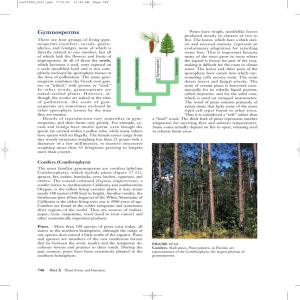
Gymnosperms
... megasporangium called the nucellus. The nucellus itself is completely sur- FIGURE 37.13 rounded by a thick layer of cells called Life cycle of a typical pine. The male and female gametophytes are dramatically reduced the integument that has a small open- in size in these plants. Wind generally dispe ...
... megasporangium called the nucellus. The nucellus itself is completely sur- FIGURE 37.13 rounded by a thick layer of cells called Life cycle of a typical pine. The male and female gametophytes are dramatically reduced the integument that has a small open- in size in these plants. Wind generally dispe ...
Reproduction and Domestication of Flowering Plants
... Reproduction and Domestication of Flowering Plants ...
... Reproduction and Domestication of Flowering Plants ...
Chapter 30 - Worksheet 3
... Exam I – Ch. 30 – WS 3 Chapter 30 – The Evolution of Seed Plants 1. Seed plants are divided into what two groups? Gymnosperms Angiosperms 2. What are some of the advantages to seed plants? Pollen grain replaces swimming sperm - no need for water for fertilization Gametophyte is reduce and ma ...
... Exam I – Ch. 30 – WS 3 Chapter 30 – The Evolution of Seed Plants 1. Seed plants are divided into what two groups? Gymnosperms Angiosperms 2. What are some of the advantages to seed plants? Pollen grain replaces swimming sperm - no need for water for fertilization Gametophyte is reduce and ma ...
Section 3
... protection • Embryo produces stems, roots, and leaves • New plants develop faster from seeds than spores • Gymnosperms and angiosperms are seed plants. Gymno. produce seeds in cones, angio. in flowers and fruit ...
... protection • Embryo produces stems, roots, and leaves • New plants develop faster from seeds than spores • Gymnosperms and angiosperms are seed plants. Gymno. produce seeds in cones, angio. in flowers and fruit ...
Ch27
... 5. Double fertilization: egg + sperm embryo and 2 polar nuclei + sperm endosperm. 6. Seeds enclosed in a fruit. MONOCOTS have floral parts in multiples of three and the seed contains one cotyledon. The endosperm provides the food for the embryo. Venation is usually parallel (there are exceptions ...
... 5. Double fertilization: egg + sperm embryo and 2 polar nuclei + sperm endosperm. 6. Seeds enclosed in a fruit. MONOCOTS have floral parts in multiples of three and the seed contains one cotyledon. The endosperm provides the food for the embryo. Venation is usually parallel (there are exceptions ...
Gymnosperms - National Botanic Gardens
... – n). Pollination may occur when the cone is small, but the endosperm continues to grow to completion before fertilisation occurs. When fully grown the endosperm develops archegonia in which single large nuclei act as egg cells. Only now does fertilisation occur, sometimes 12 months or more after po ...
... – n). Pollination may occur when the cone is small, but the endosperm continues to grow to completion before fertilisation occurs. When fully grown the endosperm develops archegonia in which single large nuclei act as egg cells. Only now does fertilisation occur, sometimes 12 months or more after po ...
Angiosperm Reproduction
... diploid cells undergo MEIOSIS to make haploid MICROSPORES Microspores develop into MALE GAMETOPHYTE = POLLEN GRAIN w/2 haploid nuclei TUBE NUCLEUS makes POLLEN TUBE-delivers sperm to female gametophyte GENERATIVE NUCLEUS divides to make 2 sperm cells IN OVARY OVULES form with diploid cell that under ...
... diploid cells undergo MEIOSIS to make haploid MICROSPORES Microspores develop into MALE GAMETOPHYTE = POLLEN GRAIN w/2 haploid nuclei TUBE NUCLEUS makes POLLEN TUBE-delivers sperm to female gametophyte GENERATIVE NUCLEUS divides to make 2 sperm cells IN OVARY OVULES form with diploid cell that under ...
Lab 6 - Gymnosperms
... -advanced vascular tissue with tracheids and vessel elements -herbaceous and woody -annuals and perennials ...
... -advanced vascular tissue with tracheids and vessel elements -herbaceous and woody -annuals and perennials ...
Gymnosperms
... • Male cones are usually lower on the tree to assist with out-crossing • Pollination takes place in the spring when female cones are small (about 1/2 inch) ...
... • Male cones are usually lower on the tree to assist with out-crossing • Pollination takes place in the spring when female cones are small (about 1/2 inch) ...
Gymnosperm and Angiosperm Notes
... The largest group of gymnosperms are the _______________________. Ex: pine trees Conifers are an important source for building materials and paper products Conifers have 2 types of ________________________; male and female Male cones produce ______________________ that carry sperm cells Female cones ...
... The largest group of gymnosperms are the _______________________. Ex: pine trees Conifers are an important source for building materials and paper products Conifers have 2 types of ________________________; male and female Male cones produce ______________________ that carry sperm cells Female cones ...
Chapter 1: Classifying Organisms
... • Conifer=‘to bear cones’ • Phylum Pinophyta (old name: Coniferophyta) • Evolved a bit later than ferns • Major conifers: pine, spruce, fir, cypress, junipers, etc. • Either needle-leaved or scale-leaved • Adapted for cold & dry env. ...
... • Conifer=‘to bear cones’ • Phylum Pinophyta (old name: Coniferophyta) • Evolved a bit later than ferns • Major conifers: pine, spruce, fir, cypress, junipers, etc. • Either needle-leaved or scale-leaved • Adapted for cold & dry env. ...
Ncumisa_Mnotoza
... Conifers are used to make softwood timber.This wood is commonly used in temperate regions for lumber constrution making: polywoods, particleboards, and ...
... Conifers are used to make softwood timber.This wood is commonly used in temperate regions for lumber constrution making: polywoods, particleboards, and ...
Chapter 6 Plants
... The food supply and the coat help the embryo survive for long periods of time, until conditions are right for growth ...
... The food supply and the coat help the embryo survive for long periods of time, until conditions are right for growth ...
Document
... into a fruit with seeds inside, while the rest of the flower dies B. Fruits help protect the seeds until they mature and help scatter seeds into new habitats -Fruits are the part of the plant that contains seeds: cucumbers, maple “helicopters”, green peppers, squash are all fruits. ...
... into a fruit with seeds inside, while the rest of the flower dies B. Fruits help protect the seeds until they mature and help scatter seeds into new habitats -Fruits are the part of the plant that contains seeds: cucumbers, maple “helicopters”, green peppers, squash are all fruits. ...
Biology 203
... woody. In the pollen cone, microsporocytes inside a microsporangium undergo meiosis and become 1N. These nuclei then undergo mitosis to form two or more nuclei. This is the highly reduced male gametophyte and includes the sperm. The male gametophyte is called a pollen grain. The young female cone (a ...
... woody. In the pollen cone, microsporocytes inside a microsporangium undergo meiosis and become 1N. These nuclei then undergo mitosis to form two or more nuclei. This is the highly reduced male gametophyte and includes the sperm. The male gametophyte is called a pollen grain. The young female cone (a ...
Seed Plant Notes
... plants to make pollen. They do not need water to reproduce because pollen is transported by wind, bees, & birds. ...
... plants to make pollen. They do not need water to reproduce because pollen is transported by wind, bees, & birds. ...
Kingdom Plantae
... into pollen grains and rest on the edges of the cone. These are carried by the wind, and some will reach the female cones in pollination.. The pollen grains then directly enter the diploid sporangium in the ovule, and a female spore is produced by a meiotic division inside the sporangium; this spore ...
... into pollen grains and rest on the edges of the cone. These are carried by the wind, and some will reach the female cones in pollination.. The pollen grains then directly enter the diploid sporangium in the ovule, and a female spore is produced by a meiotic division inside the sporangium; this spore ...
Nerve activates contraction
... 4. During pollination, windblown pollen falls on the ovulate cone and is drawn into the ovule through the micropyle. • The pollen grain germinates in the ovule, forming a pollen tube that digests its way through the megasporangium. 5. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four hapl ...
... 4. During pollination, windblown pollen falls on the ovulate cone and is drawn into the ovule through the micropyle. • The pollen grain germinates in the ovule, forming a pollen tube that digests its way through the megasporangium. 5. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four hapl ...
Organismal Biology/30B2
... 4. During pollination, windblown pollen falls on the ovulate cone and is drawn into the ovule through the micropyle. • The pollen grain germinates in the ovule, forming a pollen tube that digests its way through the megasporangium. 5. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four hapl ...
... 4. During pollination, windblown pollen falls on the ovulate cone and is drawn into the ovule through the micropyle. • The pollen grain germinates in the ovule, forming a pollen tube that digests its way through the megasporangium. 5. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four hapl ...
Seed plants
... supply of food that aids its establishment 2. The majority of extant plants are seed plants ...
... supply of food that aids its establishment 2. The majority of extant plants are seed plants ...
PLANT REPRODUCTION AND HOW IT WORKS!
... FUNCTIONS OF SEEDS • Protection -from drying out and disease • Nourishment – contain cotyledons (seed leaf) that supply organic nutrients • Dispersal – by wind, water, and animals • Delayed growth – do not germinate until conditions are favorable ...
... FUNCTIONS OF SEEDS • Protection -from drying out and disease • Nourishment – contain cotyledons (seed leaf) that supply organic nutrients • Dispersal – by wind, water, and animals • Delayed growth – do not germinate until conditions are favorable ...
Plants
... – Pollen is released from the anther and is transferred to the stigma. A pollen tube forms and grows through the style. The pollen tube reaches an ovule within the ovary, where the sperm fertilizes the egg. ...
... – Pollen is released from the anther and is transferred to the stigma. A pollen tube forms and grows through the style. The pollen tube reaches an ovule within the ovary, where the sperm fertilizes the egg. ...
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 12 extant division-level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae (Viridiplantae) and 10 within the extant land plants. Pinophytes are gymnosperms, cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue. All extant conifers are woody plants with secondary growth, the great majority being trees with just a few being shrubs. Typical examples of conifers include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews. The division contains approximately eight families, 68 genera, and 630 living species.Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are of immense ecological importance. They are the dominant plants over huge areas of land, most notably the boreal forests of the northern hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. The narrow conical shape of northern conifers, and their downward-drooping limbs, help them shed snow. Many of them seasonally alter their biochemistry to make them more resistant to freezing, called ""hardening"". While tropical rainforests have more biodiversity and turnover, the immense conifer forests of the world represent the largest terrestrial carbon sink, i.e. where carbon from atmospheric CO2 is bound as organic compounds.They are also of great economic value, primarily for timber and paper production; the wood of conifers is known as softwood.Conifer is a Latin word, a compound of conus (cone) and ferre (to bear), meaning ""the one that bears (a) cone(s)"".