Document
... vent and breaks into drops. These drops harden into cinders that form a steep cone around the vent. ...
... vent and breaks into drops. These drops harden into cinders that form a steep cone around the vent. ...
Volcanoes - davis.k12.ut.us
... terrible things. They are windows to the center of the earth and help scientists learn more about the inside of the earth. But they have many downsides too. If you want to know more about volcanoes, read on! ...
... terrible things. They are windows to the center of the earth and help scientists learn more about the inside of the earth. But they have many downsides too. If you want to know more about volcanoes, read on! ...
3 TYPES OF FAULTS (MOTIONS) 3 TYPES OF VOLCANOES
... A sudden release of this in the lithosphere causes an earthquake. 9. geyeser A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air. This forms where water collects in an underground chamber then erupts through a narrow channel. 10. Tsunami: A water wave triggered by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, o ...
... A sudden release of this in the lithosphere causes an earthquake. 9. geyeser A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air. This forms where water collects in an underground chamber then erupts through a narrow channel. 10. Tsunami: A water wave triggered by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, o ...
2.4-Volcanic features
... Deadly Lahars from Nevado del Ruiz, Colombia November 13, 1985 Within four hours of the beginning of the eruption, lahars had traveled 100 km and left behind a wake of destruction: more than 23,000 people killed, about 5,000 injured, and more than 5,000 homes destroyed ...
... Deadly Lahars from Nevado del Ruiz, Colombia November 13, 1985 Within four hours of the beginning of the eruption, lahars had traveled 100 km and left behind a wake of destruction: more than 23,000 people killed, about 5,000 injured, and more than 5,000 homes destroyed ...
Volcano Glossary III
... Fragments of rock, mineral and volcanic glass that are smaller than 2 mm on diameter. Ash is created during an explosive volcanic eruption from volcanic gas pressure or from the interaction of magma with external water (groundwater or surface water). Ash can rise very high during an eruption and for ...
... Fragments of rock, mineral and volcanic glass that are smaller than 2 mm on diameter. Ash is created during an explosive volcanic eruption from volcanic gas pressure or from the interaction of magma with external water (groundwater or surface water). Ash can rise very high during an eruption and for ...
Cinder Cone Volcanoes!
... material (tephra) and water that flows down the side of a volcano Can flow down the side of the volcano at 60 mph. At Pinatubo, Lahars were formed by the typhoon that was passing through the area at the time, increasing ...
... material (tephra) and water that flows down the side of a volcano Can flow down the side of the volcano at 60 mph. At Pinatubo, Lahars were formed by the typhoon that was passing through the area at the time, increasing ...
Why Do Volcanoes Erupt? A Step by Step Guide
... molten rock, called magma, rises up into the mountain and the mountain is ready to erupt. When the volcanoes in Hawaii, like this one, erupt, the magna, the molten rock, flows out like lava, but when the scientists studied Mt. St. Helens, they found that the magma was very thick and gooey. It could ...
... molten rock, called magma, rises up into the mountain and the mountain is ready to erupt. When the volcanoes in Hawaii, like this one, erupt, the magna, the molten rock, flows out like lava, but when the scientists studied Mt. St. Helens, they found that the magma was very thick and gooey. It could ...
Student Science Volcano Project
... active volcano in Indonesia than anywhere else on Earth 130! Perhaps the most dangerous volcano in called Merapi, or "Mountain of Fire" on the island of Java. Since 1548, Merapi has erupted violently 68 times. In 1998, it became active again, and people began to evaluate. When the island of Krakatau ...
... active volcano in Indonesia than anywhere else on Earth 130! Perhaps the most dangerous volcano in called Merapi, or "Mountain of Fire" on the island of Java. Since 1548, Merapi has erupted violently 68 times. In 1998, it became active again, and people began to evaluate. When the island of Krakatau ...
a geological-petrological model of the karymsky volcanic center
... Research on deep structure, the geological-structural location of volcanoes in the central part of the Karymsky circular structure (KCS), and study of the eruptive products of Karymsky volcano and a new eruptive center (NEC, Tokarev’s crater) from 1996-2000 provides the basis for the following petro ...
... Research on deep structure, the geological-structural location of volcanoes in the central part of the Karymsky circular structure (KCS), and study of the eruptive products of Karymsky volcano and a new eruptive center (NEC, Tokarev’s crater) from 1996-2000 provides the basis for the following petro ...
TURNING 2011`S DISASTERS INTO EDUCATIONAL SURGES
... Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by volcanic eruptions and the associated volcano hazards. ...
... Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by volcanic eruptions and the associated volcano hazards. ...
Types of Volcanoes Article File
... Volcanic or lava domes are formed by relatively small, bulbous masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently, on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, sp ...
... Volcanic or lava domes are formed by relatively small, bulbous masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently, on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, sp ...
Principal Types of Volcanoes
... Volcanic or lava domes are formed by relatively small, bulbous masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently, on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, sp ...
... Volcanic or lava domes are formed by relatively small, bulbous masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently, on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, sp ...
Volcanoes - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... Radioactive decay is a breaking apart of the nucleus of an atom; as a nucleus breaks apart, it releases energy which is changed into heat. ...
... Radioactive decay is a breaking apart of the nucleus of an atom; as a nucleus breaks apart, it releases energy which is changed into heat. ...
What are Volcanoes?
... are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
... are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... of rock particles and lava. Violent eruptions followed by quiet lava flows are the reasoning for the alternating layers. ...
... of rock particles and lava. Violent eruptions followed by quiet lava flows are the reasoning for the alternating layers. ...
WebQuest Questions - Tenafly Public Schools
... 2. In ___________ a terrible earthquake left Pompeii devastated. Then the second and ________ disaster hit the eruption of ______________________. 3. For ___________ days, volcanic matter covered Pompeii, making a blanket ___________to _____________ feet deep over the entire area. 4. The survivors w ...
... 2. In ___________ a terrible earthquake left Pompeii devastated. Then the second and ________ disaster hit the eruption of ______________________. 3. For ___________ days, volcanic matter covered Pompeii, making a blanket ___________to _____________ feet deep over the entire area. 4. The survivors w ...
Volcanoes Booklet Info Basic Info
... Use the information above to help you decide what you think about the good and bad things of life near a volcano. Then answer this question: Would you live under a volcano? You must give reasons. ...
... Use the information above to help you decide what you think about the good and bad things of life near a volcano. Then answer this question: Would you live under a volcano? You must give reasons. ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... 13. This map shows where geologists discovered deep layers of ash in the soil around Mt. Hekia, an active volcano in Iceland. The numbers represent different thicknesses (in meters) of ash deposited around the volcano. Geologists believe the ash deposits formed when Mt. Hekia erupted about 4000 year ...
... 13. This map shows where geologists discovered deep layers of ash in the soil around Mt. Hekia, an active volcano in Iceland. The numbers represent different thicknesses (in meters) of ash deposited around the volcano. Geologists believe the ash deposits formed when Mt. Hekia erupted about 4000 year ...
magma and lava
... It depends on the type of magma/lava that the volcano is made up of. It can either be felsic or mafic lava. Felsic lava is associated with explosive eruptions because it is high in silica which means it is more viscous. Since it is more viscous the dissolved gases within it cannot escape easily whic ...
... It depends on the type of magma/lava that the volcano is made up of. It can either be felsic or mafic lava. Felsic lava is associated with explosive eruptions because it is high in silica which means it is more viscous. Since it is more viscous the dissolved gases within it cannot escape easily whic ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
Chapter 8: Major Elements
... Volcanic Hazards Pyroclastic Flows Video of pyroclastic flow on Mt. Unzen ...
... Volcanic Hazards Pyroclastic Flows Video of pyroclastic flow on Mt. Unzen ...
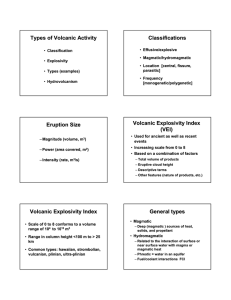
Types of Volcanic Activity Classifications Eruption Size Volcanic
... • Rare events (2(2-3 per century) • Highly evolved magmas, abundant pumice ...
... • Rare events (2(2-3 per century) • Highly evolved magmas, abundant pumice ...
Ch 3 Sec 4: Volcanic Landforms
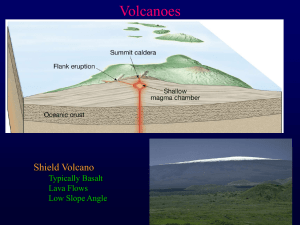
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. Landforms formed when lava flows build up: 1. shield volcanoes- At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava p ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. Landforms formed when lava flows build up: 1. shield volcanoes- At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava p ...
Mount Pelée

Mount Pelée (/pəˈleɪ/; French: Montagne Pelée ""Bald Mountain"") is an active volcano at the northern end of Martinique, an island and French overseas department in the Lesser Antilles island arc of the Caribbean. Its volcanic cone is composed of layers of volcanic ash and hardened lava.The stratovolcano is famous for its eruption in 1902 and the destruction that resulted, dubbed the worst volcanic disaster of the 20th century. The eruption killed about 30,000 people. Most deaths were caused by pyroclastic flows and occurred in the city of Saint-Pierre, which was, at that time, the largest city on the island.Pyroclastic flows completely destroyed St. Pierre, a town of 30,000 people, within minutes of the eruption. The eruption left only two survivors in the direct path of the flows: Louis-Auguste Cyparis survived because he was in a poorly ventilated, dungeon-like jail cell; Léon Compère-Léandre, living on the edge of the city, escaped with severe burns. Havivra Da Ifrile, a young girl, reportedly escaped with injuries during the eruption by taking a small boat to a cave down shore, and was later found adrift two miles (3 km) from the island, unconscious. The event marked the only major volcanic disaster in the history of France and its overseas territories.