Types of Volcanic Activity Classifications Eruption Size Volcanic
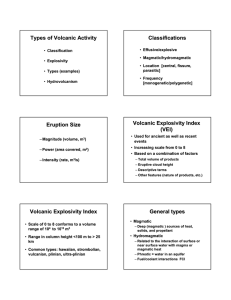
... Volcanic Explosivity Index • Scale of 0 to 8 conforms to a volume range of 104 to 1012 m3 • Range in column height <100 m to > 25 km • Common types: hawaiian, hawaiian, strombolian, vulcanian, plinian, ultraultra-plinian ...
... Volcanic Explosivity Index • Scale of 0 to 8 conforms to a volume range of 104 to 1012 m3 • Range in column height <100 m to > 25 km • Common types: hawaiian, hawaiian, strombolian, vulcanian, plinian, ultraultra-plinian ...
Volcanoes
... earth’s formation; more heat is generated by the decay of radioactive elements in the earth • Volcanoes are generated at: ...
... earth’s formation; more heat is generated by the decay of radioactive elements in the earth • Volcanoes are generated at: ...
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... ejected from the volcano and deposited around the vent produces the shape. B. Types 1. Cinder Cone- is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly ...
... ejected from the volcano and deposited around the vent produces the shape. B. Types 1. Cinder Cone- is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly ...
Landforms at plate margins – Volcanoes and supervolcanoes
... A supervolcano is a volcano that erupts with a massive volume of material, much more than from a normal volcano – at least 1000km3 of magma. To give you some idea of the great volume, the big eruption of Mount St Helens in the USA in 1980 produced 1km3. A super-volcanic eruption alters the landscape ...
... A supervolcano is a volcano that erupts with a massive volume of material, much more than from a normal volcano – at least 1000km3 of magma. To give you some idea of the great volume, the big eruption of Mount St Helens in the USA in 1980 produced 1km3. A super-volcanic eruption alters the landscape ...
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... ejected from the volcano and deposited around the vent produces the shape. B. Types 1. Cinder Cone- is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly ...
... ejected from the volcano and deposited around the vent produces the shape. B. Types 1. Cinder Cone- is a small, steep-sided volcano made mostly of cinders & tuff (tephra), often with lava flows intermixed. The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly ...
Lab 5 Lecture
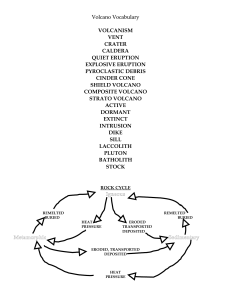
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... • Lithosphere pulls apart. • Less pressure on underlying rocks • Partial melting occurs • Large quantities of fluid basaltic magma are produced. ...
... • Lithosphere pulls apart. • Less pressure on underlying rocks • Partial melting occurs • Large quantities of fluid basaltic magma are produced. ...
Earth Science--Ch 9 Volcanoes Review Guide
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
Chapter 5 lesson 2
... a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano the area covered by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent a bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening a material found in magma that i ...
... a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano the area covered by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent a bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening a material found in magma that i ...
1 - Daniel O`Brien
... 2. Most Active Volcanic Region and Recent Eruption in Canada The most active volcanic region in Canada is the Stikine Volcanic Belt (or Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province). This massive volcanic region stretches from just north of Prince Rupert, into the Yukon Territory and the Alaska border, an ...
... 2. Most Active Volcanic Region and Recent Eruption in Canada The most active volcanic region in Canada is the Stikine Volcanic Belt (or Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province). This massive volcanic region stretches from just north of Prince Rupert, into the Yukon Territory and the Alaska border, an ...
File
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
Lesson 2 - Humanities.Com
... Try to write down a definition for volcanoes Try to note down a famous volcano. ...
... Try to write down a definition for volcanoes Try to note down a famous volcano. ...
Volcano Notes - MrTestaScienceClass
... Areas of Earth’s surface through which magma & volcanic gas passes Creative Forces forming fertile farmland & large mountains Destructive Forces Turning mountains into clouds of ash & rock, destroying forests & homes ...
... Areas of Earth’s surface through which magma & volcanic gas passes Creative Forces forming fertile farmland & large mountains Destructive Forces Turning mountains into clouds of ash & rock, destroying forests & homes ...
Section 6.1 Volcanic eruptions
... Areas of Earth’s surface through which magma & volcanic gas passes Creative Forces forming fertile farmland & large mountains Destructive Forces Turning mountains into clouds of ash & rock, destroying forests & homes ...
... Areas of Earth’s surface through which magma & volcanic gas passes Creative Forces forming fertile farmland & large mountains Destructive Forces Turning mountains into clouds of ash & rock, destroying forests & homes ...
File - Dengelscience
... Judge, then, what must have been our astonishment, as we entered the basin at mid-afternoon of our second day's travel, to see in the clear sunlight, at no great distance, an immense volume of clear, sparkling water projected into the air to the height of one hundred and twenty-five feet. "Geysers! ...
... Judge, then, what must have been our astonishment, as we entered the basin at mid-afternoon of our second day's travel, to see in the clear sunlight, at no great distance, an immense volume of clear, sparkling water projected into the air to the height of one hundred and twenty-five feet. "Geysers! ...
Challenge and Extension - Effingham County Schools
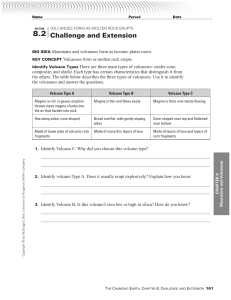
... KEY CONCEPT Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts. Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it from the others. The table below describes the three types of volcanoes. Use it to identify ...
... KEY CONCEPT Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts. Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it from the others. The table below describes the three types of volcanoes. Use it to identify ...
Volcanoes - LambertEarth
... through which magma and volcanic gases pass. Explosion of a volcanic eruption can turn an entire ...
... through which magma and volcanic gases pass. Explosion of a volcanic eruption can turn an entire ...
Unit test review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Distribution of volcanoes Geologic formations (pillow basalt, columnar jointing, plateau basalt) What comes out of a volcano? How does it affect surrounding areas? Effects of ash fall? Viscosity of lava: Aa, pahoehoe, what changes it’s viscosity Pysroclastic flow: how is it formed Volcanic dome Erup ...
... Distribution of volcanoes Geologic formations (pillow basalt, columnar jointing, plateau basalt) What comes out of a volcano? How does it affect surrounding areas? Effects of ash fall? Viscosity of lava: Aa, pahoehoe, what changes it’s viscosity Pysroclastic flow: how is it formed Volcanic dome Erup ...
volcanoes-and-climate
... • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic eruptions can blast material up into the stratospher ...
... • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic eruptions can blast material up into the stratospher ...
Guidance for GEOGRAPHY End of Year
... covered in geography during this academic year. You will have some lesson time in Week 3 to revise, but you may want to take your exercise book home to do some extra revision. The questions in the examination will be based on the unit ‘Earthquakes and Volcanoes’. Here is a breakdown of what yo ...
... covered in geography during this academic year. You will have some lesson time in Week 3 to revise, but you may want to take your exercise book home to do some extra revision. The questions in the examination will be based on the unit ‘Earthquakes and Volcanoes’. Here is a breakdown of what yo ...
The Nature of Volcanoes and Types updated.notebook
... Click on the image above to watch a clip of volcanic hazards and preventions. ...
... Click on the image above to watch a clip of volcanic hazards and preventions. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... – Gases expand within a magma as it nears the Earth’s surface due to decreasing pressure – The violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma ...
... – Gases expand within a magma as it nears the Earth’s surface due to decreasing pressure – The violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape from magma ...
Cascades?
... impending eruption, but together with other observations (deformation, gas emission, temperature changes) they provide one important and early clue when eruptions may be approaching. Volcano seismologists track not only earthquakes, but also various kinds of seismic signals with special characterist ...
... impending eruption, but together with other observations (deformation, gas emission, temperature changes) they provide one important and early clue when eruptions may be approaching. Volcano seismologists track not only earthquakes, but also various kinds of seismic signals with special characterist ...
Chapter 9 - Volcanoes
... time and are composed of pyroclastic materials such as ash. • Composite Cones – one of the most common types formed from alternating explosive/nonexplosive eruptions and lava flows. ...
... time and are composed of pyroclastic materials such as ash. • Composite Cones – one of the most common types formed from alternating explosive/nonexplosive eruptions and lava flows. ...
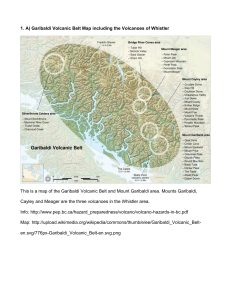
Mount Edziza volcanic complex

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.Most of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex is encompassed within a large provincial park called Mount Edziza Provincial Park. Named after Mount Edziza, this 2,660.95 km2 (1,027.40 sq mi) park was established in 1972 to preserve the volcanic and cultural treasures unique to the northern British Columbia area. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is remote, and, without roads, accessible only along trails. The easiest access is from Highway 37 and a spur road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek. From Kinaskan Lake, on Highway 37, a poorly maintained trail extends west for 30 kilometres (19 mi) into the heart of the complex. From Telegraph Creek another trail extends east for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to the north slope of Mount Edziza.