Plant Divisions
... 3. Have a protective layer – cuticle (waxy outer layer) to keep from drying out 4. Specialized structures for reproduction including spores & seeds that do not dry out ...
... 3. Have a protective layer – cuticle (waxy outer layer) to keep from drying out 4. Specialized structures for reproduction including spores & seeds that do not dry out ...
Plant Structure - Willimon-PHS
... pollen from the anther pollen grows a tube down through the style ovary produces females gamete and protects developing seed ...
... pollen from the anther pollen grows a tube down through the style ovary produces females gamete and protects developing seed ...
Ch30 PowerPoint LN
... evolution through their interactions and thus affecting the selected adaptations of each organism. • insects were favored to evolve with those plants that kept their reproductive parts off of the ground. ...
... evolution through their interactions and thus affecting the selected adaptations of each organism. • insects were favored to evolve with those plants that kept their reproductive parts off of the ground. ...
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary
... 2) A genetic system that prevents the elongation of the pollen tube on a stigma of the same plant (selfincompatibility) (b) 3) A genetic system that prevents genes expressed in cells at the stigma surface allow genetically distinct pollen from flowers of the same species, but not genetically identic ...
... 2) A genetic system that prevents the elongation of the pollen tube on a stigma of the same plant (selfincompatibility) (b) 3) A genetic system that prevents genes expressed in cells at the stigma surface allow genetically distinct pollen from flowers of the same species, but not genetically identic ...
Alternation of generations
... to have much the same level of organisation they do in fact have very different evolutionary histories. It was long known that their storage products and chlorophyll types differed, but it has only recently been shown from studies of DNA sequences that the date at which they split into the three col ...
... to have much the same level of organisation they do in fact have very different evolutionary histories. It was long known that their storage products and chlorophyll types differed, but it has only recently been shown from studies of DNA sequences that the date at which they split into the three col ...
Lake Sediments and Climate Change
... low carbonate content, contain particular minerals, or have organic matter fractions with isotopic signatures suggestive of C 4 vegetation. Lake sediments also contain a variety of microfossils that provide information about past climate, such as pollen grains, fern spores, charcoal fragments, and d ...
... low carbonate content, contain particular minerals, or have organic matter fractions with isotopic signatures suggestive of C 4 vegetation. Lake sediments also contain a variety of microfossils that provide information about past climate, such as pollen grains, fern spores, charcoal fragments, and d ...
PLANTS!! - Woodstown-Pilesgrove Regional School District
... • Whisk ferns • No leaves, sporangia are yellow, look like whisk broom ...
... • Whisk ferns • No leaves, sporangia are yellow, look like whisk broom ...
Lab 5: Plants: Nontracheophytes and Seedless Vascular Plants Part 2
... pollen. The seed plants, unlike the seedless plants, have a gametophyte stage that is nutritionally dependent on the sporophyte generation. The reduced gametophyte stages are enclosed their entire lives by parental sporophyte tissue (whether on the plant itself or wrapped in a seed coat). The gameto ...
... pollen. The seed plants, unlike the seedless plants, have a gametophyte stage that is nutritionally dependent on the sporophyte generation. The reduced gametophyte stages are enclosed their entire lives by parental sporophyte tissue (whether on the plant itself or wrapped in a seed coat). The gameto ...
Daffodil Biology Lab Text - American Daffodil Society
... with blade down on the paper plate and fingers out of the way b. Stem—use scissors to cut through the flower stem in various directions: across, down, diagonal, and compare with each other. What do you see? (channels or openings in the stem, water) c. Line up the stem slices on a paper plate. If not ...
... with blade down on the paper plate and fingers out of the way b. Stem—use scissors to cut through the flower stem in various directions: across, down, diagonal, and compare with each other. What do you see? (channels or openings in the stem, water) c. Line up the stem slices on a paper plate. If not ...
Document
... A film of water is necessary for sperm to come in contact with eggs. 11. Which characteristic below is not unique to seed plants? ovules pollen spores seed coat 12. The diploid generation of the plant life cycle always _____. produces spores is called the gametophyte is larger and more conspicuous t ...
... A film of water is necessary for sperm to come in contact with eggs. 11. Which characteristic below is not unique to seed plants? ovules pollen spores seed coat 12. The diploid generation of the plant life cycle always _____. produces spores is called the gametophyte is larger and more conspicuous t ...
video slide
... 2 The pollen tube discharges two sperm into the female gametophyte (embryo sac) within an ovule. 3 One sperm fertilizes the egg, forming the zygote. The other sperm combines with the two polar nuclei of the embryo sac’s large central cell, forming a triploid cell that develops into the nutritive tis ...
... 2 The pollen tube discharges two sperm into the female gametophyte (embryo sac) within an ovule. 3 One sperm fertilizes the egg, forming the zygote. The other sperm combines with the two polar nuclei of the embryo sac’s large central cell, forming a triploid cell that develops into the nutritive tis ...
Class: 12 Subject: Biology Topic: Sexual reproduction in
... Triple fusion is the fusion of the male gamete with two polar nuclei inside the embryo sac of the angiosperm. This process of fusion takes place inside the embryo sac. When pollen grains fall on the stigma, they germinate and give rise to the pollen tube that passes through the style and enters into ...
... Triple fusion is the fusion of the male gamete with two polar nuclei inside the embryo sac of the angiosperm. This process of fusion takes place inside the embryo sac. When pollen grains fall on the stigma, they germinate and give rise to the pollen tube that passes through the style and enters into ...
Classification of Angiosperms
... Opening through which the pollen tube grows to deliver pollen to the ovary (ovules) Epicotyl + embryonic leaves First leaves to emerge during germination ...
... Opening through which the pollen tube grows to deliver pollen to the ovary (ovules) Epicotyl + embryonic leaves First leaves to emerge during germination ...
CHAPTER 39 REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
... a. The stigma is an enlarged sticky knob on end of a style; stigma serves to receive pollen grains. b. The style is a slender stalk that connects stigma with the ovary. c. The ovary is an enlarged base of a carpel that contains a number of ovules. 8. Not all flowers have sepals, petals, stamens, and ...
... a. The stigma is an enlarged sticky knob on end of a style; stigma serves to receive pollen grains. b. The style is a slender stalk that connects stigma with the ovary. c. The ovary is an enlarged base of a carpel that contains a number of ovules. 8. Not all flowers have sepals, petals, stamens, and ...
Parts of a Plant Labeling Parts of a Flower:
... The flower is the reproductive unit of some plants (angiosperms). Parts of the flower include petals, sepals, one or more carpels (the female reproductive organs), and stamens (the male reproductive organs). The Female Reproductive Organs: The pistil is the collective term for the carpel(s). Each ca ...
... The flower is the reproductive unit of some plants (angiosperms). Parts of the flower include petals, sepals, one or more carpels (the female reproductive organs), and stamens (the male reproductive organs). The Female Reproductive Organs: The pistil is the collective term for the carpel(s). Each ca ...
Primary Upper Block Cycles: Reproduction in Plants Introduction to
... 9. I______________ help in pollinating flowers when they look for nectar. 10. The process by which the n______________ of the pollen fuses with the egg to produce a f_______________ egg is called f______________________. 11. After f_______________, the ovary develops into a f_________________ while ...
... 9. I______________ help in pollinating flowers when they look for nectar. 10. The process by which the n______________ of the pollen fuses with the egg to produce a f_______________ egg is called f______________________. 11. After f_______________, the ovary develops into a f_________________ while ...
Plant Evolutionary Trends
... • The only diploid structure is a stalk and spore capsule, which grow out of the haploid plant body. • Peat moss is used to help soil hold water. It can also be used as fireplace fuel when it is dried. Peat bogs are very acidic, which allows plants like cranberries and blueberries to grow. – Also, t ...
... • The only diploid structure is a stalk and spore capsule, which grow out of the haploid plant body. • Peat moss is used to help soil hold water. It can also be used as fireplace fuel when it is dried. Peat bogs are very acidic, which allows plants like cranberries and blueberries to grow. – Also, t ...
Flowering and Pollination
... In Fast Plants the developmental process known as microsporogenesis occurs in the developing anthers when the first flower bud of the apical whorl is about one millimeter in diameter and leads to the production of pollen. Within the anthers specialized tissues undergo meiosis to form the microspore ...
... In Fast Plants the developmental process known as microsporogenesis occurs in the developing anthers when the first flower bud of the apical whorl is about one millimeter in diameter and leads to the production of pollen. Within the anthers specialized tissues undergo meiosis to form the microspore ...
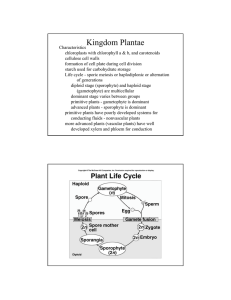
Kingdom Plantae
... Anthers have four patches of tissue Each patch composed of many diploid microspore mother cells Undergo meiosis to produce four microspores each Nucleus of each divides once by mitosis Two layered wall develops around each microspore Binucleate microspores are now pollen grains Outer layer called ex ...
... Anthers have four patches of tissue Each patch composed of many diploid microspore mother cells Undergo meiosis to produce four microspores each Nucleus of each divides once by mitosis Two layered wall develops around each microspore Binucleate microspores are now pollen grains Outer layer called ex ...
chapt42_lecture_anim_ppt
... • Microspore develops by mitosis into pollen • Generative cell in the pollen grain will later divide to form two sperm cells ...
... • Microspore develops by mitosis into pollen • Generative cell in the pollen grain will later divide to form two sperm cells ...
42_lecture_ppt
... • Microspore develops by mitosis into pollen • Generative cell in the pollen grain will later divide to form two sperm cells ...
... • Microspore develops by mitosis into pollen • Generative cell in the pollen grain will later divide to form two sperm cells ...
Reproduction - I Teach Bio
... by meiosis in the anther. 2. The pistil is the female reproductive organ. It consists of the stigma, where pollen grains are deposited; a stalk called the style; and the ovary, containing ovules in which gametes are produced by meiosis and where fertilization occurs. 3. Other structures. Modifie ...
... by meiosis in the anther. 2. The pistil is the female reproductive organ. It consists of the stigma, where pollen grains are deposited; a stalk called the style; and the ovary, containing ovules in which gametes are produced by meiosis and where fertilization occurs. 3. Other structures. Modifie ...
Pollen

Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the female cone of coniferous plants. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics.Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower.