volcano characteristics and activity
... explosions such as ash. Ash-cinder, and composite (stratovolcano) are often composed of tephra which has been erupted in explosive events therefore are more common at convergent plate boundaries. These may be associated with ash, lapilli, bombs, pyroclastic flows and viscous lava. ...
... explosions such as ash. Ash-cinder, and composite (stratovolcano) are often composed of tephra which has been erupted in explosive events therefore are more common at convergent plate boundaries. These may be associated with ash, lapilli, bombs, pyroclastic flows and viscous lava. ...
Volcanoes
... Other Volcanic Activity • Geyser – Rising hot water and steam that gets trapped underground and builds pressure until it sprays to the surface ...
... Other Volcanic Activity • Geyser – Rising hot water and steam that gets trapped underground and builds pressure until it sprays to the surface ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Pyroclastic volcano (cinder or scoria cones, 2 km across and < 0.3 km high) volcanic complex Dome lava flow ash-flow tuff (ignimbrite) flood basalt caldera Extrusive bodies – Fissure Landforms Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic ...
... Pyroclastic volcano (cinder or scoria cones, 2 km across and < 0.3 km high) volcanic complex Dome lava flow ash-flow tuff (ignimbrite) flood basalt caldera Extrusive bodies – Fissure Landforms Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic ...
Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
... and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colo ...
... and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colo ...
Mount Edziza volcanic complex

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.Most of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex is encompassed within a large provincial park called Mount Edziza Provincial Park. Named after Mount Edziza, this 2,660.95 km2 (1,027.40 sq mi) park was established in 1972 to preserve the volcanic and cultural treasures unique to the northern British Columbia area. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is remote, and, without roads, accessible only along trails. The easiest access is from Highway 37 and a spur road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek. From Kinaskan Lake, on Highway 37, a poorly maintained trail extends west for 30 kilometres (19 mi) into the heart of the complex. From Telegraph Creek another trail extends east for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to the north slope of Mount Edziza.