Part 2 - Kirkwood Community College
... • Cerebellum receives impulses of the intent to initiate voluntary muscle contraction • Proprioceptors and visual signals “inform” the cerebellum of the body’s condition • Cerebellar cortex calculates the best way to perform a movement • A “blueprint” of coordinated movement is sent to the cerebral ...
... • Cerebellum receives impulses of the intent to initiate voluntary muscle contraction • Proprioceptors and visual signals “inform” the cerebellum of the body’s condition • Cerebellar cortex calculates the best way to perform a movement • A “blueprint” of coordinated movement is sent to the cerebral ...
module b6: brain and mind – overview
... understand that humans are more likely to remember information if they can see a pattern in it (or impose a pattern on it), if there is repetition of the information, especially over an extended period of time, or if there is a strong stimulus associated with it, including colour, light, smell, soun ...
... understand that humans are more likely to remember information if they can see a pattern in it (or impose a pattern on it), if there is repetition of the information, especially over an extended period of time, or if there is a strong stimulus associated with it, including colour, light, smell, soun ...
Limbic System
... Emotional state – we learn best when we are alert, motivated, and aroused Rehearsal – repeating or rehearsing material enhances memory Association – associating new information with old memories in LTM enhances memory Automatic memory – subconscious information stored in LTM ...
... Emotional state – we learn best when we are alert, motivated, and aroused Rehearsal – repeating or rehearsing material enhances memory Association – associating new information with old memories in LTM enhances memory Automatic memory – subconscious information stored in LTM ...
Psych B – Module 22
... distress that follow responsiveness to a when a person who drug, prompting the is dependent on a user to increase the drug discontinues the dosage to achieve use of the drug effects previously obtained by lower – Withdrawal symptoms are usually doses of the drug the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
... distress that follow responsiveness to a when a person who drug, prompting the is dependent on a user to increase the drug discontinues the dosage to achieve use of the drug effects previously obtained by lower – Withdrawal symptoms are usually doses of the drug the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
Dementia and memory loss with the elderly
... Most people with dementia remember the distant past more clearly than recent events. This is because memories tend to decline in reverse order to when they were experienced. People will often have difficulty remembering what happened a few minutes or hours ago, but can recall, in detail, life when t ...
... Most people with dementia remember the distant past more clearly than recent events. This is because memories tend to decline in reverse order to when they were experienced. People will often have difficulty remembering what happened a few minutes or hours ago, but can recall, in detail, life when t ...
Drugs and Consciousness
... Withdrawal & Dependence 1. Withdrawal: Upon stopping use of a drug (after addiction), users may experience the undesirable effects of withdrawal. 2. Dependence: Absence of a drug may lead to a feeling of physical pain, intense cravings (physical dependence), and negative emotions (psychological dep ...
... Withdrawal & Dependence 1. Withdrawal: Upon stopping use of a drug (after addiction), users may experience the undesirable effects of withdrawal. 2. Dependence: Absence of a drug may lead to a feeling of physical pain, intense cravings (physical dependence), and negative emotions (psychological dep ...
Team GALACA Project _3 Presentation
... its electrical resistance Retains that state after power is turned off This is a perfect feature for nonvolatile memory This coupled with tinier circuits could lead to instant-on computers. ...
... its electrical resistance Retains that state after power is turned off This is a perfect feature for nonvolatile memory This coupled with tinier circuits could lead to instant-on computers. ...
Nervous System
... What is mind? • Many traditions, including psychology, separate “brain” from “mind.” • What we perceive as “mind” (thought, will, selfperception) does produce evidence of brain activity in brain scans. • That “brain” influences “mind” is well-established; but some evidence shows “mind” can influenc ...
... What is mind? • Many traditions, including psychology, separate “brain” from “mind.” • What we perceive as “mind” (thought, will, selfperception) does produce evidence of brain activity in brain scans. • That “brain” influences “mind” is well-established; but some evidence shows “mind” can influenc ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in
... Withdrawal & Dependence 1. Withdrawal: Upon stopping use of a drug (after addiction), users may experience the undesirable effects of withdrawal. 2. Dependence: Absence of a drug may lead to a feeling of physical pain, intense cravings (physical dependence), and negative emotions (psychological dep ...
... Withdrawal & Dependence 1. Withdrawal: Upon stopping use of a drug (after addiction), users may experience the undesirable effects of withdrawal. 2. Dependence: Absence of a drug may lead to a feeling of physical pain, intense cravings (physical dependence), and negative emotions (psychological dep ...
14/15 April 2008
... How many memories can be stored in the network? To store M memories, each of length N bits, in a network of N neurons, we first ask how many stable patterns can be reached? In 1987, McEliece et al derived an upper limit for the number of memories that can be stored accurately: M = N/(2 logN). e.g. f ...
... How many memories can be stored in the network? To store M memories, each of length N bits, in a network of N neurons, we first ask how many stable patterns can be reached? In 1987, McEliece et al derived an upper limit for the number of memories that can be stored accurately: M = N/(2 logN). e.g. f ...
Effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra Root Extract on Learning
... animal. [3] The hippocampus is a major component of the brain of humans and other mammals. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in long-term memory and spatial navigation. The central cholinergic pathways play a prominent role in learning and memory processes. [4] Memory is the ...
... animal. [3] The hippocampus is a major component of the brain of humans and other mammals. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in long-term memory and spatial navigation. The central cholinergic pathways play a prominent role in learning and memory processes. [4] Memory is the ...
Eagleman Ch 9. Memory
... memories of specific events. The medial temporal lobe, particularly the hippocampus, are important for storing and recalling episodic memories. Semantic memories are memories of facts, without details of when or where you learned the fact. ...
... memories of specific events. The medial temporal lobe, particularly the hippocampus, are important for storing and recalling episodic memories. Semantic memories are memories of facts, without details of when or where you learned the fact. ...
Gluck_OutlinePPT_Ch12
... recognized more facts than 4-year-olds. 6- and 8-year-olds had better recall of source, with more intra-experimental errors (i.e., knew it was learned in experiment, confused source). 4-year-olds made more extra-experimental errors (i.e., thought learning was outside experiment, for example at schoo ...
... recognized more facts than 4-year-olds. 6- and 8-year-olds had better recall of source, with more intra-experimental errors (i.e., knew it was learned in experiment, confused source). 4-year-olds made more extra-experimental errors (i.e., thought learning was outside experiment, for example at schoo ...
Memory Capacity of a Hebbian Learning Model with Inhibition
... parameters governing the stochastic learning process are fixed, the storage capacity of the model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If the coding level (proportion of active neurons) of the stimuli can vary with N as f ∼ ...
... parameters governing the stochastic learning process are fixed, the storage capacity of the model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If the coding level (proportion of active neurons) of the stimuli can vary with N as f ∼ ...
Chapter 2: Biopsychology Study Guide
... Flight" phenomenon because of its control over the necessary bodily changes needed when we are faced with a situation where we may need to defend ourselves or escape. Imagine walking down a dark street at night by yourself B. regulates primarily involuntary activity such as heart rate, breathing, bl ...
... Flight" phenomenon because of its control over the necessary bodily changes needed when we are faced with a situation where we may need to defend ourselves or escape. Imagine walking down a dark street at night by yourself B. regulates primarily involuntary activity such as heart rate, breathing, bl ...
Clinical Research Center for Brain Sciences, Herzog Hospital
... Using EEG, neurocognitive function, and personalized tACS protocols to delay MCI and the onset of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease. Evidence that ageing is related to lower resting EEG alpha power (i.e., amplitude of alpha). ...
... Using EEG, neurocognitive function, and personalized tACS protocols to delay MCI and the onset of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease. Evidence that ageing is related to lower resting EEG alpha power (i.e., amplitude of alpha). ...
Set 3
... (hippocampus and amygdala) and their connections with the hypothalamus and its output pathway (that control autonomic, somatic, and endocrine functions) ...
... (hippocampus and amygdala) and their connections with the hypothalamus and its output pathway (that control autonomic, somatic, and endocrine functions) ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... identical electrical signals, muscles to contract (in a few cases, to relax also). The majority of neurons, however, are neither sensory nor motor- they exist in between the input and the output. They are thus usually polarized cells, with inputs at one end (called dendrites) and outputs at the othe ...
... identical electrical signals, muscles to contract (in a few cases, to relax also). The majority of neurons, however, are neither sensory nor motor- they exist in between the input and the output. They are thus usually polarized cells, with inputs at one end (called dendrites) and outputs at the othe ...
Psychoactive Drugs Power Point
... The effects vary from person to person Users can be dangerous to themselves and others. Mimics & blocks the reuptake of serotonin. Flashbacks, psychotic reactions can occur. ...
... The effects vary from person to person Users can be dangerous to themselves and others. Mimics & blocks the reuptake of serotonin. Flashbacks, psychotic reactions can occur. ...
A leading centre for innovation, expertise, and discovery
... mouse models that malfunction of the gene DISC 1, previously associated with ...
... mouse models that malfunction of the gene DISC 1, previously associated with ...
Deanne Boules presentation pdf
... • New ideas or behaviours use the working memory • Working memory is a limited resource • 20 minutes of concentration is the limit • 4 bits of information leads to overload • Brain prefers to hardwire repeated behaviours, thoughts, activities • Significant effort required to leverage brains preferen ...
... • New ideas or behaviours use the working memory • Working memory is a limited resource • 20 minutes of concentration is the limit • 4 bits of information leads to overload • Brain prefers to hardwire repeated behaviours, thoughts, activities • Significant effort required to leverage brains preferen ...
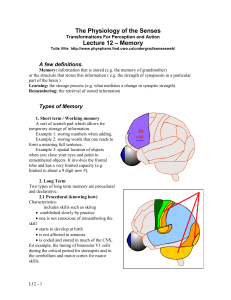
Types of Memory
... permanent changes in synaptic strength between assemblies of neurons. For example, rats raised in a rich environment have a thicker cortex with larger and more synapses. In the case of procedural memory, the changes are produced gradually by repeated exposure to the stimulus. ...
... permanent changes in synaptic strength between assemblies of neurons. For example, rats raised in a rich environment have a thicker cortex with larger and more synapses. In the case of procedural memory, the changes are produced gradually by repeated exposure to the stimulus. ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... recieving neuron and excite or inhibit a new action potential. The sender neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters. This is reuptake. ...
... recieving neuron and excite or inhibit a new action potential. The sender neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters. This is reuptake. ...
Luis V. Colom, MD, PhD VP of Research Center for Biomedical Studies
... altered somatic functions and subsequent death of cholinergic and glutamatergic septal neurons (injured cortical axons will lead to neuronal death in additional basal forebrain structures). Altered properties of the surviving septal neurons Oxidative Stress ...
... altered somatic functions and subsequent death of cholinergic and glutamatergic septal neurons (injured cortical axons will lead to neuronal death in additional basal forebrain structures). Altered properties of the surviving septal neurons Oxidative Stress ...
303A.pdf
... To help facilitate discussion, I will distribute some “thought questions” a week ahead of each class. These are mainly intended to help you orient to and integrate the reading. You will also be required to write a 2-page "thought paper" before each class. In these papers, I merely ask that you refle ...
... To help facilitate discussion, I will distribute some “thought questions” a week ahead of each class. These are mainly intended to help you orient to and integrate the reading. You will also be required to write a 2-page "thought paper" before each class. In these papers, I merely ask that you refle ...