notable events and disasters of 2014. highlights of volcanic eruptions
... WHAT HAPPENED? • After a week of seismic activity rattled the uninhabited area 200 miles (320 kilometers) east of the capital of Reykjavik with thousands of earthquakes, Iceland's Bardarbunga volcano began erupting Saturday (Aug. 23rd) under the country's largest glacier. ...
... WHAT HAPPENED? • After a week of seismic activity rattled the uninhabited area 200 miles (320 kilometers) east of the capital of Reykjavik with thousands of earthquakes, Iceland's Bardarbunga volcano began erupting Saturday (Aug. 23rd) under the country's largest glacier. ...
Types of Volcanoes
... Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills out of a central vent or group of vents. A broad shaped, gently sloping cone is formed. This is caused by the very fluid, basaltic lava which can't be piled up into steep mounds Shield volcanoes may be ...
... Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills out of a central vent or group of vents. A broad shaped, gently sloping cone is formed. This is caused by the very fluid, basaltic lava which can't be piled up into steep mounds Shield volcanoes may be ...
VOLCANOES
... • Eight main islands are exposed tips of the Hawaiian Ridge. • Age range is modern to ~6 million years old. • Volcanoes develop on the Pacific Plate as it moves across the Hawaiian Hotspot. ...
... • Eight main islands are exposed tips of the Hawaiian Ridge. • Age range is modern to ~6 million years old. • Volcanoes develop on the Pacific Plate as it moves across the Hawaiian Hotspot. ...
Hazards Chapter 3a
... destruction machines that we often make them out to be: (1) volcanoes frequently give us warning of their actions (2) many volcanoes are located in rural uninhabited places (3) if the eruption produces lava flows rather than poisonous gas or flaming particulates, it is more possible to evacuate and ...
... destruction machines that we often make them out to be: (1) volcanoes frequently give us warning of their actions (2) many volcanoes are located in rural uninhabited places (3) if the eruption produces lava flows rather than poisonous gas or flaming particulates, it is more possible to evacuate and ...
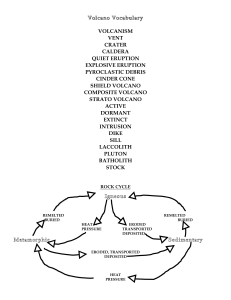
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... AA lava: Blocky, sharp and rough lava Columnar Joints: 5- to 7-sided columns of basalt. Produced by slow cooling. Pillow Lava: Surface like pile of pillows. Erupted under water Pyroclastics: (Tephra) Lava Fragments. Bomb: Large pieces. More than 64 mm in diameter. Cinders: (Lapilli) Up to 64mm Ash: ...
... AA lava: Blocky, sharp and rough lava Columnar Joints: 5- to 7-sided columns of basalt. Produced by slow cooling. Pillow Lava: Surface like pile of pillows. Erupted under water Pyroclastics: (Tephra) Lava Fragments. Bomb: Large pieces. More than 64 mm in diameter. Cinders: (Lapilli) Up to 64mm Ash: ...
Geology 101 Homework 4
... 4) Explain the three ways magma forms inside the Earth (p. 140). What is the relationship between plate tectonic setting and the way magma forms? (p. 156) Which magma formation process occurs most frequently inside the Earth? 5) What shapes do bodies of igneous rock form when they intrude the Earth? ...
... 4) Explain the three ways magma forms inside the Earth (p. 140). What is the relationship between plate tectonic setting and the way magma forms? (p. 156) Which magma formation process occurs most frequently inside the Earth? 5) What shapes do bodies of igneous rock form when they intrude the Earth? ...
Problem 13 - Macmillan Learning
... apart, South America moved substantially westward over a period of about 220 million years. During that time it is estimated South America became about 38 km narrower in its east-west dimension due to strain. WQ13.1. If we take the width of the continent to be 3800 km, what has been the average stra ...
... apart, South America moved substantially westward over a period of about 220 million years. During that time it is estimated South America became about 38 km narrower in its east-west dimension due to strain. WQ13.1. If we take the width of the continent to be 3800 km, what has been the average stra ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park - Cook/Lowery15
... changed over time so they can predict where the best place would be to plant new plants in an area where they predict might not be damaged by lava. ...
... changed over time so they can predict where the best place would be to plant new plants in an area where they predict might not be damaged by lava. ...
Geo Fun - Latitude Festival
... 4. What is another word for the "hole", or vent, in the top of the volcano? 5. Where is the main vent of the paper model volcano? Can you find a second vent drawn on the side of the model volcano? 6. Why are most volcanoes on Earth cone-shaped? VOCABULARY (Discuss the meanings and usage of the follo ...
... 4. What is another word for the "hole", or vent, in the top of the volcano? 5. Where is the main vent of the paper model volcano? Can you find a second vent drawn on the side of the model volcano? 6. Why are most volcanoes on Earth cone-shaped? VOCABULARY (Discuss the meanings and usage of the follo ...
Notes -
... starts from Northern California and stretches to northern Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The subduction zone has created large earthquakes, including the Cascadia earthquake, which took place at the evening of January 26, 1700 by a magnitude 8.7 - 9.2 megathrust earthquake. Unlike in most subdu ...
... starts from Northern California and stretches to northern Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The subduction zone has created large earthquakes, including the Cascadia earthquake, which took place at the evening of January 26, 1700 by a magnitude 8.7 - 9.2 megathrust earthquake. Unlike in most subdu ...
Volcano - watertown.k12.wi.us
... 1. ___________________________ - is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________ ...
... 1. ___________________________ - is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________ ...
clozevolcanonotes
... 1. ___________________________ - is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________ ...
... 1. ___________________________ - is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________ ...
UNDERSTANDING VOLCANOS
... Other volcanic landforms Fissure eruptions and lava plateaus Fluid basaltic lava extruded from crustal fractures called fissures Example: Columbia River Plateau Lava domes Bulbous mass of congealed lava Associated with explosive eruptions of gas-rich magma ...
... Other volcanic landforms Fissure eruptions and lava plateaus Fluid basaltic lava extruded from crustal fractures called fissures Example: Columbia River Plateau Lava domes Bulbous mass of congealed lava Associated with explosive eruptions of gas-rich magma ...
DStroupTalk3
... environments on Mars; these are places that prebiotic chemistry or life could be going on • “Follow the Water” has become the new slogan for NASA’s new Mars Program ...
... environments on Mars; these are places that prebiotic chemistry or life could be going on • “Follow the Water” has become the new slogan for NASA’s new Mars Program ...
Types of Volcanoes Dangers from Composite Cones Pyroclastic
... Pahoehoe flow - looks like twisted and braided rope. aa flow – rough, jagged blocks with sharp edges. Melted rhyolitic rock flows very slowly. ...
... Pahoehoe flow - looks like twisted and braided rope. aa flow – rough, jagged blocks with sharp edges. Melted rhyolitic rock flows very slowly. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – Crater - steep-walled depression at the summit, generally less than 1 km in diameter – Caldera - a summit depression typically greater than 1 km in diameter, produced by collapse following a massive eruption ...
... – Crater - steep-walled depression at the summit, generally less than 1 km in diameter – Caldera - a summit depression typically greater than 1 km in diameter, produced by collapse following a massive eruption ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – Crater - steep-walled depression at the summit, generally less than 1 km in diameter – Caldera - a summit depression typically greater than 1 km in diameter, produced by collapse following a massive eruption ...
... – Crater - steep-walled depression at the summit, generally less than 1 km in diameter – Caldera - a summit depression typically greater than 1 km in diameter, produced by collapse following a massive eruption ...
QR-Volcanoes 59 points Using separate pieces of paper, answer
... 9. Name a prominent volcano and geographical location for each of the three main types. 10. Sketch a volcano and identify its morphologic parts: crater, volcanic conduit, flanks, magma chamber, and caldera (assuming the volcano is dormant) 11. Extensive pyroclastic flow deposits are associated with ...
... 9. Name a prominent volcano and geographical location for each of the three main types. 10. Sketch a volcano and identify its morphologic parts: crater, volcanic conduit, flanks, magma chamber, and caldera (assuming the volcano is dormant) 11. Extensive pyroclastic flow deposits are associated with ...
Classifying Volcanoes
... a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being released as an eruption b. Magma- liquid rock that is beneath the surface of the Earth c. Lava- liquid rock that is above the surface of the Earth d. Central Pipe- main tube that magma flows through from the magma chamber e ...
... a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being released as an eruption b. Magma- liquid rock that is beneath the surface of the Earth c. Lava- liquid rock that is above the surface of the Earth d. Central Pipe- main tube that magma flows through from the magma chamber e ...
Volcanic Eruptions - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is
... - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is forced to the Earth’s surface - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano ...
... - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is forced to the Earth’s surface - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano ...
F08 5 Emplacement
... Hey…it’s a rough world out there! Earth’s surface is dynamic Advantages: transfer of abundant energy ...
... Hey…it’s a rough world out there! Earth’s surface is dynamic Advantages: transfer of abundant energy ...
Volcanic Landforms
... fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of flows of highly fluid ...
... fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of flows of highly fluid ...
Mount Edziza volcanic complex

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.Most of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex is encompassed within a large provincial park called Mount Edziza Provincial Park. Named after Mount Edziza, this 2,660.95 km2 (1,027.40 sq mi) park was established in 1972 to preserve the volcanic and cultural treasures unique to the northern British Columbia area. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is remote, and, without roads, accessible only along trails. The easiest access is from Highway 37 and a spur road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek. From Kinaskan Lake, on Highway 37, a poorly maintained trail extends west for 30 kilometres (19 mi) into the heart of the complex. From Telegraph Creek another trail extends east for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to the north slope of Mount Edziza.