Monitoring Methods
... Chemistry — As the molten material (magma) rises to shallow levels, gases are released and they rise to the surface. Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured ...
... Chemistry — As the molten material (magma) rises to shallow levels, gases are released and they rise to the surface. Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured ...
Volcano Facts
... area believed that Vulcano was the chimney of the forge of Vulcan -- the blacksmith of the Roman gods. ...
... area believed that Vulcano was the chimney of the forge of Vulcan -- the blacksmith of the Roman gods. ...
Build a Volcano
... Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the surface of Earth. The term ...
... Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the surface of Earth. The term ...
10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions
... There are three major types of volcanoes (and one minor): • Shield volcanoes • Cinder cones • Composite/Stratovolcano • Lava domes (minor) ...
... There are three major types of volcanoes (and one minor): • Shield volcanoes • Cinder cones • Composite/Stratovolcano • Lava domes (minor) ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... middle of the Atlantic Ocean. There is under the ocean a long range of volcanic mountains called the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Range. Scientists believe that the volcano and earthquake activity are due to the formation of new parts of the Earth’s crust along the ridge. The volcanic island of Iceland is par ...
... middle of the Atlantic Ocean. There is under the ocean a long range of volcanic mountains called the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Range. Scientists believe that the volcano and earthquake activity are due to the formation of new parts of the Earth’s crust along the ridge. The volcanic island of Iceland is par ...
Volcano Menu
... • Volcanic Hazards – Time between eruptions for composite cones can span hundreds of years. (Dormant Volcano) – Example: Mt. St. Helens 123 years. – People may be unaware of the danger. ...
... • Volcanic Hazards – Time between eruptions for composite cones can span hundreds of years. (Dormant Volcano) – Example: Mt. St. Helens 123 years. – People may be unaware of the danger. ...
Parts of a Volcano
... Another theory is that hot spots are magma plumes along cracks in the plates. Hot spots always form long chains of islands. What theory is true??? Yellowstone is a hot spot. It is unusual to have a hot spot under a continent. ...
... Another theory is that hot spots are magma plumes along cracks in the plates. Hot spots always form long chains of islands. What theory is true??? Yellowstone is a hot spot. It is unusual to have a hot spot under a continent. ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
Types of Volcano
... built up only from layers of lava. They produce lots of lava but they tend not to erupt violently. Layers of Lava ...
... built up only from layers of lava. They produce lots of lava but they tend not to erupt violently. Layers of Lava ...
Do All VolCAnoES ERupT In THE SAmE WAy?
... of volcano. There are four main types New Guinea, on 21 January 1951 took local people of volcano and they each erupt in by surprise. Many people had not even realised different ways: the mountain was a volcano until the minor • Shield volcanoes have a low, flat shape. eruption three days earlier. ...
... of volcano. There are four main types New Guinea, on 21 January 1951 took local people of volcano and they each erupt in by surprise. Many people had not even realised different ways: the mountain was a volcano until the minor • Shield volcanoes have a low, flat shape. eruption three days earlier. ...
Introduction to Volcanism and Plate Tectonic Overview
... vesicular: frothy (trapped gas bubbles)! ...
... vesicular: frothy (trapped gas bubbles)! ...
Volcanoes
... moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface 3. Vent – the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano 4. Lava flow – the area cover by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent 5. Crater – a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening ...
... moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface 3. Vent – the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano 4. Lava flow – the area cover by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent 5. Crater – a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening ...
Shield Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Cinder Cone Volcanoes
... Cinder cone volcanoes are smaller than shield volcanoes and composite volcanoes. If the eruption contains thick magma, the gas pressure shatters the rock within the volcano into small pieces. In other cases, the lava in the air may harden and fall as fragments. These small pieces are called cinders. ...
... Cinder cone volcanoes are smaller than shield volcanoes and composite volcanoes. If the eruption contains thick magma, the gas pressure shatters the rock within the volcano into small pieces. In other cases, the lava in the air may harden and fall as fragments. These small pieces are called cinders. ...
Volcanoes
... oLife span of a few years oCommonly built from gravel size lava rock fragments called cinders oViolent eruptions, dangerous when close---High pressure gas bubbles causes thick lava to explode into the air, lava begins to cool as it rises and falls becoming very sticky oWhen lava hits the ground it s ...
... oLife span of a few years oCommonly built from gravel size lava rock fragments called cinders oViolent eruptions, dangerous when close---High pressure gas bubbles causes thick lava to explode into the air, lava begins to cool as it rises and falls becoming very sticky oWhen lava hits the ground it s ...
PowerPoint explanation of volcanic impact on climate
... • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic eruptions can blast material up into the stratospher ...
... • If the air is then warmer than the surrounding air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic eruptions can blast material up into the stratospher ...
Volcanoes by Marida Torosyan and Ani Tashyan
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
Volcano Glossary III
... Lava flows that are characterized by rough, broken rock fragments on the surface and top of the flow, and a molten center. As the flow is moving slowly the bottom stays in place and the front moves forward, while breaking up and then flowing over its own debris. Gas from the molten lava interior mig ...
... Lava flows that are characterized by rough, broken rock fragments on the surface and top of the flow, and a molten center. As the flow is moving slowly the bottom stays in place and the front moves forward, while breaking up and then flowing over its own debris. Gas from the molten lava interior mig ...
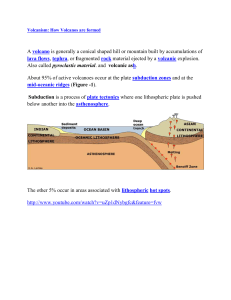
A volcano is generally a conical shaped hill or mountain built by
... Investigations have discovered that over the last 2 million years this volcano has exploded on a regular interval of about 700,000 years. The last eruption occurred 630,000 years ago and the next could take place anytime. When the Yellowstone caldera last erupted, it blasted 1,000 cubic kilometers o ...
... Investigations have discovered that over the last 2 million years this volcano has exploded on a regular interval of about 700,000 years. The last eruption occurred 630,000 years ago and the next could take place anytime. When the Yellowstone caldera last erupted, it blasted 1,000 cubic kilometers o ...
Earth Science
... 13. The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption. 14. The large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof of a volcano’s magma chamber collapses. 15. A fountain of water and steam that builds up pressure underground and erupts at regular intervals. 16 ...
... 13. The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption. 14. The large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof of a volcano’s magma chamber collapses. 15. A fountain of water and steam that builds up pressure underground and erupts at regular intervals. 16 ...
Assignment #22A - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (review info on page 87, fig. 4.2) 1) Shield volcano: broad, gently slopping - constructed from lava flows - central vent not built up Islands of Hawaii are a series of shield volcanoes - eruptions not spectacular lava less viscous and is fluid types of lava associated with Shield volcanoes: - pahoe ...
... (review info on page 87, fig. 4.2) 1) Shield volcano: broad, gently slopping - constructed from lava flows - central vent not built up Islands of Hawaii are a series of shield volcanoes - eruptions not spectacular lava less viscous and is fluid types of lava associated with Shield volcanoes: - pahoe ...
Mount Edziza volcanic complex

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.Most of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex is encompassed within a large provincial park called Mount Edziza Provincial Park. Named after Mount Edziza, this 2,660.95 km2 (1,027.40 sq mi) park was established in 1972 to preserve the volcanic and cultural treasures unique to the northern British Columbia area. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is remote, and, without roads, accessible only along trails. The easiest access is from Highway 37 and a spur road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek. From Kinaskan Lake, on Highway 37, a poorly maintained trail extends west for 30 kilometres (19 mi) into the heart of the complex. From Telegraph Creek another trail extends east for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to the north slope of Mount Edziza.