Benzodiazepines - Sarah M. Brothwell
... the antianxiety effects, however they may reach a plateau. It is now common for doctors to prescribe BZs concurrently with SSRIs for long-term antianxiety purposes. After 6-8 weeks patients should slowly discontinue their use of BZs. ...
... the antianxiety effects, however they may reach a plateau. It is now common for doctors to prescribe BZs concurrently with SSRIs for long-term antianxiety purposes. After 6-8 weeks patients should slowly discontinue their use of BZs. ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Dissociative Fugue Dissociative Identity Disorder Depersonalization Disorder ...
... Dissociative Fugue Dissociative Identity Disorder Depersonalization Disorder ...
Learning and Memory - Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
... Although it was accepted by the early 1970s that there are two major types of memory, little was known about how either type is formed. We could not distinguish experimentally, for example, between two leading—and conflicting—approaches to the mechanisms of memory storage: the aggregate field approa ...
... Although it was accepted by the early 1970s that there are two major types of memory, little was known about how either type is formed. We could not distinguish experimentally, for example, between two leading—and conflicting—approaches to the mechanisms of memory storage: the aggregate field approa ...
Summary of the Known Major Neurotransmitters
... Excitatory: It produces muscle contractions and is found in the motor neurons; in the hippocampus, it is involved in memory formation, learning and general intellectual ...
... Excitatory: It produces muscle contractions and is found in the motor neurons; in the hippocampus, it is involved in memory formation, learning and general intellectual ...
Working memory
... The wiring diagram of the hippocampus is traditionally presented as a trisynaptic loop. The major input is carried by axons of the perforant path, which convey polymodal sensory information from neurons in layer II of the entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus. Perforant path axons make excitatory s ...
... The wiring diagram of the hippocampus is traditionally presented as a trisynaptic loop. The major input is carried by axons of the perforant path, which convey polymodal sensory information from neurons in layer II of the entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus. Perforant path axons make excitatory s ...
Biopsychology of Memory
... Human Brain? • Erickson et al. (1998) - made use of DNA marker (BrdU) used in mice - only labels DNA in cells (i.e., stem cells) preparing to divide - marker inherited by daughter cells and future descendants of original dividing cell - BrdU will be observed in mature neurons - given to certain canc ...
... Human Brain? • Erickson et al. (1998) - made use of DNA marker (BrdU) used in mice - only labels DNA in cells (i.e., stem cells) preparing to divide - marker inherited by daughter cells and future descendants of original dividing cell - BrdU will be observed in mature neurons - given to certain canc ...
European Neuroscience Conference for Doctoral Students
... views of hippocampus, the changes in firing patterns of hippocampal neurons occurring during learning, the existence of “time cells” that fire at specific time points during a task, etc. To do so, Dr. Eichenbaum laboratory has adopted a multidisciplinary point of view, using disparate techniques, su ...
... views of hippocampus, the changes in firing patterns of hippocampal neurons occurring during learning, the existence of “time cells” that fire at specific time points during a task, etc. To do so, Dr. Eichenbaum laboratory has adopted a multidisciplinary point of view, using disparate techniques, su ...
Memories of punishment and relief in a mini-brain - Schram
... Flies, when trained with an odour that precedes electric shock, later on avoid this odour as a signal for the “painful” punishment. When the timing of odour and shock are reversed, such that the odour follows shock, this odour is subsequently approached as it signals a “feeling of relief”. Thus, an ...
... Flies, when trained with an odour that precedes electric shock, later on avoid this odour as a signal for the “painful” punishment. When the timing of odour and shock are reversed, such that the odour follows shock, this odour is subsequently approached as it signals a “feeling of relief”. Thus, an ...
Analogical Episodes are More Likely to be Blended than Superficially... Veselina Feldman ( )
... and Zareva (2001) and Zareva and Kokinov (2003) demonstrated that blending can occur even between dissimilar episodes. This kind of very complicated blending is not explainable within the above models since the features representing the two episodes are very different and therefore the two memory tr ...
... and Zareva (2001) and Zareva and Kokinov (2003) demonstrated that blending can occur even between dissimilar episodes. This kind of very complicated blending is not explainable within the above models since the features representing the two episodes are very different and therefore the two memory tr ...
PSY 368 Human Memory - the Department of Psychology at Illinois
... • Duration of retrograde amnesia typically shrinks as time passes • e.g., Russell (1959) described case of TBI as a result of a motorcycle ...
... • Duration of retrograde amnesia typically shrinks as time passes • e.g., Russell (1959) described case of TBI as a result of a motorcycle ...
Mechanisms of emotional arousal and lasting declarative memory
... involve that structure. Furthermore, after modulation by AC stimulation, the memory should not be disrupted by inactivating the AC during retention testing. To examine these implications, amphetamine was micro-infused into the amygdala, hippocampus or caudate nucleus immediately after rats were trai ...
... involve that structure. Furthermore, after modulation by AC stimulation, the memory should not be disrupted by inactivating the AC during retention testing. To examine these implications, amphetamine was micro-infused into the amygdala, hippocampus or caudate nucleus immediately after rats were trai ...
Bauer 2006 - Ericastiftelsen
... hippocampus would present challenges to consolidation, and therefore storage, of new information [34]. As these structures and connections between them develop we should see age-related changes in long-term recall (as well as in spatial memory tasks: [35]). Changes in encoding Although encoding cann ...
... hippocampus would present challenges to consolidation, and therefore storage, of new information [34]. As these structures and connections between them develop we should see age-related changes in long-term recall (as well as in spatial memory tasks: [35]). Changes in encoding Although encoding cann ...
U3 Neurobiology Summary
... (e) Cerebral cortex is the centre of conscious thought; it also recalls memories and alters decision making behaviour in the light of experience. The cerebral cortex also receives sensory information and coordinates voluntary movement. (f) Different parts of the cerebrum control different aspects of ...
... (e) Cerebral cortex is the centre of conscious thought; it also recalls memories and alters decision making behaviour in the light of experience. The cerebral cortex also receives sensory information and coordinates voluntary movement. (f) Different parts of the cerebrum control different aspects of ...
LeDoux outlines his theory of emotions and memory
... During a car crash a man smashes his head on the steering wheel, setting off the car’s horn and crushing his nose. He’s hurt, scared and the horn is deafening. A few months later, a car horn blares outside his house and triggers the memory of the accident: He remembers the facts, including the road ...
... During a car crash a man smashes his head on the steering wheel, setting off the car’s horn and crushing his nose. He’s hurt, scared and the horn is deafening. A few months later, a car horn blares outside his house and triggers the memory of the accident: He remembers the facts, including the road ...
Neurotransmisson Practice
... 6. Neurotransmitters influence neurons either by _______________ or ______________ their readiness to fire. 7. Excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed to the sending neuron in a process called _______________________. 8. Among the neurotransmitters that researchers have pinpointed is ________, which ...
... 6. Neurotransmitters influence neurons either by _______________ or ______________ their readiness to fire. 7. Excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed to the sending neuron in a process called _______________________. 8. Among the neurotransmitters that researchers have pinpointed is ________, which ...
TAP3_LecturePowerPointSlides_Module09
... the Powerpoint slides are identical to those in the textbook. ...
... the Powerpoint slides are identical to those in the textbook. ...
Memory - Sinauer Associates
... PET scans made during eye-blink tests show increased activity in several brain regions, but not all may be essential. Patients with unilateral cerebellar damage can acquire the conditioned eye-blink response only on the intact side. ...
... PET scans made during eye-blink tests show increased activity in several brain regions, but not all may be essential. Patients with unilateral cerebellar damage can acquire the conditioned eye-blink response only on the intact side. ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 57 [10-31
... 29. What is consciousness? The continuing stream of awareness of either our surroundings or our sequential thoughts 30. What are memory traces? Memories are stored in the brain by changing the basic sensitivity of synaptic transmission between neurons as a result of previous neural activity. The new ...
... 29. What is consciousness? The continuing stream of awareness of either our surroundings or our sequential thoughts 30. What are memory traces? Memories are stored in the brain by changing the basic sensitivity of synaptic transmission between neurons as a result of previous neural activity. The new ...
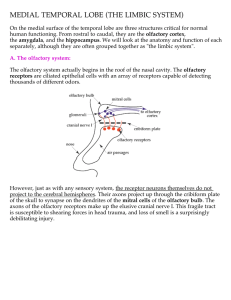
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... recognize the emotional significance of objects, and for example, show no fear when presented with a snake or another aggressive monkey. This has disastrous social consequences for the monkey. Epilepsy surgery provides an opportunity to stimulate areas of the brain to determine the extent of the epi ...
... recognize the emotional significance of objects, and for example, show no fear when presented with a snake or another aggressive monkey. This has disastrous social consequences for the monkey. Epilepsy surgery provides an opportunity to stimulate areas of the brain to determine the extent of the epi ...
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5
... 1) Warrington reported cases of amnesic patients who had lost the recency effect while retaining the primacy effect. 2) When plotted on log-log axes, the retention graphs do not suggest two stages. Rather, they indicate that the rate at which information is lost (i.e., the forgetting rate) slows dow ...
... 1) Warrington reported cases of amnesic patients who had lost the recency effect while retaining the primacy effect. 2) When plotted on log-log axes, the retention graphs do not suggest two stages. Rather, they indicate that the rate at which information is lost (i.e., the forgetting rate) slows dow ...
Click here to get the file
... The more recent version has added a third storage buffer, termed the episodic buffer, as a system that can serve as both an auxiliary store when the primary ones are overloaded or disrupted, and also as a site in which to integrate diverse types of information such as verbal and spatial content with ...
... The more recent version has added a third storage buffer, termed the episodic buffer, as a system that can serve as both an auxiliary store when the primary ones are overloaded or disrupted, and also as a site in which to integrate diverse types of information such as verbal and spatial content with ...
Eduction for children with Batten Disease - ICEVI
... given an answer, the child continues in asking over and over again. This period will pass. Later the child’s thought process becomes disrupted, without warning and generally without clear reason. It is terrifying for the child in particularly as here is no logical solution. There is no good solution ...
... given an answer, the child continues in asking over and over again. This period will pass. Later the child’s thought process becomes disrupted, without warning and generally without clear reason. It is terrifying for the child in particularly as here is no logical solution. There is no good solution ...
File
... • Encoding – process of getting information into the memory system • Storage – retention encoded information over time • Retrieval – process of getting information out of memory storage ...
... • Encoding – process of getting information into the memory system • Storage – retention encoded information over time • Retrieval – process of getting information out of memory storage ...