Lassen Peak Volcanic National Park
... •Abundant pyroclastic activity •deadly airborne debris •Explosive eruptions – very hazardous ...
... •Abundant pyroclastic activity •deadly airborne debris •Explosive eruptions – very hazardous ...
Volcanoes
... Discussion: Why do some volcanoes erupt explosively, whereas others erupt in a more subdued fashion that is not explosive? Water in magma ...
... Discussion: Why do some volcanoes erupt explosively, whereas others erupt in a more subdued fashion that is not explosive? Water in magma ...
Quiz # 1 Chapters 1 and 2
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
S05_4359_L24
... lamproite volcanic vents, Pt, Ni, Cr in layered basaltic intrusions, rare metals and gems in pegmatite veins and dikes). Secondary deposits are mainly hydrothermal, resulting from circulating water in the crust, such as Porphyry Copper & Molybdenum, Epithermal (hot spring) Gold & Silver, Massive Sul ...
... lamproite volcanic vents, Pt, Ni, Cr in layered basaltic intrusions, rare metals and gems in pegmatite veins and dikes). Secondary deposits are mainly hydrothermal, resulting from circulating water in the crust, such as Porphyry Copper & Molybdenum, Epithermal (hot spring) Gold & Silver, Massive Sul ...
VOLCANOES
... having an elevated temperature. Most hot springs result from the emergence of groundwater that has passed through or near recently formed, hot, igneous rocks. ...
... having an elevated temperature. Most hot springs result from the emergence of groundwater that has passed through or near recently formed, hot, igneous rocks. ...
Volcano and extrusive igneous rock notes
... • shield volcanoes have gently sloping sides and a broad base. The tallest mountains in the solar system are shield volcanoes: Hawaii (Earth) and Olympus Mons (Mars). All of the Hawaiian Islands are shield volcanoes. • composite volcanoes or stratavolcanoes have steeply sloping sides and a relativel ...
... • shield volcanoes have gently sloping sides and a broad base. The tallest mountains in the solar system are shield volcanoes: Hawaii (Earth) and Olympus Mons (Mars). All of the Hawaiian Islands are shield volcanoes. • composite volcanoes or stratavolcanoes have steeply sloping sides and a relativel ...
Practice04c
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
Homework for Volcanoes from Geology 1200
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
Eruption
... They are formed when molten, sticky rock called magma, forces its way through a crack in the Earth’s crust. The melted rock that spills out of the crater on the top of the volcano is called lava. The lava destroys everything in its path because it is very, very hot! ...
... They are formed when molten, sticky rock called magma, forces its way through a crack in the Earth’s crust. The melted rock that spills out of the crater on the top of the volcano is called lava. The lava destroys everything in its path because it is very, very hot! ...
What is like living near a volcano?
... • Locals economies can profit from volcanism throughout the year, whereas skiing, for example, has only a limited winter season. • In Uganda, a country trying hard to increase its tourist industry, the volcanic region around Mt Elgon is being heavily promoted for it's landscape, huge waterfalls, wil ...
... • Locals economies can profit from volcanism throughout the year, whereas skiing, for example, has only a limited winter season. • In Uganda, a country trying hard to increase its tourist industry, the volcanic region around Mt Elgon is being heavily promoted for it's landscape, huge waterfalls, wil ...
3-2 Notes: Volcanoes Eruptions • Volcano
... • In AD 79, Mt. Vesuvius erupted and buried the town of Pompeii in a deadly pyroclastic flow, killing almost ________ people immediately. Volcanoes Form Along Plate Boundaries • Volcanoes are common along tectonic plate boundaries at subduction zones and _________________ boundaries. • Volcanoes can ...
... • In AD 79, Mt. Vesuvius erupted and buried the town of Pompeii in a deadly pyroclastic flow, killing almost ________ people immediately. Volcanoes Form Along Plate Boundaries • Volcanoes are common along tectonic plate boundaries at subduction zones and _________________ boundaries. • Volcanoes can ...
volcanism lava tube pahoehoe aa columnar jointing pillow lava
... A type of lava flow with a smooth, ropy surface. ...
... A type of lava flow with a smooth, ropy surface. ...
Volcanoes Power Point - Boone County Schools
... A volcano occurs anytime magma reaches the surface of the Earth. • A volcano is a vent or 'chimney' that connects molten rock (magma) from within the Earth’s crust to the Earth's surface. • The volcano includes the surrounding cone of erupted material. ...
... A volcano occurs anytime magma reaches the surface of the Earth. • A volcano is a vent or 'chimney' that connects molten rock (magma) from within the Earth’s crust to the Earth's surface. • The volcano includes the surrounding cone of erupted material. ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... • The blast from an explosive eruption can knock down trees, destroy buildings, and kill humans and animals. ...
... • The blast from an explosive eruption can knock down trees, destroy buildings, and kill humans and animals. ...
Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions
... destructive boundaries: Crustal plate boundaries that converge (come together) with each other. May also be referred to as subduction zones. constructive boundaries: They exist between two crustal plates that are moving away from each other, causing new crustal rocks to form. May also be referred to ...
... destructive boundaries: Crustal plate boundaries that converge (come together) with each other. May also be referred to as subduction zones. constructive boundaries: They exist between two crustal plates that are moving away from each other, causing new crustal rocks to form. May also be referred to ...
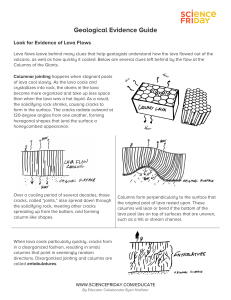
Geological Evidence Guide
... of rocks called igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form when magma (hot liquid rock) cools and solidifies, either underground or after erupting onto earth’s surface as lava. By examining the crystal size and composition of igneous rocks, you can infer their origins. ...
... of rocks called igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form when magma (hot liquid rock) cools and solidifies, either underground or after erupting onto earth’s surface as lava. By examining the crystal size and composition of igneous rocks, you can infer their origins. ...
The World of Volcanoes
... Where are these “Subduction Zones?” • Many volcanoes are located at plate boundaries around the Pacific plate. • The Pacific plate is often called the “Ring of Fire” ...
... Where are these “Subduction Zones?” • Many volcanoes are located at plate boundaries around the Pacific plate. • The Pacific plate is often called the “Ring of Fire” ...
Igneous Rocks Magma • molten rock material consisting of liquid
... over 100 meters thick and cover thousands of square kilometers. As the mass of rock cools, columnar joints may form. Volcano Type: Stratovolcano or Composite Cone ...
... over 100 meters thick and cover thousands of square kilometers. As the mass of rock cools, columnar joints may form. Volcano Type: Stratovolcano or Composite Cone ...
Igneous Rocks - Crafton Hills College
... over 100 meters thick and cover thousands of square kilometers. As the mass of rock cools, columnar joints may form. Volcano Type: Stratovolcano or Composite Cone ...
... over 100 meters thick and cover thousands of square kilometers. As the mass of rock cools, columnar joints may form. Volcano Type: Stratovolcano or Composite Cone ...
Ch 6 power point
... • More explosive than Hawaiian • Create loose volcanic rock called spatter cones or cinder cones ...
... • More explosive than Hawaiian • Create loose volcanic rock called spatter cones or cinder cones ...
Analysis on Rock Textures Submitted by WWW
... (generally feldspars) that had been formed in the magma before it was ejected are also deposited with the other pyroclastics. A tuff is composed of fine‐grained pyroclastic material and is named by the most distinctive component, such as anash tuff or crystal tuff. A welded tuff is a rock that consi ...
... (generally feldspars) that had been formed in the magma before it was ejected are also deposited with the other pyroclastics. A tuff is composed of fine‐grained pyroclastic material and is named by the most distinctive component, such as anash tuff or crystal tuff. A welded tuff is a rock that consi ...
Mount Edziza volcanic complex

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.Most of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex is encompassed within a large provincial park called Mount Edziza Provincial Park. Named after Mount Edziza, this 2,660.95 km2 (1,027.40 sq mi) park was established in 1972 to preserve the volcanic and cultural treasures unique to the northern British Columbia area. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is remote, and, without roads, accessible only along trails. The easiest access is from Highway 37 and a spur road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek. From Kinaskan Lake, on Highway 37, a poorly maintained trail extends west for 30 kilometres (19 mi) into the heart of the complex. From Telegraph Creek another trail extends east for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to the north slope of Mount Edziza.